About:
-
- It a constitutional body constituted by the President under Article 280 of the Constitution.
- It is a quasi-judicial body.
- It functions as a balancing wheel of fiscal federalism and an instrument of cooperative federalism.
Role:
It recommends to the President of India on the following matters:
-
- The distribution of the net proceeds of taxes between Centre and States, and allocation between States of the respective shares of such proceeds.
- The principles that should govern the grants-in-aid to the States by the Centre.
- The measures to augment the Consolidated Fund of a State to supplement the resources of the Panchayats and the Municipalities.
- Any other matter referred to it by the President in the interests of sound finance.
Promoting cooperative fiscal federalism:
-
- Equitable Resource Distribution: Recommends for Vertical devolution and Horizontal devolution.
- 14th Finance commission recommended vertical devolution of 42%.
- Recommend Governance Reforms
- The 13th Finance Commission, recommended reforms in GST like a single rate of 12%.
- The Finance Commission, suggested reforms for rationalisation of Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS).
- Ensuring Fiscal Discipline: Promoting fiscal consolidation and responsible financial management.
- Recommended reforms like accrual accounting, and a fiscal roadmap for FRBM Act.
- Others: Strengthening local self-governance, sector-specific grants, Performance-based grants and strengthening State Finance Commissions.
- Equitable Resource Distribution: Recommends for Vertical devolution and Horizontal devolution.
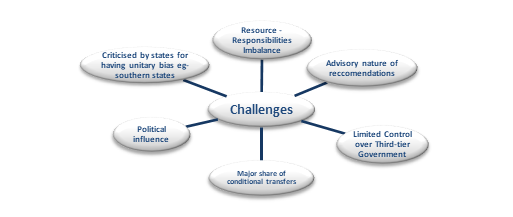
Challenges
Way forward:
-
- Punchhi commission- FC to be made a permanent body to create an institutional memory.
- Vijay Kelkar- Integrate 4 pillars of fiscal federalism– GSTCouncil, NITI Aayog, Finance Commission, Inter-state Council.
Issues before 16th finance commission:
-
- Maintaining sanctity of tax devolution: Avoid dilution through cess and surcharges
- Proliferation of centrally sponsored schemes (CSS)
- Conditional vs. unconditional grants: Promoting fiscal autonomy.
- About 57% of the total transfers are conditional transfers.
- Freebies and fiscal stability
- Fiscal consolidation roadmap: Ensuring fiscal prudence
- Balancing equity and efficiency: Addressing the North-South divide
- About 17% of the horizontal devolution goes to Uttar Pradesh alone, which is almost equal to that of all southern states combined.
- Absorptive capacity of backward states: Enhancing the ability of backward states to utilize resources efficiently
- Grants to local bodies
Way forward:
-
- Policy guidelines for resource sharing
- Optimizing Centrally Sponsored Schemes
- Promoting fiscal discipline
- Strengthening local governance
- Transition to accrual-based budgeting and introduction of sunset clauses




