The BioE3 Policy, formally known as the Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment Policy, marks a significant initiative by the Indian government to leverage biotechnology as a catalyst for economic growth, environmental sustainability, and job creation. Approved in August 2024, this policy aims to position India as a global leader in biotechnology by fostering high-performance biomanufacturing and promoting innovative solutions to pressing societal challenges.
Objectives of the BioE3 Policy
The BioE3 Policy is built around several core objectives that reflect its comprehensive approach:
- High-Performance Biomanufacturing: The policy seeks to enhance the production of bio-based products across various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and energy. By focusing on advanced biomanufacturing techniques, India aims to improve efficiency and sustainability in production processes.
- Economic Growth: By harnessing biotechnology for economic development, the policy aims to significantly contribute to India’s GDP. It emphasizes establishing biomanufacturing hubs and biofoundries that can accelerate technology development and commercialization.
- Environmental Sustainability: The BioE3 Policy aligns with national goals such as achieving a ‘Net Zero’ carbon economy and promoting a circular bioeconomy. It focuses on sustainable practices that minimize environmental impact while maximizing resource efficiency.
- Job Creation: The policy is expected to generate substantial employment opportunities, particularly in tier-II and tier-III cities. By establishing biomanufacturing hubs that utilize local resources, it aims to create jobs that contribute to regional economic development.
- Innovation in Research and Development: The policy emphasizes innovation-driven support for research and development across thematic sectors. It encourages collaboration between academia, industry, and government to foster entrepreneurship and technological advancements.
Core Themes of the BioE3 Policy
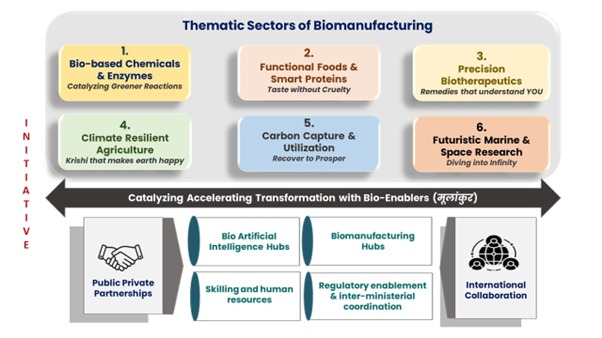
The BioE3 Policy identifies several strategic sectors crucial for India’s biotechnology landscape:
- Bio-Based Chemicals and Enzymes: Development of advanced bio-based chemicals and enzymes aimed at reducing environmental impact and enhancing manufacturing efficiency.
- Functional Foods and Smart Proteins: Innovations in functional foods and smart proteins to improve nutrition and food security, addressing dietary needs and health challenges.
- Precision Biotherapeutics: Advancements in precision medicine through biotherapeutics that target specific diseases based on individual genetic profiles.
- Climate Resilient Agriculture: Promotion of agricultural practices that are resilient to climate change, ensuring food security while minimizing environmental degradation.
- Carbon Capture and Utilization: Fostering technologies for efficient carbon capture and its utilization across various industries to mitigate climate change impacts.
- Marine and Space Biotechnology: Expanding research in marine and space biotechnology to explore new frontiers in biomanufacturing, potentially leading to innovative applications in extreme environments.
Implementation Strategies
To ensure the successful implementation of the BioE3 Policy, several strategies have been outlined:
- Establishment of Biomanufacturing Hubs: Creating specialized hubs that facilitate research, development, and production of bio-based products.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Encouraging collaborations between government agencies, private sector companies, and academic institutions to drive innovation.
- Regulatory Alignment: Harmonizing national regulations with global standards to enhance competitiveness while ensuring ethical biosafety practices.
- Skill Development Initiatives: Expanding India’s skilled biotechnology workforce through targeted training programs that align with industry needs.
- Sustainability Focus: Promoting sustainable practices in biomanufacturing processes to ensure minimal environmental impact.
Challenges Ahead
While the BioE3 Policy presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation, several challenges remain:
- Infrastructure Development: Establishing the necessary infrastructure for biomanufacturing hubs requires substantial investment and coordination.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex regulatory frameworks can pose challenges for startups and small enterprises in the biotechnology sector.
- Market Acceptance: Gaining acceptance for bio-based products among consumers may require extensive awareness campaigns emphasizing their benefits.
- Global Competition: Competing with established biotechnology markets globally necessitates continuous innovation and investment in R&D.
Conclusion
The BioE3 Policy represents a transformative approach to integrating biotechnology into India’s economic framework while addressing environmental sustainability and job creation. By focusing on high-performance biomanufacturing and fostering innovation across strategic sectors, this policy aims to position India as a leader in the global biotechnology landscape. As India embarks on this ambitious journey towards a regenerative bioeconomy, effective implementation of the BioE3 Policy will be crucial in addressing pressing societal challenges while promoting sustainable growth. The success of this policy could not only enhance India’s economic prospects but also contribute significantly to global efforts against climate change and resource depletion.
Practice Questions for UPSC Mains Examination
Q1. Analyze the key features of the BioE3 Policy and discuss how it aims to integrate economic growth, environmental sustainability, and employment generation through biotechnology innovations. What are the potential challenges in implementing this policy effectively?
Spread the Word

