1. Poverty Line: The poverty line is the minimum amount of money a person needs to fulfil the basic necessities of life, like shelter and food. It can be expressed in terms of calorie intake or minimum income. As per the World Bank, the International Poverty Line for extreme poverty is at $1.9 per person per day (Purchasing Power Parity or PPP) and low middle-income poverty at $ 3.2 per person per day (PPP).
2. Headcount Ratio (HCR): It is the percentage of people living below poverty line (BPL) out of the total population in a country.
HCR = Total no. of BPL people/Total Population *100
Categorising Poverty in India
Poor people in India can be categorised into 3 types. They are:
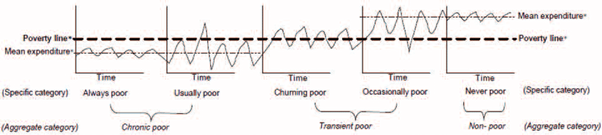
1. Chronic Poor: Those people who are below the poverty line most of the time and reach above the poverty line once in a while are called the chronic poor. It includes:
(a) Always Poor: Those who are always below the poverty line.
(b) Usually Poor: Those who are mostly below the poverty line but occasionally they cross the poverty line.
2. Transient poor: Those people who keep fluctuating between the category of poor and non-poor are called transient poor. It includes:
(a) Churning poor: Those people who regularly move in and out of poverty. These are seasonally employed people. When they have jobs, they are above the poverty line and when they don’t have a job, they are below the poverty line.
(b) Occasionally poor: Those who are rich most of the time but sometimes, out of a business downturn or other causes, fall into poverty.
3. Non-Poor: These are the people who have never gone below the poverty line ever.
Poverty Line estimation types
1. Income-based estimation: A minimum per day or per month per person income is defined which acts as thresholds. Person earning below that level is considered poor.
2. Consumption expenditure-based estimation: Various food and non-food items are created into various baskets and then expenditure on them is surveyed and then a poverty line is created based on minimum consumption expenditure (expressed in monetary terms).
3. Multidimensional Poverty: This is the latest concept where income is replaced by various dimensions of poverty which are measured by various indicators. It takes poverty estimation towards more social indicators rather than monetary indicators.
Spread the Word



