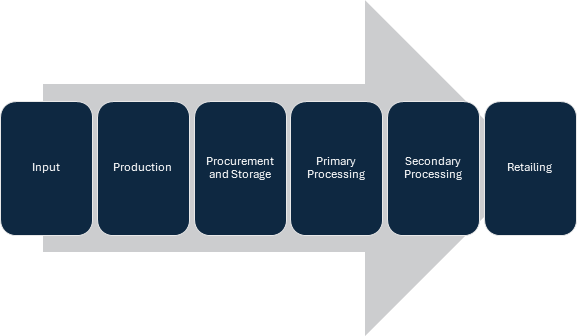
The food processing industry involves several stages, each crucial in transforming raw materials into consumable products. These stages are:
1. Input: The initial stage where raw materials are sourced from agriculture, horticulture, or animal husbandry. This includes crops, fruits, vegetables, milk, meat, and fish.
2. Production: Transformation of raw materials into primary products. This involves basic processes like washing, cutting, sorting, and initial preservation methods to prepare them for further processing.
3. Procurement and Storage: Involves the collection, procurement, and storage of raw and semi-processed materials. Proper storage facilities like cold storage and warehouses are essential to maintain the quality and extend the shelf life of products.
4. Primary Processing: This stage includes the conversion of raw agricultural produce and animal products into a form that is fit for consumption. It involves processes such as cleaning, grading, sorting, and packaging.
5. Secondary Processing: Combining ingredients and transforming them into final food products. This can change the basic properties of raw food materials. Examples include baking, fermenting, and making ready-to-eat products.
6. Retailing: The final stage where processed food products are distributed and sold to consumers. This involves packaging, branding, and marketing to ensure the products reach end-users effectively.
Importance of Food Processing
1. GDP Share: The food processing industry in India is estimated to be worth $380 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11% to reach $540 billion by 2025. The Agro- food processing industry is a vital contributor in the Indian economy, contributing to 8% of the GDP of the nation.
2. Reduction in Wastage: By converting perishable items into processed products, the industry minimizes post-harvest losses and ensures better utilization of agricultural produce. Around 74 million tonnes of food is lost in India every year, which is 22% of foodgrain output or 10% of total foodgrain and horticulture production, put together.
3. Employment Generation: It is a significant employment generator, supporting around 1.93 million jobs in the registered sector and approximately 5.1 million in the unregistered sector.
4. Export Growth: Processed food exports rose from $8.56 billion in 2020-21 to $10.42 billion in 2021-22, making up 22.6% of agri-food exports.
5. Enhancing Farmers’ Income: By providing better price realization and market access, the industry boosts farmers’ incomes and promotes rural development.
6. Nutritional Security: Processed foods offer convenience, extended shelf life, and improved nutritional quality, addressing food and nutritional security challenges.
Challenges in the food processing sector
1. Fragmented Supply Chain: Poor coordination between farmers, processors, and retailers results in inefficiencies and increased costs.
2. Access to Credit and Technology: Limited access to credit and modern technology hinders the growth of micro and small enterprises in the sector.
3. Market Access Issues: Small and medium enterprises often face difficulties in accessing larger markets due to lack of branding, marketing skills, and networking opportunities.
4. Regulatory Hurdles: Complex regulations and compliance requirements can be burdensome for small players. Simplification and streamlining of regulatory processes are needed.
5. Quality and Safety Standards: Ensuring consistent quality and adherence to food safety standards is challenging, particularly for smaller and unorganized units.
6. Inadequate Skilled Labour: There is a shortage of trained personnel in the food processing sector, affecting productivity and innovation.
Spread the Word