1. Road Transport
-
- Investment Surge: Road sector investment rose to 1.0% of GDP (₹3.01 lakh crore) in FY24, with asset monetization exceeding ₹1 lakh crore since FY19.
- Highway Expansion: National highways increased 1.6x from 2014-2024; construction pace tripled to ~34 km/day, improving India’s Logistics Performance Index ranking to 38 in 2023.
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY): A total of 8,29,409 km of road length has been sanctioned under PMGSY out of which, 7,63,308 km of road length has been completed as on 18th June 2024 under various interventions/verticals of PMGSY at an expenditure of ₹3.23 lakh crore (including state share).
- Development of Industrial Corridors: The Government is developing 11 industrial corridor projects as part of the national industrial corridor programme in a phased manner. The programme is aimed at providing multi-modal connectivity with complete “plug and play” infrastructure.
2. Rail Transport
-
- Indian Railways, with over 68,584 route km (as of 31st March 2024) and 12.54 lakh employees (as of 1st April 2024), is the fourth largest network in the world under single management.
-
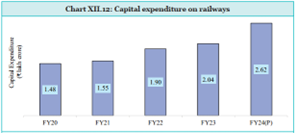
- Capital expenditure on Railways has increased by 77 per cent over the past 5 years (₹2.62 lakh crore in FY24) with significant investments in the construction of new lines, gauge conversion, and doubling.
- Railways achieved its highest-ever production for both locomotives and wagons in FY24.
- 51 pairs of Vande Bharat have been introduced until March 2024.
- Kavach as automatic train protection (ATP) system has been deployed on 1,465 route kilometres (RKM) on south central railways.
- Under the Mission 100 per cent Electrification Programme, electrified network of IR has been extended to 63,456 km (96.4 per cent).
Initiatives for Railway Enhancement
1. Amrit Bharat Station Scheme: Launched in August 2023 for development, modernisation and upgradation of stations on a continuous basis. 1,324 stations have been identified for upgradation so far.
2. Mumbai-Ahmedabad High Speed Rail (MAHSR) project: Under this 508 Km project, executed with cooperation from Govt. of Japan, land acquisition and civil conduct award have been completed. Overall physical progress of 41.7 per cent has been achieved till March 2024.
3. Dedicated freight corridors (DFCs): Two DFCs are under implementation namely the eastern DFC with route length of 1,337 kilometre and the western DFC with route length of 1,506 kilometre.
3. Water Transport
-
- Port Expansion: Major port capacity nearly doubled since 2014; union capital expenditure on ports, shipping, and waterways grew by 27% from FY23 to FY24.
-
- Global Ranking: India’s rank in the World Bank Logistics Performance Index’s International Shipments category improved from 44th in 2014 to 22nd in 2023.
- Initiatives: ‘Harit Sagar’- Green Port guidelines were launched in May 2023 – under which four major ports are already generating more renewable energy than their demand. ‘Sagar Aankalan’, a national benchmarking of Indian ports performance applicable to all Indian seaports was released in February 2024.
- Island Development: Under the Maritime India Vision 2030, Andaman & Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep Islands are planned to be developed for tourism and other initiatives in a phased manner.
- Ship building, repair and recycling: The Recycling of Ships Act, 2019 and Rules thereunder aim to set international standards for ship recycling and ensuring safe and environmentally sound practices subsequent to accession to the Hong Kong International Convention.
4. Civil Aviation
-
- The number of airports in India has more than doubled since 2014 from 74 to 148.
- India’s airport sector saw ₹72,000 crore spent in FY20-FY24; AAI contributed ₹23,000 crore, while PPPs and other operators spent ₹49,000 crore.
- The Government planned over ₹26,000 crore for airport development from FY20 to FY25.
- 21 Greenfield airports were accorded in-principal approval, out of which 12 airports have been operationalised.
- During FY24, new terminal buildings at 21 airports have been operationalised which has led to an overall increase in passenger handling capacity of these airports by approximately 62 million passengers per annum.
5. Coastal Shipping and Inland Water Transport
-
- India has a large endowment of rivers, canals, and other waterways, with a total navigable length of around 14,500 km.
- With the focus of the Government to foster coastal shipping, the gross tonnage through this mode has increased from 1.19 million GT as on 1, April 2014 consisting of 846 vessels to 1.72 million GT with 1039 vessels as on 1, April 2024.
- Capital expenditure by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) for FY24 was ₹1010.5 crore.