-
- No person shall be deprived of his property except by authority of law.
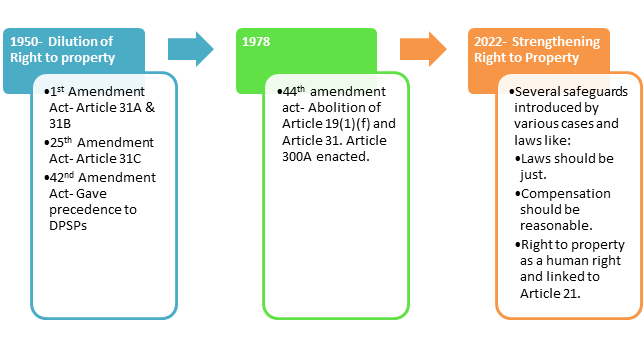
- 44th Amendment Act abolished and made it a legal right under Article 300A in Part XII of the Constitution.
Evolution
Right to property (Under FR vs Article 300A)
| Before 1978 | After 1978 |
|---|---|
| • Right to property a fundamental right. • Justiciable • Direct constitutional remedy under Article 32. • High level of protection. | • Right to property a constitutional right. • Non-Justiciable • Constitutional remedy under Article 226. • Low level of protection. |
How Right to property still significant?
-
- Easy acquisition of land important for economic development like smart city development, PPP projects, mining etc.
- Right to property considered benchmark for evaluation of functioning of democracy.
- Property rights give people sense of belongingness, association, hopefulness as against sense of deprivation and lack of livelihood security.
Safeguards:
-
- Hari Krishna Mandir Trust case– Right to property cannot be denied without authority of law.
- Jilubhai Nanbhai Khachar case- Right to property declared constitutional right.
- Vidhya Devi case- Right to property considered a human right.
- Jayalaxmi & ors. Case- SC brings jurisdiction of Article 21.
Difference between Constitutional Right and Legal Right
| Constitutional Right | Legal Right |
|---|---|
| • Mentioned in any part of the Constitution. • Safeguards through Article 226. • Can be considered rights available outside FRs. | • Mentioned as per law/statute- RTI, FRA etc. • Safeguards as per statute. • Can be considered in general sense like right to information. |




