Polity
Extradition law in India:
-
- Extradition is a formal process where one country surrenders a person accused or convicted of a crime to another country to face trial or punishment, preventing evasion by crossing borders.
- Under the Extradition Act, 1962, India has treaties with 48 countries, and arrangements with 12 more; offences must generally be criminal in both countries (“dual criminality”) for extradition to proceed.
- The extradition process begins with a formal request, followed by judicial inquiry; the final surrender decision rests with the government, and safeguards exist like the principle of “speciality” and possibility of release if extradition is delayed.
- Grounds for refusal include if offence is political or military in nature, if person is already facing trial or serving sentence in India, if extradition targets race, religion or political opinions, or if there is no assurance the fugitive will only be tried for specified offence.
- Current context: India has provided assurances to Belgium regarding humane detention conditions for Mehul Choksi if extradited, including adequate personal space and facilities, addressing human rights concerns which are often key hurdles in extradition.
- Extradition is complicated by requirement for strong evidence, human rights concerns, differences in crime recognition, and political issues, making it a difficult legal and diplomatic process.
(IE)
International Developments
M23 rebel group:
-
- March 23 Movement (M23) is a rebel group active mainly in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), particularly in provinces of North Kivu and South Kivu.
- It was formed in 2012 by ex-members of CNDP (National Congress for Defence of People), who mutinied citing DRC government’s failure to implement 2009 peace agreement.
- M23 is reportedly backed by Rwanda, which has provided weapons, supplies, and military support, including troops.
- M23 seized provincial capital, Goma, in 2012 and again in 2025, along with other strategic towns, leading to significant displacement and civilian suffering.
- M23 claims to protect Tutsi population in DRC and opposes DRC government.
- The conflict is also driven by control over rich mineral resources and regional power dynamics.
(TH)
Art and culture
Gyan Bharatam:
-
- Ministry of Culture is launching the ‘Gyan Bharatam’ Mission, a major national initiative to preserve, digitise, and share India’s manuscript heritage.
- The initiative includes a national survey and cataloguing of manuscripts, large-scale digitisation with AI tools, creation of a National Digital Repository, and mechanisms to extract and publish knowledge from diverse subjects such as science, medicine, literature, and spirituality.
- The program will be implemented through collaborations with libraries, religious institutions, private custodians, and will encourage public participation; global partnerships and educational integration are also planned.
- The Gyan Bharatam International Conference (11-13 September 2025), hosted in New Delhi, will gather over 1,100 participants, feature eight working groups on topics such as script decipherment, conservation, and legal frameworks.
- Gyan-Setu AI innovation challenge is part of the mission, with innovative tech solutions to be presented during the conference.
(PIB)
“Adi Sanskriti” – A Digital Learning Platform for Tribal Artforms:
-
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs has launched Beta Version of Adi Sanskriti, a pioneering digital platform for tribal artforms and heritage, designed to empower and connect tribal communities in India with the world.
- It is envisioned as world’s first Digital University for preservation and promotion of tribal culture and will function as both a learning platform and an online marketplace for tribal products.
- The platform is built in collaboration with State Tribal Research Institutes (TRIs) from 14 states, ensuring grassroots participation and authenticity in documenting and digitally mapping tribal artforms.
- It integrates three components: education (“Shiksha”), empowerment (“Sampada”), and marketplace (“Haat”), bringing knowledge, livelihoods, and economic opportunities to tribal communities.
- The platform will provide certifications and advanced research through a Tribal Digital University.
- This launch follows earlier digital initiatives like Adi Vaani (AI-based translator for tribal languages), underlining the Ministry’s focus on cultural preservation and digital empowerment for the vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
(PIB)
Science & Technology
Small satellite launch vehicles (SSLV):
-
- Context: ISRO inks agreement with HAL for transfer of SSLV technology.
- Technology transfer (ToT) is the process of transferring knowledge, skills, and technology from one owner to another, often from a research institution or individual to a business or organization, to create new products, services, and benefits for society.
- Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) is a 3 stage Launch Vehicle configured with three Solid Propulsion Stages and liquid propulsion-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) as a terminal stage.
- SSLV is capable of launching ~500kg satellite in 500km planar orbit from SDSC/SHAR.
- The key features of SSLV are Low cost, with low turn-around time, flexibility in accommodating multiple satellites, Launch on demand feasibility, minimal launch infrastructure requirements, etc.
(TH)
ENGAGEMENT OF INDIAN NAVY’S 1TS ON LONG RANGE TRAINING DEPLOYMENT:
-
- Ships of the Indian Navy’s First Training Squadron (1TS)—INS Tir & ICGS Sarathi (at La Réunion) and INS Shardul (at Port Louis, Mauritius), arrived in Southwest Indian Ocean Region on 8 September 2025 as part of a long-range training deployment.
- At La Réunion, Indian and French navies conducted joint exercises (PASSEX), professional exchanges, diving exercises, yoga sessions, and sports, strengthening the India–France naval partnership and discussing future collaboration for regional security.
- INS Shardul, at Port Louis, conducted joint patrolling and EEZ surveillance with Mauritian forces before arrival and engaged in exchanges with Mauritian officials, reaffirming strong bilateral ties.
- Planned activities in Mauritius include joint training in diving, firefighting, damage control, familiarisation drills, plus outreach events (yoga, culture, sports, ship tours) for public awareness and diaspora engagement.
- These simultaneous port calls highlight India’s commitment to maritime collaboration, regional stability, and interoperability under the MAHASAGAR vision, enhancing India’s role as a trusted partner in the Indian Ocean Region.
(PIB)
Geography & Environment
New species discovered:
-
- Indian scientists from the MACS-Agharkar Research Institute in Pune have discovered two new species of black aspergillus fungi (Aspergillus section Nigri) in the Western Ghats and reported two other species for the first time in India.
- Two new species identified are Aspergillus dhakephalkarii and Aspergillus patriciawiltshireae; researchers also recorded aculeatinus and A. brunneoviolaceus in India for the first time.
- The study used advanced polyphasic (integrative) taxonomic methods, combining morphological features with molecular phylogenetic analysis across multiple gene loci for precise classification.
- Both newly discovered species show distinctive colony and reproductive traits and have potential uses in diverse industrial applications, especially citric acid production and phosphate solubilisation.
- This is the first Indian team to use such advanced polyphasic taxonomy on Aspergillus section Nigri, marking a significant scientific contribution to mycology in the region.
(PIB)
Sankosh river:
-
- The Sankosh River (also known as Puna Tsang Chu) is a river that originates in the northern Himalayan ranges of Bhutan, formed by the confluence of the Mo Chu and Pho Chu
- It flows into India, emptying into the Brahmaputra River in the Dhubri district of Assam.
- It serves as a boundary between the Indian states of Assam and West Bengal and is known for annual flooding in its lower reaches (Jalpaiguri, Alipurduar and Malda).
- River flows to the west of Raimona National Park and runs along the Indo-Bhutan border, forming part of the park’s boundary, while Saralbhanga Riverflows along its eastern side. Both are tributaries of Brahmaputra.
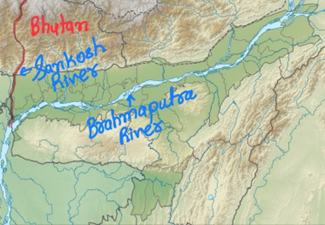
(TH)
Bandipur Tiger Reserve:
-
- It was established in 1974, is nestled in the Western Ghats of Karnataka.
- It was originally a private hunting reserve of the Maharaja of Mysore.
- Geographically, it is an “ecological confluence” as the western and Eastern Ghats meet and constitute this area as distinctive and extraordinary from the point of its fauna and flora.
- It forms a crucial part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, the first Biosphere Reserve in India (1986).
- It harbors rich biodiversity with tropical habitats supporting 35 species of mammals and over 300 species of birds.
- Tiger reserves are constituted using a core and buffer conservation method.
- The core area is free of all human usewhile the buffer area has conservation-oriented land use.
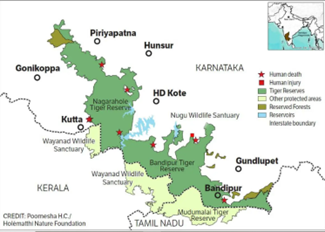
(TH)
Places in the News
North Kivu and South Kivu:
-
- Both provinces are in the eastern part of the DRC.
- North Kivu shares borders with Rwanda and Uganda, while South Kivu borders Rwanda and Burundi.
- The region is characterized by mountainous landscapes, including the Albertine Rift Valley, and includes Lake Kivu.
- Goma serves as the provincial capital of North Kivu, located on the northern shore of Lake Kivu.
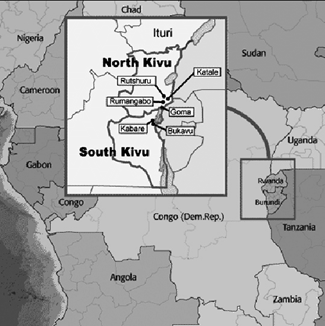
(TH)
Terms in the News
Wood wide web:
-
- The Wood Wide Web is a nickname for the intricate underground network of mycorrhizal fungi that connects trees and other plants, allowing them to share resources like nutrients and water, and even communicate via chemical signals to warn each other of dangers.
- This symbiotic relationship, where fungi benefit from sugars from the trees and the trees gain access to otherwise inaccessible soil nutrients, creates a complex, collaborative forest ecosystem.
(TH)
PRACTICE MCQ’s
Q1. Consider the following statements:
1. Sankosh river is a west flowing river.
2. It serves as a part of the border between Assam and West Bengal and is considered a right-bank tributary of the Brahmaputra.
3. Tributaries of the Sankosh River are Mo Chu and Pho Chu rivers.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: Sankosh river is a east flowing river.
Statement 2 is correct: It serves as a part of the border between Assam and West Bengal and is considered a right-bank tributary of the Brahmaputra.
Statement 3 is correct: Tributaries of the Sankosh River are Mo Chu and Pho Chu rivers.
Q2. Consider the following statements:
1. North Kivu and South Kivu are provinces in the western part of the DRC.
2. North Kivu shares borders with Rwanda and Burundi, while South Kivu borders Rwanda and Uganda.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: D
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: North Kivu and South Kivu are provinces in the eastern part of the DRC.
Statement 2 is incorrect: North Kivu shares borders with Rwanda and Uganda, while South Kivu borders Rwanda and Burundi.
Q3. With reference to the Shilp Samagam Mela, consider the following statements:
1. Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) is a 3 stage Launch Vehicle configured with three Solid Propulsion Stages.
2. Can carry multiple small satellites in a single mission.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) is a 3 stage Launch Vehicle configured with three Solid Propulsion Stages.
Statement 2 is correct: Can carry multiple small satellites in a single mission.
Q4. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: The Wood Wide Web is a nickname for the intricate underground network of mycorrhizal fungi that connects trees and other plants.
Statement II: This allows them to share resources like nutrients and water.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is not correct
d) Statement-I is not correct but Statement-II is correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The Wood Wide Web is a nickname for the intricate underground network of mycorrhizal fungi that connects trees and other plants.
Statement 2 is correct: This allows them to share resources like nutrients and water.
Q5. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: India’s extradition law is primarily governed by the Extradition Act, 1962, which provides a legislative framework for the process of extraditing fugitive criminals between India and other countries.
Statement II: Offences must generally be criminal in both countries (“dual criminality”) for extradition to proceed.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is not correct
d) Statement-I is not correct but Statement-II is correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: India’s extradition law is primarily governed by the Extradition Act, 1962, which provides a legislative framework for the process of extraditing fugitive criminals between India and other countries.
Statement 2 is correct: Offences must generally be criminal in both countries (“dual criminality”) for extradition to proceed.
Spread the Word



