About:
-
- It aims to secure accountability of the Executive to the Parliament.
- They assist the Parliament in debating more effectively.
- There are 24 standing committees– 8 under Rajya Sabha and 16 Lok Sabha.
- 31 members (21 from Lok Sabha and 10 from Rajya Sabha).
- The members nominated by the presiding officer of the house.
- Minister cannot be nominated as a member
- The term of office is one year.
Role
-
- Consider the demands for grants before being voted.
- Examine the bills pertaining to the concerned ministries / departments
- Consider annual reports of ministries / departments
- Consider national basic long-term policy documents presented to the Houses
Limitations:
-
- Cannot consider the matters of day-to-day administration
- Cannot consider the matters considered by other committees.
- Recommendations are advisory in nature
Significance:
-
- Gap between legislature and executive reduced
- Significant development in Indian Parliamentary democracy
- Keeps administrators on toes
Weakness of Parliamentary committees:
-
- Recommendatory nature and lack of penal powers
- Short tenure of members
- Not mandatory to refer bills to committees and so bypassed
- No independent secretariat with specialized support like in UK & US.
- Politicization of committees
Diminishing trend:
-
- Bills are passed without much discussion like 35% bills passed within 30 minutes.
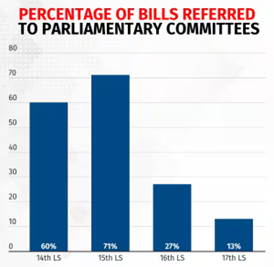
- Committees being bypassed like in 17th Lok Sabha, only 13% of the bills referred to committees.
- Open discussions not allowed by ruling party members, for example in Pegasus case.
- Poor attendance of members i.e. below 50%.
Cause
-
- Overall decline in the quality of politics, debate and discussion.
- Decline in quality of members of Parliament.
- Decline in quality of mutual relationship between ruling party and opposition.
- A notion that bills should be passed without debate to tackle policy paralysis and promotion of ease of doing business.
- Weak leadership role by leader of opposition.
Consequences
-
- Affects the legitimacy of Parliamentary democracy
- It curtails policy discourse in society
- Affects democratic policy making
- Undermines and delegitimizes the role of committees
Way forward:
-
- Referring bills to committees should be a mandatory practice.
- Long tenure of members.
- An independent specialized secretariat.
- Committees as part and parcel of parliamentary process.




