APPROACH
Introduction: Describe briefly Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS).
THE BODY
• Explain the process of CCUS and Role of CCUS in tackling climate change.
Conclusion: Write the importance of CCUS.
The Introduction:
Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) is a group of technologies designed to capture carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions from sources like power plants and industrial facilities, utilize the CO₂ in useful products, or store it safely underground to prevent atmospheric release.
The Body:
-
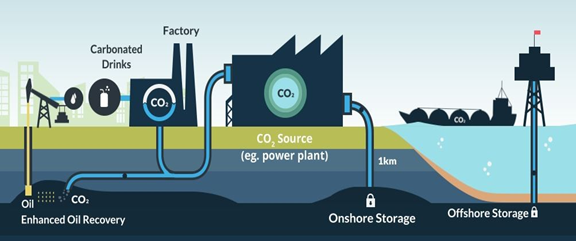
- CCUS involves capturing CO₂ emissions at their source or from the air, transporting them, and then either utilizing the CO₂ in industrial applications or storing it deep underground.
- As global temperatures climb and the need for climate action grows, CCUS is increasingly recognized as an essential technology for achieving deep decarbonization, especially in sectors where switching to renewables is challenging.
- A CCUS application consists of three stages: capture, transport and storage (or usage) of CO2. The main methods for capturing CO2 are:
i. Post-combustion,
ii. Pre-combustion, and
iii. Oxy-fuel combustion.
A carbon sink is anything that absorbs more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases – for example, plants, the ocean and soil.
Role of CCUS in tackling climate change:
-
- Reduce industrial emissions: CCUS directly reduces emissions from hard-to-abate sectors such as steel, cement, and chemicals, where renewable alternatives are limited.
- Supports low-carbon hydrogen production: By enabling ‘blue hydrogen’ from natural gas with CO₂ capture, CCUS provides a pathway to decarbonize transport and industry.
- Removes existing atmospheric CO₂: Technologies such as bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) and direct air carbon capture and storage (DACCS) help achieve negative emissions, a key requirement for net-zero targets.
- Enhances energy security and flexibility: Enhances Energy Security and Flexibility: CCUS diversifies the energy mix and supports reliable power supply as countries phase out fossil fuels.
- Complements renewables: CCUS works alongside renewable energy by addressing emissions from sectors where renewables alone are not enough.
- Examples: Projects like Norway’s Sleipner and Canada’s Quest demonstrate large-scale CCUS deployment. While current global capture capacity is significant, it still needs rapid scaling to meet climate targets.
The Conclusion:
CCUS is widely acknowledged by organizations such as the IPCC and IEA as an indispensable part of the global strategy to limit warming to well below 2°C. While it confronts challenges, including cost, infrastructure needs, and storage risks, its ability to mitigate difficult emissions and deliver negative emissions makes it a crucial complement to renewable energy and other climate actions.
Spread the Word



