Society
Swasth Nari, Sashakt Parivar Abhiyaan:
-
- Prime Minister will launch “Swasth Nari, Sashakt Parivar Abhiyaan” and 8th Poshan Maah on 17th September 2025.
- It is a major initiative to strengthen healthcare and nutrition for women, adolescent girls, and children across India.
- The campaign is jointly led by Ministry of Health & Family Welfare and Ministry of Women & Child Development, emphasizing preventive, promotive, and curative services through health camps and Anganwadi mobilisation.
- More than one lakh health camps will be held across Ayushman Arogya Mandirs, Government health centres, and hospitals nationwide from 17th September to 2nd October 2025, providing the largest-ever health outreach for women and children.
- Key services include screening for non-communicable diseases, anaemia, and sickle cell disease; cancer checks; nutrition and menstrual hygiene counselling; TB screening and linkage; maternal and child health support; immunisations; and mental health sessions.
- The campaign aims to mobilise youth and citizens for voluntary blood/organ donation, TB patient support, and a nationwide push for healthy lifestyle practices, supported by whole-of-government convergence across multiple ministries.
(PIB)
Polity
Kolhan’s Manki-Munda system:
-
- The Manki-Munda system is a traditional, decentralised self-governance system of the Ho tribe in Jharkhand’s Kolhan region, where the village head (Munda) resolves socio-political disputes within the village, and the Manki oversees a group (pidh) of 8 to 15 villages for unresolved cases.
- The Manki and Munda had no responsibilities for revenue collection or land-related issues.
- With British colonial rule, Captain Thomas Wilkinson codified the traditional system in 1833 through ‘Wilkinson’s Rules’, integrating it into the British administrative framework while preserving tribal autonomy and turning community leaders into agents of governance.
- The system helped maintain socio-political order but also facilitated demographic changes with increased non-tribal influx and introduced new concepts like private land ownership.
- This system represents a long-standing indigenous governance institution adapting amid modern administrative pressures and evolving social dynamics.
(IE)
How India treats foreign divorce decrees?
-
- The Gujarat High Court ruled that marriages solemnised under the Hindu Marriage Act (HMA) 1955 cannot be dissolved by foreign courts if the grounds for divorce do not align with the HMA; specifically, “irretrievable breakdown of marriage” recognized in some foreign jurisdictions is not a ground under the HMA.
- In a case where an Indian-origin couple married under HMA moved to Australia and got divorced there on the ground of irretrievable breakdown, the Gujarat HC held that the Australian divorce decree is not valid in India because the HMA governs the marriage dissolution, regardless of changed citizenship.
- Indian personal laws, including the HMA, continue to apply to marriages conducted in India, even if the spouses acquire foreign domicile or citizenship.
- Foreign divorce decrees are not automatically recognized in India; Section 13 of the Code of Civil Procedure (CPC) sets exceptions including lack of jurisdiction, absence of merit, or application of foreign law not recognized in India.
- The Supreme Court precedent in Y. Narasimha Rao v. Venkata Lakshmi (1991) laid down two key rules: recognition requires the divorce to be on grounds accepted under Indian law and both parties must have voluntarily submitted to the foreign court’s jurisdiction.
- Indian courts emphasize that foreign courts cannot impose their own laws on HMA marriages; they may only dissolve such marriages by applying the HMA if jurisdiction is accepted.
- This ensures the supremacy of Indian personal law over foreign divorce laws for Hindu marriages conducted under the HMA, prioritizing statutory grounds and jurisdictional requirements.
(IE)
Economy
Country’s first bamboo-based ethanol plant:
-
- Prime Minister inaugurated the country’s first bamboo-based ethanol plant in eastern Assam’s Golaghat district.
- He also laid the foundation stone for a ₹7,230-crore polypropylene plant at the Numaligarh Refinery.
- The bioethanol plant would benefit local farmers and tribal communities.
- Bamboo was earlier categorised as a tree and there was a ban to cut it. It is now categorised as
- Five lakh tonnes of green bamboo would be sourced yearly from four northeastern states, including Arunachal Pradesh and Assam, to produce of ethanol, acetic acid, furfural, and food grade liquid carbon dioxide.
(TH)
Pink tax:
-
- Pink tax is neither a real tax, nor is it a government-imposed fee. It’s just a pricing phenomenon wherein women pay more for buying a product exclusively made for them or enjoying a service tailor-made for them.
(TH)
Geography & Environment
Gandhi Sagar wildlife sanctuary:
-
- Madhya Pradesh officials plan to introduce a female cheetah to Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary to mate with existing males, expanding the cheetah population beyond Kuno National Park, with Gandhi Sagar as a second home for cheetahs in the state.
- Under Project Cheetah, 29 cheetahs (including 19 cubs) have adapted well at Kuno. Gandhi Sagar spans 2,500 sq km with suitable habitat and currently supports a carrying capacity of 10 cheetahs.
- Concerns include high leopard density (co-predators) threatening expectant mothers, leading to relocation of leopards from the cheetah enclosure, and the need for adequate prey density to support the cheetah population.
- The project aims to build a sustainable metapopulation of 60-70 cheetahs across Gandhi Sagar and Kuno landscapes, reinforcing India’s efforts to reintroduce this extinct species and boost local biodiversity.
(IE)
Erra Matti Dibbalu:
-
- Erra Matti Dibbalu (Red Sand Hills in Telugu) near Visakhapatnam and Tirumala Hills in Andhra Pradesh have been added to the UNESCO Tentative List of World Heritage Sites, marking the first formal step toward global recognition and conservation commitment.
- It spans about 1,500 acres and consists of sand, silt, and clay with a distinct reddish colour due to natural oxidation over thousands of years.
- It is a rare coastal geological formation from the late Quaternary period, featuring dendritic drainage patterns and sediment layers that record ancient sea level and climate changes.
- Only two other similar red sand dune sites exist globally (in Sri Lanka and Tamil Nadu).
- The site is also archaeologically significant due to Stone Age tools found there and was declared a National Geo-heritage Monument by the Geological Survey of India in 2016.
- Tirumala Hills include Eparchaean Unconformity, a geological boundary showing rocks over 2.5 billion years old meeting younger formations, and Natural Arch (Silathoranam), a rare rock formation over 1.5 billion years old.
- The area is part of Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve and Venkateswara National Park, rich in biodiversity.
- These sites qualify under UNESCO themes of geological and ecological significance: Erra Matti Dibbalu for Tectonic and Coastal Systems; Tirumala Hills for Earth history and evolution.

(TH+IE)
Saltwater crocodiles:
-
- They are the largest reptiles on Earth, with males growing significantly larger (up to 6-7m) than females.
- They have a pointed snout and a powerful, wide-snouted jaw.
- They possess thick, armoured skin with bony deposits called osteoderms on their backs.
- They can tolerate saltwater and travel vast distances in the open ocean, which contributes to their wide distribution.
- They have a tremendously powerful bite, the strongest of any living animal, used to hold prey.
- As apex predators, they are at the top of the food chain, keeping other populations in check.
- They communicate using a variety of sounds, including barks, growls, and hisses.
- They are found in tropical and warm temperate regions of the eastern Indian and western Pacific oceans.
- They inhabit mangrove forests, swamps, and estuaries, easily transitioning between saltwater and freshwater environments.
- IUCN: Least concern; CITES; Appendix I (except the populations of Australia, Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea, which are included in Appendix II); and WPA (1972): Schedule I

(TH)
Zamfara state:
-
- Nigeria’s Zamfara State is a state in the northwestern part of the country, with its capital in
- Established in 1996, it was formerly part of Sokoto State.
- Zamfara is known for its fertile land, but it is severely affected by the Nigerian Bandit conflict (cattle-rustling gangs known as “bandits”), leading to mass kidnappings and massacres.
- The state is rich in minerals such as gold and lithium, and its economy is based on agriculture, with significant potential for food and cash crop production.
(TH)
Government Schemes
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri-Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PMJAY):
-
- It is a government-funded health assurance scheme.
- It provides a benefit of up to ₹5,00,000 per family per year for medical treatment.
- Beneficiaries receive cashless and paperless access to services at the point of service, meaning they don’t have to pay upfront at the hospital.
- The scheme covers a broad range of services, including medical consultations, diagnostics, medicines (including 15 days of post-discharge medication), hospitalization, food, and lodging.
- There is no restriction on the family size, age, or gender of the beneficiaries.
- All pre-existing health conditions are covered from day one.
- Benefits can be availed at any empanelled public or private hospital anywhere in India.
- The scheme targets poor and vulnerable families, based on the Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011.
- The scheme is fully funded by the Government of India, with implementation costs shared between the Central and State Governments.
(TH)
Terms in the News
Hindi Diwas 2025:
-
- Hindi Diwas is observed every year on September 14 to commemorate the Constituent Assembly’s decision in 1949 to make Hindi the official language of the Union government, written in Devanagari script.
- After extensive discussions over three days, the Assembly adopted the Munshi-Ayyangar formula as a compromise, which declared Hindi the official language with English to continue for 15 years for official purposes.
- The choice of Hindi as official, not national, language was made amid arguments from various members supporting Hindi, Sanskrit, Hindustani, and English based on cultural, practical, and linguistic reasons.
- Concerns from non-Hindi-speaking regions (notably Tamil Nadu) arose after the 15-year period, resulting in the Official Languages Act that upheld English alongside Hindi as official languages to prevent imposition fears.
- The debates reflected India’s linguistic diversity and the efforts to balance unity with regional identities through the official language policy embedded in the Constitution’s Article 343.
(IE)
Facts/Data
Polity:
-
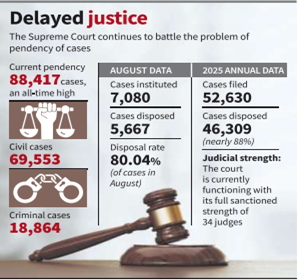
- The pendency of cases in the Supreme Court has reached an all-time high of 88,417, even when the court is currently functioning with its full sanctioned judicial strength of 34 judges.
- The court has 69,553 civil cases and 18,864 criminal matters pending currently, the National Judicial Data Grid shows.
- In 2025, 52,630 cases were filed while 46,309, nearly 88%, were disposed.
- The escalation is despite decision to have more Benches working during the SC’s summer recess.
(TH)
Society:
-
- West Bengal has the highest proportion of females getting married before the age of 18 (6.3%), according to the latest Sample Registration System (SRS) statistical report for 2023.
- The report, compiled by the Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India.
- After West Bengal, Jharkhand had the highest proportion of females married before the age of 18 (4.6%), while Kerala had the lowest rate (0.1%).
- The report pegged the national rate at 2.1%.
(TH)
Environment:
-
- The OECD’s ‘Global Plastic Outlook’ reveals that global plastic consumption has increased significantly due to the growth of emerging economies and markets.
- Plastics production doubled from 2000 to 2019, reaching 460 million tonnes, while waste generation grew to 353 million tonnes.
- Nearly two-thirds of plastic waste has a lifespan of less than five years, with 40% coming from packaging, 12% from consumer goods, and 11% from clothing and textiles. Among this waste, only 9% is recycled.
- Another 19% is incinerated, 50% ends up in landfills, and 22% evades waste management systems, often entering uncontrolled dumpsites, being burned in pits, or ending up in terrestrial or aquatic environments, especially in poorer countries.
- According to the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee on Plastic Pollution, in 2024 alone, 500 million tonnes of plastic were produced or used, generating around 400 million tonnes of waste.
- If the current trends continue, global plastic waste could almost triple by 2060, reaching 1.2 billion tonnes.
- The Ocean Conservancy data reveal that each year, 11 million tonnes of plastic enter the ocean, in addition to the estimated 200 million tonnes that already flow through our marine environment.
(TH)
Miscellaneous
5th Coast Guard Global Summit:
-
- India will host the 5th Coast Guard Global Summit (CGGS) in Chennai in 2027, coinciding with the Indian Coast Guard’s Golden Jubilee celebrations.
- It will feature an International Coast Guard Fleet Review and a World Coast Guard Seminar, promoting global maritime dialogue and cooperation.
- The decision was made unanimously at the 4th CGGS in Rome.
(PIB)
Indian Naval Ship Trikand:
-
- It is a stealth frigate, has made significant port calls in Alexandria (Egypt) and Salamis Bay (Greece) during its ongoing deployment to the Mediterranean in September 2025.
- It represented India in Exercise Bright Star 2025 in Egypt, a major multilateral exercise involving air, land, and sea forces from India, USA, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Greece, and Italy, focusing on regional security, cooperation, and interoperability against hybrid threats.
- In Greece, INS Trikand is participating in the first-ever bilateral maritime exercise between India and Greece, aimed at enhancing interoperability, tactical skills, and operational synergy.
(PIB)
Androth:
-
- Indian Navy has received Androth, the second Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW SWC).
- It is the second vessel delivered under the series of Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts for the Indian Navy.
- The delivery marks a step-up in India’s capability for anti-submarine operations in coastal/shallow waters.
- The new vessel will enhance underwater surveillance and the Navy’s operational readiness for countering submarine threats.
- This induction is part of the ongoing modernization of the Indian Navy’s fleet, reinforcing maritime security.
(PIB)
World boxing championships in Liverpool, U.K.:
-
- Indian women finished with two gold, a silver and a bronze, while the men drew a blank.
- Minakshi got past Kazakh Paris Olympics bronze medallist Nazym Kyzaibay 4-1 in the women’s 48kg final, while Jaismine rallied to stun Polish Olympics silver medallist Julia Szeremeta 4-1 in the 57kg summit clash.
(TH)
PRACTICE MCQ’S
Q1. Which of the following statements correctly explain the term ‘Pink tax’, recently seen in the news?
a) It refers to the tax on income earned by women employees.
b) It refers to the tax missed by the government on unpaid domestic work done by women.
c) It refers to the extra amount paid by women for product exclusively made for them.
d) It refers to the tax on imported luxury items.
Answer: C
Explanation:
-
- Pink tax is neither a real tax, nor is it a government-imposed fee. It’s just a pricing phenomenon wherein women pay more for buying a product exclusively made for them or enjoying a service tailor-made for them.
Q2. Consider the following statements about PM-JAY:
1. It provides a benefit of up to ₹5,00,000 per family per year.
2. There is no restriction on the family size, age, or gender of the beneficiaries.
3. Benefits can be availed only in public hospitals in India.
How many of the statements given are correct?
a) Only one
b) Only two
c) All three
d) None
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: It is a government-funded health assurance scheme. It provides a benefit of up to ₹5,00,000 per family per year for medical treatment.
Statement 2 is correct: There is no restriction on the family size, age, or gender of the beneficiaries. All pre-existing health conditions are covered from day one.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Benefits can be availed at any empanelled public or private hospital anywhere in India.
Q3. Which of the following statements are correct?
1. They are the largest crocodile species on the earth.
2. They inhabit mangrove forests, swamps, and estuaries.
3. They communicate using sounds like barks, growls, and hisses.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: They are the largest reptiles on Earth, with males growing significantly larger (up to 6-7m) than females.
Statement 2 is correct: They can tolerate saltwater and travel vast distances in the open ocean, which contributes to their wide distribution. They are found in tropical and warm temperate regions of the eastern Indian and western Pacific oceans.
Statement 3 is correct: They communicate using a variety of sounds, including barks, growls, and hisses.
Q4. Cattle-rustling gangs known as “bandits” were recently in news. They are from which of the following countries?
a) Nigeria
b) Myanmar
c) Nepal
d) Yemen
Answer: A
Explanation:
Zamfara state:
-
- Nigeria’s Zamfara State is a state in the northwestern part of the country, with its capital in Gusau.
- Established in 1996, it was formerly part of Sokoto State.
- Zamfara is known for its fertile land, but it is severely affected by the Nigerian Bandit conflict (cattle-rustling gangs known as “bandits”), leading to mass kidnappings and massacres.
- The state is rich in minerals such as gold and lithium, and its economy is based on agriculture, with significant potential for food and cash crop production.
Q5. Consider the following statements about ‘Erra Matti Dibbalu’ recently added to the UNESCO Tentative List of World Heritage Sites:
1. These are red sand hills found in Telangana.
2. The distinct reddish colour is due to natural oxidation occurring over thousands of years.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Erra Matti Dibbalu (Red Sand Hills in Telugu) near Visakhapatnam and Tirumala Hills in Andhra Pradesh have been added to the UNESCO Tentative List of World Heritage Sites, marking the first formal step toward global recognition and conservation commitment.
Statement 2 is correct: It spans about 1,500 acres and consists of sand, silt, and clay with a distinct reddish colour due to natural oxidation over thousands of years. It is a rare coastal geological formation from the late Quaternary period, featuring dendritic drainage patterns and sediment layers that record ancient sea level and climate changes. Only two other similar red sand dune sites exist globally (in Sri Lanka and Tamil Nadu).
Spread the Word



