Polity
National Security Act (NSA):
-
- It is a preventive detention law enabling both central and state governments to detain individuals who threaten national security, public order, or essential supplies.
- Enacted in 1980, NSA empowers authorities to detain persons without formal charges for up to 12 months if their actions are deemed prejudicial to the security of India, public order, or the maintenance of essential services.
- Detention orders can be issued by the Central or State Governments and, in certain cases, by District Magistrates or Commissioners of Police (subject to approval by the government within 12 days).
- Grounds for detention may include defense concerns, relations with foreign countries, supply disruptions, or promoting communal disharmony.
- The detainee must be informed of the grounds for detention as soon as possible, and an Advisory Board comprising High Court judges must review the case within three months.
- The act allows for preventive detention even in the absence of a specific offense, suspending several standard legal rights such as immediate access to bail and legal representation during initial detention.
- The act includes provisions for temporary release, legal protection for authorities acting in good faith, and judicial review through habeas corpus petitions in High Court.
- NSA is often invoked in cases involving threats to internal security, serious public disturbances, or regions prone to terrorism and communal violence.
(IE)
Sixth Schedule under Article 244:
-
- It provides for special administrative arrangements in select tribal areas of the Northeast, ensuring autonomy and protection for indigenous communities.
- The Sixth Schedule applies to tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram, and empowers them to be governed as Autonomous Districts and Regions with substantial self-governance.
- It protects tribal land and resources by prohibiting transfer to non-tribals, thereby safeguarding cultural and social identity.
- Each Autonomous District has a District Council, usually with 30 members (4 nominated by the Governor, 26 elected by adult franchise for a five-year term), enjoying legislative, executive, and judicial powers on matters like land, forests, customs, village administration, health, and policing.
- The Governor has wide powers to reorganize, alter boundaries, and create Autonomous Regions within districts, especially if there are multiple tribal groups; laws passed by councils need the Governor’s assent.
- District Councils can form village councils and local courts for customary dispute resolution among tribals; the jurisdiction of higher courts in tribal cases is determined by the Governor.
- Acts of Parliament or State Legislatures do not automatically apply unless extended with modifications specific to the local context.
- The Schedule’s core objective is to prevent exploitation of tribal populations and to preserve their unique traditions while promoting their welfare through self-administered governance models.
(IE)
Economy
Repo Rate:
-
- The repo rate is the benchmark interest rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends short-term funds to commercial banks against government securities, playing a central role in the country’s monetary policy.
- The repo rate (repurchase agreement rate) is used by RBI to regulate liquidity, control inflation, and stabilize the economy by influencing bank lending rates and money availability in the market.
- When the repo rate increases, borrowing costs for banks rise, which leads to higher interest rates for customers and slows down spending, thereby helping to control inflation.
- When the repo rate decreases, banks can borrow more cheaply, so loan and deposit interest rates fall, which encourages investment and boosts economic growth.
- Commercial banks borrow from the RBI by pledging government securities as collateral, with an agreement to repurchase them at a future date and a higher price.
- The Monetary Policy Committee of RBI periodically reviews and sets the repo rate, taking into account inflation, growth, and liquidity conditions.
- As of August 2025, the current repo rate in India is 50%, following a recent 50 basis points reduction.
(IE)
Art and Culture
Dhrupad:
-
- Dhrupad (meaning ‘structured’) is a style of rendering a raga under a rigid composition and rhythm structure and is either sung or played on a rudra veena with a pakhawaj and tanpura.
- Dhrupad is believed to be the oldest form of Hindustani classical music extant today. With its complex grammar and aesthetics, it is primarily a form of worship, in which offerings are made to the divine.
- Many of the texts sung in dhrupad are drawn from Hindu devotional poetry, specially from that of the Bhakti Movement.
- Dhrupad is also more rigid than khayal or thumri, in which the rhythm and sonic structure can vary and is improvised.
- Dhrupad isn’t folk and erotic like a thumri and does not have taans and sargams like a khayal.
- Famous dhrupad personalities include historical figures like Tansen, Swami Haridas, and Dagar family.
(IE)
Dagarvani:
-
- The renowned Dagar family of musicians traces its musical lineage to Swami Haridas (Tansen’s guru).
- For generations, the family, among a few others, has been custodians of dhrupad. Such has been their contribution that the Dagar family’s style of dhrupad rendition is known as
- The tradition traces its history back to Baba Gopal Das Pandey, father of Ustad Behram Khan, known to be the pioneer of the Dagar musical gharana.
- As the legend goes, the 18th-century Mughal ruler in Delhi, Muhammad Shah Rangila, once offered a paan to Gopal Das, who accepted it.
- This led to his ostracisation from the Brahmin community, and Gopal Das decided to convert to Islam. Since then, generations of Dagars, as practising Muslims, have continued to pray to Saraswati and chant hymns from the Vedas.
- Allabande Khan and Zakiruddin Khan are prominent members of the Dagar family from the 19th century.
(IE)
Science & Technology
Astrosat:
-
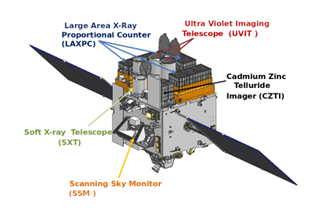
- Astrosat is India’s first dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory, providing simultaneous observation capability in ultraviolet, optical, and X-ray bands, and marking a major milestone in Indian space science.
- Launched by ISRO on September 28, 2015, aboard PSLV-C30 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- Enables simultaneous multi-wavelength observations (UV, optical, and X-ray) of celestial objects using five co-aligned telescopes on a single satellite.
- Major scientific goals include studying star formation, black holes, neutron stars, galaxies, and revealing details of high-energy cosmic phenomena.
- Payloads include Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UVIT), Soft X-ray Telescope (SXT), Large Area X-ray Proportional Counter (LAXPC), Cadmium-Zinc-Telluride Imager (CZTI), and Scanning Sky Monitor (SSM).
(TH)
Geography & Environment
UNESCO’s World Network of Biosphere Reserves:
-
- India’s Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve in Himachal Pradesh has been included in UNESCO’s World Network of Biosphere Reserves during the 37th Session of UNESCO’s International Coordinating Council – Man and the Biosphere held on September 27, 2025.

-
- With this addition, India now has a total of 13 biosphere reserves listed in the UNESCO World Network, reflecting the country’s commitment to biodiversity conservation and community-led sustainable development.
- Biosphere reserves are “learning places for sustainable development,” combining conservation of biodiversity with sustainable use of natural resources in terrestrial, marine, and coastal ecosystems.
- The network spans over 7,442,000 sq km across 134 countries, involving about 275 million people globally, under the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme.
- Each biosphere reserve has three main zones: a strictly protected core area, a buffer zone for regulated activities that support conservation and research, and a transition zone where sustainable economic and human activities occur.
- Biosphere reserves promote research, education, monitoring, and sustainable community development, helping reconcile environmental conservation with socio-economic well-being.
- The World Network facilitates international cooperation, knowledge exchange, south-south and north-south collaboration, and capacity building to address global environmental challenges.
(PIB)
Ramsar sites:
-
- India added two new Ramsar sites from Bihar (Gokul Jalashay (448 ha) in Buxar district and Udaipur Jheel (319 ha) in West Champaran district).
- The total number of Ramsar Sites in the country has reached
- Ramsar sites are wetlands designated under the Ramsar Convention, an international treaty established in 1971 to conserve and promote the sustainable use of wetlands globally.
- Wetlands include diverse ecosystems such as marshes, rivers, lakes, peatlands, mangroves, coral reefs, and human-made water bodies; they provide critical ecosystem services like freshwater supply, biodiversity habitat, flood control, and climate regulation.
- The convention aims to ensure wise use, conservation, and management of wetlands of international importance to protect biodiversity, maintain ecological character, and support climate resilience.
- Ramsar sites are chosen based on criteria like presence of rare or unique wetland types, support for endangered species, significance for water birds, and importance as fish breeding grounds.
(PIB)
Schemes and initiatives in the News
Swachh Shehar Jodi:
-
- The Swachh Shehar Jodi (SSJ) initiative pairs 72 top-performing mentor cities with around 200 low-performing mentee cities for mentorship in urban waste management.
- Mentor cities are chosen based on high Swachh Survekshan rankings across population categories; mentee cities are selected from the lowest ranks in each State, considering geographical proximity.
- The initiative is implemented under Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban (SBM-U) and involves the signing of nearly 300 MoUs between mentor and mentee cities nationwide.
- SSJ features a 100-day program with collaborative action plans, knowledge transfer, peer learning, and experience sharing to improve mentee city outcomes.
- Progress and impact of the mentorship pairs will be evaluated in Swachh Survekshan 2026, with MoHUA providing strategic direction and support.
(PIB)
NAVYA:
-
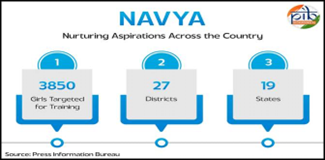
- NAVYA (Nurturing Aspirations through Vocational Training for Young Adolescent Girls) is a joint initiative by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship and Ministry of Women and Child Development launched in June 2025 to skill adolescent girls aged 16-18, especially in underserved and tribal areas.
- It integrates resources from flagship schemes like PMKVY and PM Vishwakarma to provide training in emerging sectors such as digital marketing, cybersecurity, AI-enabled services, drone assembly, professional makeup, and solar PV installation.
- The program focuses on holistic development with modules on personal hygiene, communication, workplace safety, financial literacy, nutrition, and legal awareness, aiming to empower girls with confidence, employability, and entrepreneurial skills.
- NAVYA is piloted across 27 aspirational and North-Eastern districts in 19 states, targeting 3,850 girls, linking education with sustainable livelihood opportunities including internships, apprenticeships, and self-employment.
- The initiative prioritizes gender-inclusive and safe training environments with flexible schedules and stipends, focusing on bridging socio-economic gaps for girls in remote regions and aligning with India’s Viksit Bharat 2047 vision.
(PIB)
PRACTICE MCQ’S
Q1. With reference to the National Security Act (1980), consider the following statements:
1. The Act permits preventive detention of individuals for up to 12 months even in the absence of formal charges or commission of a specific offence.
2. A detention order issued by a District Magistrate must be approved by the appropriate government within 12 days to remain valid.
3. The detainee is entitled to immediate legal representation and bail during the initial stages of detention under the NSA.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct – NSA allows preventive detention for up to 12 months even without formal charges or a specific offence.
Statement 2 is correct – Detention orders by District Magistrates or Police Commissioners require approval from the appropriate government within 12 days.
Statement 3 is incorrect – The Act suspends certain legal rights, including immediate access to bail and legal representation during the initial detention period.
Q2. With reference to the Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution, consider the following statements:
1. The Sixth Schedule empowers District Councils in certain Northeastern states to exercise legislative, executive, and limited judicial powers over matters such as land, forests, and village administration.
2. Laws enacted by District Councils under the Sixth Schedule require the assent of the President to come into force.
3. Acts of Parliament or State Legislatures do not automatically apply to areas under the Sixth Schedule and can be extended only through a notification by the Governor.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct – District Councils under the Sixth Schedule have legislative, executive, and limited judicial powers over matters like land, forests, customs, village administration, and local policing.
Statement 2 is incorrect – Laws passed by District Councils require the assent of the Governor, not the President.
Statement 3 is correct – Central and State laws do not automatically apply in Sixth Schedule areas and can be extended only by the Governor, often with modifications to suit the local context.
Q3. With reference to the Dhrupad, consider the following statements:
1. It was Derived from Vedic chants and Prabandha music, with connection to ancient texts such as the Samveda.
2. It Devotional in nature, initially in Sanskrit, but later also in Brij Bhasha often with heroic themes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Derived from Vedic chants and Prabandha music, with ancient texts such as the Samveda having a connection.
Statement 2 is correct: Devotional in nature, initially in Sanskrit, but later also in Brij Bhasha (a medieval form of Hindi), often with heroic themes.
Q4. Consider the following statements about Astrosat:
Statement I: It has the ability to conduct multi-wavelength observations of the same astronomical object at the same time.
Statement II: It was developed by the ISRO, launched by the GSLV rocket
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is not correct
d) Statement-I is not correct but Statement-II is correct
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: It has the ability to conduct multi-wavelength observations of the same astronomical object at the same time.
Statement 2 is incorrect: It was developed by the ISRO, launched by the PSLV-C30 rocket
Q5. Consider the following:
1. Gokul jalashay
2. Udaipur jheel
3. Karwar lake
4. Nagi bird Sanctury
How many of the above given Ramsar Sites are in Bihar?
a) Only one
b) Only two
c) Only three
d) All four
Answer: D
Explanation:
Recently, in September 2025 India added two new Ramsar sites from Bihar (Gokul Jalashay (448 ha) in Buxar district and Udaipur Jheel (319 ha) in West Champaran district).
All the above sites are located in Bihar.
Spread the Word



