Polity
Lee Commission (1924):
-
- It was set up in 1923 by the British Government, chaired by Lord Lee, to review and reform the Superior Civil Services in India, with equal representation from British and Indian members.
- Its main goal was to address the racial composition and recruitment methods in key civil service posts, following demands for greater Indian participation.
- The Commission recommended that recruitment to higher civil services should be: 40% British, 40% directly recruited Indians, and 20% promoted from provincial service.
- It divided services into three categories: All India Services (e.g., ICS, Indian Police), Central Services (e.g., Railways, Posts), and Provincial Services, with responsibility for recruitment accordingly allocated.
- It proposed the immediate creation of a Public Service Commission to ensure fairness and efficiency in recruitment; this later led to the establishment of the Federal Public Service Commission of India.
- The recommendations aimed for a 50:50 ratio between British and Indian officers in the Indian Civil Services within 15 years.
- Although it marked progress toward Indianization, the pace of change was slow, and dissatisfaction fuelled subsequent reforms.
(TH)
Science & Technology
Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe (IMAP):
-
- IMAP is a NASA heliophysics mission launched on September 24, 2025, to study two key coupled science topics: the acceleration of energetic particles near the Sun and the interaction of the solar wind with the local interstellar medium at the boundary of the heliosphere.
- The spacecraft is stationed at the Sun-Earth L1 Lagrange point, about 1.5 million km from Earth, providing a vantage point to continuously observe the solar wind and interstellar particles.
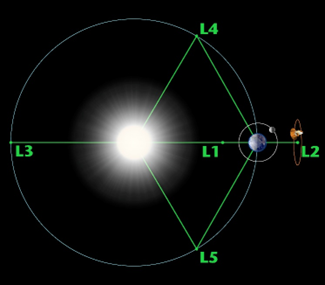
-
- IMAP carries a suite of 10 scientific instruments designed to measure charged particles, energetic neutral atoms, solar wind properties, interstellar neutral atoms, cosmic dust, and magnetic fields.
- Major science goals include understanding the composition and properties of the local interstellar medium, mapping the heliosphere boundary, investigating solar and interstellar magnetic field interactions, and studying particle injection and acceleration processes.
- IMAP will improve space weather forecasting by providing real-time data on solar wind and energetic particles, enhancing warnings for hazardous radiation events that can affect spacecraft, astronauts, and Earth’s technology infrastructure.
- The mission is managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center with Princeton University leading the science team and Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory handling project management.
- IMAP is an advanced successor to earlier missions like ACE, providing higher cadence and more detailed observations to better understand the dynamic environment of the heliosphere and its protective role around the solar system.

(TH)
Geography & Environment
Dugongs:
-
- Dugongs (Dugong dugon) are marine mammals of the order Sirenia, closely related to manatees but distinguished by a fluked, dolphin-like tail and unique skull structure.
- They are strict herbivores, feeding primarily on seagrass in shallow coastal waters across the Indian and western Pacific Oceans, earning them the nickname “sea cows”.
- Dugongs can grow up to 4 meters in length and weigh as much as 900 kilograms, although most adults are between 2.2-3.4 meters long and 230-420 kilograms in weight.
- They have a long lifespan, living up to 70 years, but reproduce slowly with females giving birth every 3 to 7 years to a single calf after a 12-month gestation.
- Dugongs are vulnerable to extinction due to threats such as habitat destruction, hunting, fishing-related deaths, and slow reproductive rates; they are protected in many countries, and international trade is restricted.
- Their populations are fragmented, with Australia hosting the largest numbers, and their distribution is limited by the presence of healthy seagrass meadows.
- Dugongs are more closely related to elephants (not whales or dolphins), and their closest extinct relative is Steller’s Sea cow.
- Socially, dugongs are typically solitary or found in pairs, though larger herds are sometimes seen; they communicate with chirps, whistles, and barks.
- The most visible step was the notification of the Dugong Conservation Reserve in Palk Bay in 2022 under the Wildlife (Protection) Act. Protecting over 12,000 hectares of seagrass meadows, it has become a model of integrated marine conservation.
- The Dugong’s status on the IUCN Red List is Vulnerable.

(TH)
Impact of climate change on Amazon rainforest trees:
-
- A new international study (published in Nature Plants) finds that the average size of Amazon rainforest trees has increased by over 3% every decade, in part due to rising atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels.
- Scientists monitored 188 long-term forest plots, some for up to 30 years, and found tree diameter increased by about 3.3% per decade, unlike typical old-growth forest stability.
- The “carbon fertilisation effect,” where higher CO2 boosts photosynthesis and growth, is credited for this unusual tree size increase.
- Larger trees can absorb more carbon, offering reassurance that Amazonia is acting as a significant carbon sink, but researchers stress this does not offset the harm of deforestation.
- Experts caution that mature, old-growth forests provide far superior carbon and biodiversity benefits than new plantations, meaning lost trees cannot be easily replaced.
- The Amazon is the world’s largest tropical rainforest, spanning nine countries, containing 10% of known wildlife species, and storing up to 150-200 billion tonnes of carbon.
(IE)
Effects of Polar geoengineering:
-
- Stratospheric aerosol injection (SAI): deliberately releasing aerosols into the earth’s atmosphere to reflect sunlight and cool the earth’s surface.
- Sea curtains/sea walls: blocking warm ocean water from reaching the ice sheets in polar regions using large buoyant structures attached to the seabed.
- Sea ice management: scattering glass microbeads over sea ice to boost their reflectivity and artificially thicken them.
- Basal water removal: reducing ice loss by removing subglacial water from under glaciers to slow the movement of ice sheets and decelerate sea level rise.
- Ocean fertilisation: drawing more CO2, from the atmosphere into the ocean by adding nutrients like iron to polar oceans to stimulate phytoplankton growth.
(TH)
Terms in the News
Environmental surveillance:
-
- It involves the systematic collection and analysis of air, water, soil, and biological samples to characterize the state of the environment and detect potential hazards such as pollutants, pathogens, or toxins.
- It is widely used for early warning and risk assessment, including tracking the spread of infectious diseases (by analyzing wastewater, sewage, and surface waters), industrial emissions, and ecological changes.
- Key methods include sensor-based monitoring, remote sensing (using satellites, UAVs), laboratory analysis, sample-based monitoring (grab and composite sampling), and the use of bioindicators to assess ecosystem health.
- Techniques such as gravimetric analysis, chromatography, spectrometry, and bioassays are deployed to measure contaminants and screen for specific pathogens.
- The data from environmental surveillance informs public health responses, policy decisions, regulatory compliance, and environmental management strategies.
(TH)
Carbon fertilisation:
-
- Carbon fertilisation, also known as the carbon dioxide fertilisation effect, refers to the increased rate of photosynthesis in plants due to rising levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Higher CO2 concentrations increase the rate at which plants convert CO2 and sunlight into sugars, leading to faster growth and greater biomass production, especially in C3 plants.
Facts and Data
Number of people killed in road accidents across India:
-
- More than 1.73 lakh people were killed and 4.47 lakh injured in road accidents across the country in 2023 with nearly 46% of the victims being two-wheeler riders, according to a report of the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB)
- The highest number of accidents (20.7% of total) were reported between 6 p.m. and 9 p.m.
- The highest number of deaths were reported on the National Highways accounting for 34.6%, followed by State Highways at 23.4%.
- Over-speeding and careless driving are the leading causes, and evening hours see the most accidents.
(TH)
Number of farmer suicides:
-
- The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) has said in its report that 10,786 farmers and agricultural workers committed suicide in 2023. The most number of cases was from Maharashtra (38.5%), followed by Karnataka (22.5%).
- The decision to waive o import duty on cotton would vitiate the situation as most of the suicides were still from the cotton belts of the country.
- Of the 10,786 suicides from the farming sector, 4,690 were farmers or cultivators, and 6,096 were agricultural workers. The farm suicides accounted for 6.3% of total suicides (1,71,418 suicides in 2023) in the country.
- Out of the 4,690 farmers who committed suicide, 4,553 were male and 137 were female, and out of the 6,096 suicides by farm workers, 5,433 were male and 663 were female.
(TH)
Miscellaneous
India re-elected to International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO):
-
- India was re-elected to ICAO’s Council (Part II) at the 42nd ICAO Assembly Session in Montreal on 27 September 2025.
- Part II of the ICAO Council comprises states making major contributions to the provision of international air navigation facilities.
- Ministry of Civil Aviation and Ministry of External Affairs actively campaigned for India’s re-election, including diplomatic engagement and hosting receptions for ambassadors and high commissioners.
- India is a founding member of ICAO (since 1944) and has maintained an uninterrupted Council presence for 81 years, playing a key role in advancing ICAO’s mission for safe, secure, sustainable, and inclusive civil aviation.
- India’s growing aviation market makes it a center of interest for global industry stakeholders, especially in aircraft manufacturing, MRO (Maintenance-Repair-Overhaul), and skill development.
- India is actively engaged in policy development, regulatory frameworks, and international aviation standards, reaffirming commitment to ICAO’s objectives for the 2025-2028 term.
- The ICAO Council consists of 36 elected members representing 193 signatory states, and the Assembly meets every three years.
(PIB)
PRACTICE MCQ’S
Q1. Which of the following statements about the Lee Commission (1924) are correct?
1. The Commission recommended that recruitment to higher civil services should consist of 40% British officers, 40% directly recruited Indians, and 20% promoted from provincial services.
2. It proposed the immediate creation of a Public Service Commission to ensure fairness and efficiency in recruitment.
3. The Commission successfully achieved a 50:50 ratio between British and Indian officers in the Indian Civil Services within 15 years of its recommendations.
4. The Lee Commission divided services into three categories: All India Services, Central Services, and Provincial Services.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
a) 1, 2, and 4 only
b) 2, 3, and 4 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) All of the above
Answer: A
Explanation: Though the Commission aimed for a 50:50 ratio of British and Indian officers within 15 years, this was not fully achieved due to slow changes and dissatisfaction.
Q2. Consider the following statements about NASA’s Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe (IMAP) mission:
1. IMAP is positioned at the Sun-Earth L1 Lagrange point to continuously observe solar wind and interstellar particles.
2. The mission aims to study only the acceleration of energetic particles near the Sun, excluding the interaction of solar wind with the local interstellar medium.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: A
Explanation:
IMAP is a heliophysics mission stationed at the Sun-Earth L1 point to observe solar wind and interstellar particles continuously. Its science objectives include studying both the acceleration of energetic particles near the Sun and the interaction of solar wind with the local interstellar medium, making statement 2 incorrect.
Q3. Consider the following statements about Dugongs (Dugong dugon):
1. Dugongs are marine mammals of the order Sirenia and are closely related to elephants rather than whales or dolphins.
2. They are omnivores feeding on a variety of marine plants and small fish in deep ocean waters.
3. The Dugong Conservation Reserve in Palk Bay, notified under the Wildlife (Protection) Act in 2022, protects over 12,000 hectares of seagrass meadows and serves as a model for marine conservation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) All of the above
Answer: B
Explanation:
Dugongs belong to the order Sirenia and share a close evolutionary relationship with elephants. They are strict herbivores feeding primarily on seagrass in shallow coastal waters, not omnivores and not found in deep ocean waters. The Dugong Conservation Reserve in Palk Bay, established in 2022, is a significant protected area for dugongs and seagrass ecosystems, exemplifying marine conservation efforts.
Q4. Consider the following statements regarding India’s re-election to the ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organization) Council for the 2025–2028 term:
1. India was re-elected to the ICAO Part II Council, which comprises states making significant contributions to international civil air navigation facilities.
2. The election took place during the 42nd ICAO Assembly Session held at Montreal, where India secured the highest-ever mandate for its re-election.
3. India, as a founding member since 1944, has maintained an uninterrupted presence on the ICAO Council.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) All of the above
Answer: D
Explanation:
India was re-elected to the ICAO Part II Council, which includes countries contributing most to international air navigation. The election, held at the Montreal assembly, marked India’s highest-ever mandate reflecting global confidence in its leadership. India, a founding member since 1944, has had an unbroken presence on the council for 81 years and plays a crucial role in shaping international aviation policies and standards, reinforcing its rising stature in global civil aviation.




