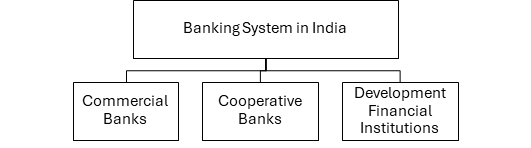
The Banking System in India is broadly divided into 3 types:
1. Scheduled Commercial Banks (or SCBs)
2. Cooperative Banks
3. Development Financial Institutions (DFIs)
A. Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs)
-
- Those banks which are listed in the Second Schedule of the RBI Act, 1934.
- SCBs are regulated under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
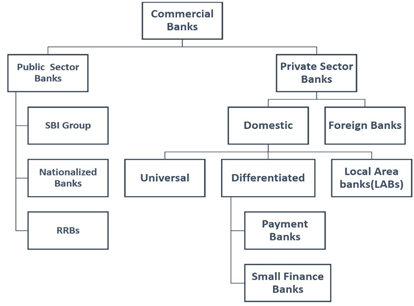
1. Public Sector Banks in India
a) State Bank of India (SBI)
-
- Nationalisation of Imperial Bank of India under the SBI Act, 1955
- Earlier, there were 7 additional associate Banks of SBI namely, State Bank of Saurashtra; State Bank of Bikaner and Jaipur; State Bank of Indore; State Bank of Mysore; State Bank of Patiala; State Bank of Travancore and State Bank of Hyderabad.
6 categories of Scheduled Banks in India
-
-
- Scheduled Public Sector Banks
- Scheduled Private Sector Banks
- Scheduled Small Finance Banks
- Scheduled Payments Banks
- Scheduled Regional Rural Banks
- Scheduled Foreign banks in India
- However, all these associate banks were merged in two phases with the State Bank of India – State Bank of Saurashtra and State Bank of Indore merged with SBI in 2010, while the remaining five associate State Banks as well as Bhartiya Mahila Bank merged with SBI in 2017.
- SBI has about 25% market share in deposits and advances.
- Moreover, SBI is a public sector bank but is different from other nationalised banks since it has always been a public sector bank since its inception and is governed by a separate act (the SBI Act, 1955).
-
b) Nationalised Banks
-
- There are other 11 Nationalised Banks in India
- It started with nationalisation of 14 major private banks in 1969, then in the second phase in 1980, six more banks were nationalised.
- Recent Development– Amalgamation of 10 Public Sector Banks (PSBs) into four PSBs bringing down the number of PSBs in India to 12 (11 Nationalised Banks and SBI) from 1 April 2020.
Benefits of Bank Nationalisation
-
- Increasing reach in rural areas
- Increasing credit in priority sector areas.
- Financial inclusion
List of Scheduled Public Sector Banks
Bank of Baroda; Bank of India; Bank of Maharashtra; Canara Bank; Central Bank of India; Indian Bank; Indian Overseas Bank; Punjab & Sind Bank; Punjab National Bank; State Bank of India; UCO Bank and Union Bank of India
c) Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
-
- They have been created under RRBs Act, 1976 which was based on the recommendations of M. Narasimhan Working Group.
- The core objectives of RRBs are to ensure banking and credit facilities getting extended to agriculture and other rural areas.
- They are owned by 3 entities: Central Government (50%), respective State Government (15%), Sponsor Bank (35%).
- They primarily cater to rural and semi-urban areas.
- They are supervised by NABARD and regulatory norms are prescribed by RBI.
2. Private Banks-Domestic
a) Universal Private Banks
-
- The RBI issued new policy guidelines in 1993, allowing private sector banks to enter the Indian banking system.
- It was based on the recommendation of Narasimhan Committee which was formed in 1991.
- This led to UTI Bank Limited becoming the first private bank to start its operations on April 2, 1994.
- By the end of 1995, India got 10 new private banks.
- They were UTI Bank Ltd., IndusInd Bank Ltd., ICICI Banking Corporation, HDFC Bank Ltd., Centurion Bank Ltd., Bank of Punjab Ltd., Development Credit Bank Ltd., Times Bank Ltd., Global Trust Bank Ltd., IDBI Bank Ltd.
b) Differentiated Banks
-
- They cater to a specific class of customers and are known as niche banks.
- They include – Small Finance Banks (SFBs) and Payments Banks (PBs).
c) Local Area Banks (LABs)
-
- Local Area Banks were set up as per a Scheme announced by the Government of India in August 1996.
- The objective of establishing the local area banks was to enable to mobilisation of the rural savings by local institutions and make them available for investments in local areas.
- The Local Area Banks can do all normal banking business, but their major function is to finance agriculture and allied activities, small scale industries, agro-industries and trading / non-farm activities in the rural and semi-urban areas.
- Presently there are 4 LABs which are operational, and they all are non-scheduled banks private banks.
3. Private Bank- Foreign
-
- Branches of foreign banks located in India.
- Eg – HSBC, American Express, Standard Chartered Bank
Non-Scheduled Banks
-
- They are not mentioned in the Second Schedule of the RBI Act, 1934.
- Depositors’ money is not insured in these banks.
- They maintain cash reserve requirement with themselves and not with the Reserve Bank of India.
- They are generally smaller in size and have a range of influence that is somewhat narrow.
- They are risky to do business with due to their financial limitations.
- The reserve capital of these banks is less than 5 lakh rupees.
- There are 11 Non-Scheduled State Cooperative Banks, 4 Local Area Banks and 1500 Non-Scheduled Urban Co-operative Banks as described by RBI.
B. Co-operative Banks
-
- They have dual regulation:
1. Management related provisions are regulated by Registrar of Cooperatives under States’ Cooperative Societies Acts of various States.
2. Banking related provisions are regulated by the RBI under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 & Banking Laws (Cooperative Societies) Act, 1955.
-
- There is a system of one member one vote in cooperative credit structure.
- They work on the principle of no profit no loss; thus, customers are the owners of the cooperative banks.
Categories of Cooperative Banks
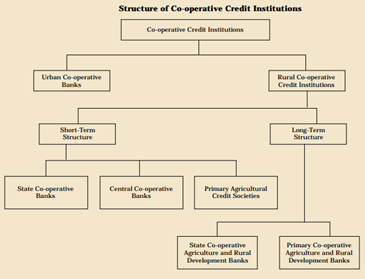
1. Urban Cooperative Banks
-
- The term Urban Co-operative Banks (UCBs), though not formally defined, refers to primary cooperative banks located in urban and semi-urban areas.
- There are more than 1500 UCBs in India.
- UCBs are largely registered as cooperative societies under the provisions of either the State Cooperative Societies Act of relevant States or the Multi State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002 if the area of operation of the bank extends to more than one state.
- Banking Regulation (Amendment) Act, 2020 brought UCBs under the single supervision and control of RBI. (Earlier, both Registrar of Cooperatives as well as RBI were regulating those entities)
2. Rural Cooperative Credit Institutions
-
- Rural Cooperative credit institutions comprise short-term and long-term co-operative credit structures.
- There is a three-tier structure of short-term rural cooperative banks to ensure flow of finance in the cooperative sector.
- There are 32 State Cooperative Banks at the Apex, 338 District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) at the district level, and about 1 lakh Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) at the grass root level (village level).
- Long term Cooperatives comprises of- SCARDBs: State Co-operative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks; PCARDBs: Primary Co-operative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks.
C. Development Financial Institutions (DFIs)
-
- They are also known as All India Financial Institutions (AIFIs).
- They are primarily involved in long-term finance and support to designated sectors of economy.
- All DFIs are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (Department of Banking Supervision).
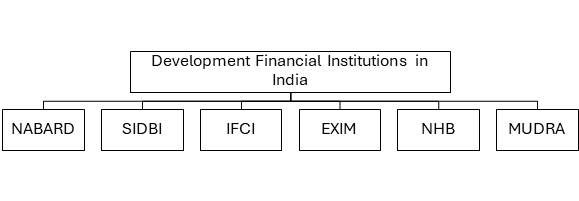
1. National Bank of Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
-
- It is a Statutory Body (NABARD Act, 1981).
Refinancing by NABARD
Borrowing of funds from NABARD at a predetermined interest rate by eligible financial entities for lending to sectors such as agriculture, rural infrastructure, rural artisans, and small businesses.
-
- It is an apex financial institution for promoting various development activities in rural areas as well as planning and promoting agricultural credit.
- NABARD conducts refinancing activities to RRBs, Small Finance Banks, NBFCs – Micro Finance Institutions (NBFC-mFIs) as well as cooperative banks.
- It also supervises RRBs and Cooperative Banks.
2. Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
-
- It is a Statutory Body (SIDBI Act, 1990).
- It primarily focuses on growth and development of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs sector).
- It provides direct credit to SMEs as well as conducts refinancing activities.
- Apart from credit, activities like supporting enterprises, skill development, and modernisation are also taken up by SIDBI.
3. National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID)
-
- It is a Statutory Body (NaBFID Act, 2021).
- The main purpose of NaBFID is ensuring medium-to-long term financial assistance to the industrial and infrastructural sector.
- It is also an NBFC (systemically important).
4. Export-Import Bank (EXIM Bank)
-
- They are Statutory Body (EXIM Bank Act, 1981).
- Aim- finance, facilitate and promote India’s international trade.
- Their services include export credit, pre-shipment credit, post-shipment credit, and overseas investment finance.
- They also undertake partnerships and collaborations with other international development banks and financial institutions to support trade and investment flows between India and other countries.
5. National Housing Bank (NHB)
-
- They are Statutory Body (NHB Act, 1987).
- They are the apex regulatory body for overall regulation and licensing of housing finance companies (HFCs) in India.
- HFCs include PNB Housing Finance, HDFC Housing Finance, LIC Housing Finance etc.
- NHB brings out RESIDEX, which is India’s first official housing price index.
- RESIDEX tracks the movement of residential property prices in various cities across India.
6. MUDRA Bank
-
- Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency Bank
- It is not a Statutory Body.
- SIDBI has been empowered to oversee its functioning.
- Purpose- Refinance MFIs and NBFCs which provide credit to micro / small business entities engaged in manufacturing, trading and service activities.
- It is the apex financial institution which has been entrusted with the task of implementation of Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY).
- 3 Category of Loans:
1. Shishu (upto Rs 50,000),
2. Kishore (Rs 50,000 to Rs 5 Lakh),
3. Tarun (Rs 5 Lakh to Rs 10 Lakh)
-
- The loans offered under the Scheme is strictly under the category of non-agri based activities.