TAG: GS-3: SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Princeton University researchers found (PURF) that Caenorhabditis elegans can gain “knowledge” about how to avoid the disease-causing bacterium, Pseudomonas vranovensis, after eating it for multiple generations.
EXPLANATION:
About C. Elegans Worm:
- C. elegans, or Caenorhabditis elegans, is a small, transparent nematode (roundworm) widely used in scientific research. C. elegans was the first multicellular organism to have its entire genome sequenced in 1998.
- It is about 1 mm in length, making it easy to study under a microscope.
- It has a simple body plan, which simplifies many types of biological research.
- It is a nematode worm which is a small, relatively simple, and precisely structured organism.
- C. elegans grows within 3-5 days from a fertilised egg to a millimetre-long adult, and it has informed profound insights into the human body, as well as biology.
- It was the first multicellular organism to have its full genome sequenced and neural wiring mapped.
- It has two sexes a hermaphrodite and a male.
- The hermaphrodite can be viewed most simply as a female that produces a limited number of sperm: she can reproduce either by self-fertilization, using her own sperm, or by cross-fertilization after transfer of male sperm by mating.
- Self-fertilization allows a single heterozygous worm to produce homozygous progeny.
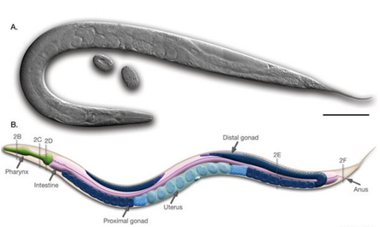
Key Features of C. Elegans Worm
- Short lifespan and quick regeneration: It has a short lifespan of about 2-3 weeks and develops from an egg to an adult in just 3-5 days. This allows for quick generation turnover and facilitates studies on genetics and developmental biology.
- Transparency: It allows researchers to easily observe its internal structures and developmental processes in real time.
- Genetic information: This has provided a wealth of genetic information and made it a powerful tool for genetic studies.
- Consistent Somatic Cell Count: Adult C. elegans have exactly 959 somatic cells, and their lineage has been fully mapped, providing a consistent model for studying cell development and death.
What are Nematodes?
- Nematodes are among the most abundant animals on Earth.
- They occur as parasites in animals and plants or as free-living forms in soil, fresh water, marine environments, and even such unusual places as vinegar, beer malts, and water-filled cracks deep within Earth’s crust.
Features:
-
- Nematodes are bilaterally symmetrical, elongate, and usually tapered at both ends.
- Some species possess a pseudocoel, a fluid-filled body cavity between the digestive tract and the body wall.
Simplified Model for Complex Biology:
- Caenorhabditis elegans is favored by scientists due to its simplicity. With only 959 cells, its entire developmental process can be mapped from fertilization to death, offering an easy-to-study model for fundamental biological processes.
- Its genome was fully sequenced in 1998, and the worm’s short life cycle and transparent body make it an “experimental dream” for researchers.
Source:
Spread the Word



