Polity
Supreme court on Aadhaar as identity proof:
-
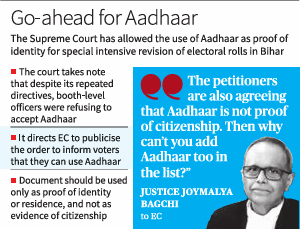
- SC has allowed the use of Aadhaar as proof of identity, but not as evidence of citizenship.
-
- Proof of identity is a document or a piece of information, often official and government-issued, that verifies who you are by providing details like your name, photo, and other unique identifying characteristics.
- Examples of common proof of identity include a driver’s license, passport, state-issued ID card, or national identity documents like the Aadhar card.
- Proof of citizenship is an official document verifying that a person is a national of a specific country.
- Proof of Indian citizenship includes documents like a valid Indian passport, a birth certificate issued under the Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969, and a Voter ID Card (EPIC).
- Other documents like a Domicile Certificate or a Certificate of Citizenship are also considered valid proof.
(TH)
The process to elect the Vice President of India:
-
- The Vice President is elected indirectly by an electoral college of both elected and nominated members of the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha; state legislatures do not participate.
- Voting follows proportional representation with a single transferable vote and secret ballot.
- Candidates must be Indian citizens, at least 35 years old, eligible to be a Rajya Sabha member, and must not hold an office of profit.
- Each nomination must have at least 20 proposers and 20 seconders (all MPs), plus a security deposit.
- The Election Commission of India supervises the election; results are declared and published in the Official Gazette.
(IE)
International Developments
Bilateral Investment Agreement (BIA):
-
- India and Israel signed a Bilateral Investment Agreement (BIA) in New Delhi.
- Agreement is expected to provide greater certainty and protection for investors, facilitating growth of trade and mutual investments by ensuring a minimum standard of treatment, and an independent dispute resolution mechanism through arbitration.
- Agreement also includes provisions to safeguard investments against expropriation, ensure transparency, and enable smooth transfers and compensation for losses.
- Both countries emphasised commitment to advancing economic cooperation in the fields of fintech innovation, infrastructure development, financial regulation, and digital payment connectivity.
(PIB)
Science & Technology
India gets its first indigenous microprocessor:
-
- Union IT Minister presented India’s first fully indigenous microprocessor (a type of semiconductor chip) to Prime Minister at Semicon India 2025.
- The chip, called Vikram 3201, has been developed by the semiconductor laboratory of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- Semiconductors are materials with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator, and their conductivity can be controlled by adding impurities (doping).
- These materials, most commonly silicon, are fundamental to modern electronics, forming the basis for transistors, integrated circuits, and memory devices used in everything from smartphones to medical equipment.
- The tiny chips are made in highly specialised manufacturing facilities (known as foundries) through a rigorous process called wafer fabrication, or wafer fab. The process begins with the slicing of semiconducting material, such as silicon, into a thin segment.
- Once the wafer has been created, it is polished and ground through a series of different, highly specialised machines, and an integrated circuit is installed on its surface.
- The fabrication requires clean rooms designed to maintain sterile conditions to prevent contamination by air particles.
(IE)
International Conference on Space 2025, Bengaluru:
-
- India aims to build a Bharatiya Space Station by 2035 and land an Indian astronaut on the Moon by 2040.
- Chandrayaan-3’s success made India the first nation to land near the lunar south pole.
- Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla became the first Indian Air Force officer to visit the International Space Station.
- Major upcoming missions include Mars, Venus, and asteroid exploration, and the Gaganyaan human spaceflight programme.
- Over 300 Indian space startups now work on launch vehicles, satellites, and other innovations due to recent reforms.
- India actively collaborates internationally, such as the NASA–ISRO NISAR mission and Chandrayaan-5 with Japan.
(IE)
Personalities in the News
Bharat Ratna Dr. Bhupen Hazarika:
-
- To commemorate the birth centenary of Bharat Ratna Dr. Bhupen Hazarika, the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways, launched a unique cultural initiative titled “Bistirna Parore: A Musical Voyage from Sadiya to Dhubri”.
- The event marked the beginning of a river journey along the Brahmaputra featuring a cultural troupe and a musical band travelling on board.
- Communities including Moran, Motok, Tea Tribe, Sonowal Kachari, Hajong, and
- Bhupen Hazarika was an iconic Indian polymath, known for his contributions as a singer, lyricist, filmmaker, and poet, and was often referred to as “Sudha Kontho” (the nightingale of Assam).
- Served as a Member of the Assam Legislative Assembly from 1967 to 1972.
- His autobiography, “Moi Eti Jajabor,” offers insights into his life.

(PIB)
Miscellaneous
Himachal Pradesh as a “fully literate State”:
-
- Chief Minister of Himachal Pradesh on 8th September 2025, declared Himachal Pradesh as a “fully literate State” on the occasion of International Literacy Day.
- A “fully literate” state or Union Territory is one that has achieved a literacy rate of 95% or more of its population, as per the Ministry of Education’s definition under the ULLAS (Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society) initiative.
(TH)
International Literacy Day (ILD) 8 September 2025:
-
- The theme was “Promoting Literacy in the Digital Era,” focusing on digital technology’s role in enhancing literacy and lifelong learning.
- Himachal Pradesh became the fourth state to achieve full functional literacy, joining Tripura, Mizoram, and Goa; Ladakh is the first fully literate Union Territory.
- India’s literacy rate rose from 74% in 2011 to 9% in 2023–24, with over 3 crore learners and 42 lakh volunteers enrolled in the ULLAS literacy program.
- ULLAS Nav Bharat Saaksharta Karyakram offers learning materials in 26 Indian languages to promote inclusivity.
- Collective efforts of communities, volunteers, and governments helped achieve full literacy in difficult terrains, demonstrating determination over geographical challenges.
- The concept of literacy has expanded to include digital literacy, with India setting an example globally through robust Digital Public Infrastructure.
(PIB)
Important data/facts
Monetization of unpaid domestic work:
-
- An average of 7,000 women have died every year, from 2017 to 2022, in horrendous cases where they are burnt — legally known as dowry deaths.
- The National Family Health Survey-5 noted that 30% of the women surveyed reported violence by an intimate partner but only 14% made a police complaint. A third of the over 4.45 lakh cases of registered crimes against women are of domestic violence.
- The State Bank of India, in a survey in 2023, showed that if unpaid work done by women was monetised it would amount to over 7% of the country’s GDP or ₹22.5 lakh crore a year.
- Time Use survey (TUS) 2024: The TUS lists two other work-related categories — unpaid domestic services (cooking, cleaning, washing) and unpaid caregiving services.
- Here, 93% of all women put in an average of seven hours a day in the first category and 41% of women put in two and a half hours in unpaid domestic care.
- The corresponding figure for men is that 70% of men do not do any domestic work.
- In the unpaid caregiving category, 79% of men do no “unpaid caregiving” while the 21% who do, put in an average of an hour and 14 minutes a day.
- If one takes the average for all men, one has this data: in the “domestic sphere” men do 26 minutes of domestic work in a day and less than 16 minutes of unpaid care giving.
(TH)
Kerala’s maternal mortality ratio rises:
-
- Kerala’s maternal mortality ratio (MMR) has “risen” steeply from 18 to 30 per one lakh live births, shows the latest Sample Registration System special bulletin of 2021-2023.
- The report shows that Kerala and Andhra Pradesh share the first spot among the States with the lowest MMR.
- The ratio is calculated by dividing the number of maternal deaths by the number of live births and multiplying the result by one lakh.
- Kerala, which used to have an average of 5 to 5.5 lakh live births annually, now has fewer than 4 lakh.
(TH)
PRACTICE MCQS
Q1. Consider the following statements about Bharat Ratna Dr. Bhupen Hazarika and the “Bistirna Parore” musical voyage:
1. The Inland Waterways Authority of India launched “Bistirna Parore: A Musical Voyage from Sadiya to Dhubri” to commemorate the birth centenary of Dr. Bhupen Hazarika.
2. The event marked the beginning of a river journey along the Ganga featuring cultural performances.
3. Bhupen Hazarika was popularly known as the “Sudha Kontho” (nightingale of Assam) and served as a Member of the Assam Legislative Assembly from 1967 to 1972.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: The Inland Waterways Authority of India launched “Bistirna Parore: A Musical Voyage from Sadiya to Dhubri” to commemorate the birth centenary of Dr. Bhupen Hazarika.
Statement 2 is incorrect: The event marked the beginning of a river journey along the Brahmaputra featuring cultural performances from communities like Moran, Motok, Tea Tribe, Sonowal Kachari, Hajong, and Chutia.
Statement 3 is correct: Dr. Bhupen Hazarika was popularly known as the “Sudha Kontho” (nightingale of Assam) and served as a Member of the Assam Legislative Assembly from 1967 to 1972.
Q2. Consider the following statements:
1. The Vice President is elected indirectly by an electoral college of both elected and nominated members of the Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha and state legislatures.
2. Candidates must be Indian citizens, at least 35 years old, eligible to be a Rajya Sabha member, and must not hold an office of profit.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The Vice President is elected indirectly by an electoral college of both elected and nominated members of the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha; state legislatures do not participate.
Statement 2 is correct: Candidates must be Indian citizens, at least 35 years old, eligible to be a Rajya Sabha member, and must not hold an office of profit.
Q3. Consider the following statements:
1. India plans to build a Bharatiya Space Station by 2035 and land an Indian astronaut on the Moon by 2040.
2. Chandrayaan-3 made India the first nation to land near the lunar south pole.
3. Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla is the first Indian to visit the International Space Station.
4. The Gaganyaan human spaceflight program involves developing reusable launch vehicles with a payload capacity of 50,000 kg to Low Earth Orbit.
Which of the following statements about India’s space program and recent developments are correct?
a) 1, 2 and 3 only
b) 2, 3 and 4 only
c) 1 and 4 only
d) All of the above
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: India plans to build a Bharatiya Space Station by 2035 and land an Indian astronaut on the Moon by 2040.
Statement 2 is correct: Chandrayaan-3 made India the first nation to land near the lunar south pole.
Statement 3 is correct: Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla is the first Indian Air Force officer to visit the International Space Station.
Statement 4 is incorrect: The reusable launch vehicle under development is expected to have about 30,000 kg payload capacity, not 50,000 kg.
Q4. Which of the following is not considered as proof of citizenship in India?
a) Passport
b) Aadhar
c) Voter Id
d) Birth Certificate
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- Proof of identity is a document or a piece of information, often official and government-issued, that verifies who you are by providing details like your name, photo, and other unique identifying characteristics.
- Examples of common proof of identity include a driver’s license, passport, state-issued ID card, or national identity documents like the Aadhar card.
- Proof of citizenship is an official document verifying that a person is a national of a specific country.
- Proof of Indian citizenship includes documents like a valid Indian passport, a birth certificate issued under the Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969, and a Voter ID Card (EPIC). Other documents like a Domicile Certificate or a Certificate of Citizenship are also considered valid proof.

