Approach
The Introduction: Explain what you understand by seawater intrusion.
The Body
-
- Write the causes of seawater intrusion
- Remedial measure to combat it
The Conclusion: Why is it crucial to address seawater intrusion.
The Introduction:
Under natural conditions, fresh water flows underground toward the ocean and keeps seawater from moving into coastal aquifers. Pumping too much groundwater from the aquifer lowers water levels and can draw seawater inland.
The Body:
-
- Salt water is denser than fresh water, so it has a greater force and naturally pushes in.
- Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers is a serious concern for India’s 7,500 km coastline as it deteriorates freshwater availability, affecting agriculture, drinking water, and ecosystems.
- In the Sundarbans seawater is intruding into the mouth of the Ganges River. The main causes there are upstream dams and water diversions from the river for irrigation and navigability, plus encroachment due to sea-level rise.
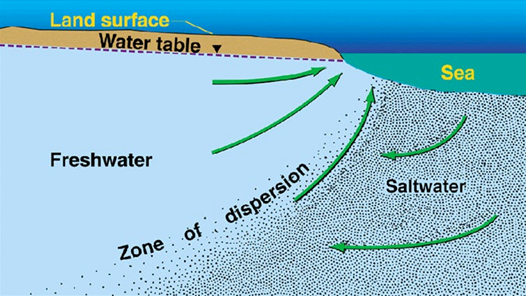
Causes of seawater intrusion:
-
- Over-extraction of groundwater:Excessive pumping for agriculture, industry, and urban use lowers freshwater levels, allowing seawater to encroach inland.
Example: This is severe in areas like Chennai and Gujarat coasts.
-
- Unregulated borewell drilling:Increases aquifer stress and disrupts the natural freshwater-saltwater balance.
- Reduced natural recharge:Urbanization, deforestation, loss of wetlands, and altered rainfall patterns decrease groundwater replenishment.
- Sea-level rise and storm surges:Climate change causes rising sea levels and extreme events, pushing seawater further into aquifers.
- Coastal land use changes:Sand mining, dredging, port expansions increase aquifer permeability, worsening intrusion.
- Hydrogeological factors:Aquifer characteristics like sediments and geology also affect susceptibility to intrusion.
Remedial measures:
-
- Demand management:Reduce groundwater extraction using efficient irrigation methods and promote reuse of treated wastewater.
- Artificial recharge:Construct recharge wells, check dams, injection boreholes to replenish aquifers with rainwater and surface water.
- Protect coastal ecosystems:Restore and conserve mangroves, wetlands, and natural buffers that mitigate seawater penetration.
- Regulate groundwater use: Implement strict controls on borewell drilling and groundwater withdrawal in vulnerable areas.
- Integrated coastal zone management:Adopt policies balancing urbanization, industrialization, and ecological sustainability.
- Monitoring and early warning:Use remote sensing, hydrogeological surveys, and groundwater quality monitoring for early detection and management.
The Conclusion:
Addressing seawater intrusion is crucial for sustaining freshwater resources, agriculture, and coastal livelihoods amid growing anthropogenic pressures and climate change in India.
Spread the Word



