About:
-
- The LoP is the one who leads the largest opposition party in either Lok Sabha or Rajya Sabha.
- Its role is defined under the Salaries and Allowances of Leader of Opposition in Parliament Act, 1977.
- The minimum numerical strengthrequired for a member to be LoP is one-tenth of the total membership of the respective House.
Evolution:
-
- Informal origin:
- Roots can be traced from concept of shadow cabinet in British Parliamentary system (Westminister model).
- In 1969, the importance of role of LoP was recognized for the first time.
- Statutory recognition (1977):
- The formal recognition of the Leader of Opposition in India came from the Salary and Allowances of Leaders of Opposition in Parliament Act, 1977.
- This Act provided for the salary, allowances, and other facilities for the Leader of Opposition.
- Constitutional amendments and parliamentary rules:
- The Forty-Fourth Amendment of 1978 formally recognized the position of the Leader of Opposition.
- Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha specify the rights and privileges of the Leader of Opposition in parliamentary proceedings, committees, and debates.
- Legal framework and status:
- The Salary and Allowances of Leaders of Opposition in Parliament Act, 1977 laid down the legal framework for the role, ensuring financial support and entitlements.
- Parliament Facilities act in 1998, provided that strength for LoP be equal to that of quorum i.e. 55 seats.
- Institutionalization of LoP
- The LoP is made a member of selection committee of important bodies like NHRC, CVC, Lokpal, CBI, CIC etc.
- The Leader of Opposition’s role in parliamentary committees like the Public Accounts Committee (PAC) to ensure oversight of government expenditure and accountability.
- Informal origin:
Significance:
-
- Check on the arbitrariness of ruling government
- Enriches parliamentary debates and discussions by providing alternative view
- Serves as a shadow cabinet
- Promoting ethical conduct
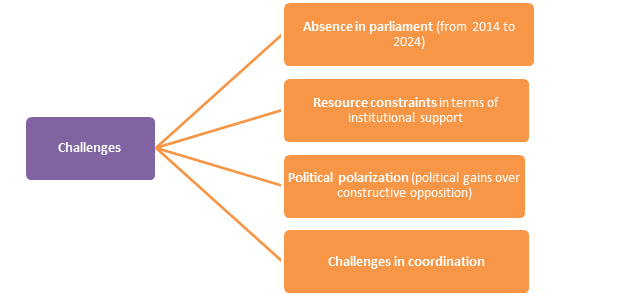
Challenges:
Way forward:
-
- Legislative reforms to clarify and strengthen the position of the LoP
- Institutional support for effective oversight.
- Cross-party collaboration and consensus-building
- Ethical Governance




