TAG: GS-2: SOCIAL ISSUES & HEALTH
THE CONTEXT: A 3-year-old girl died of suspected diphtheria in Faridkot, Punjab.
EXPLANATION:
About the Diphtheria:
- Diphtheria is a highly contagious but preventable bacterial disease. It is an infection of the nose and throat.
- A toxin produced by some strains of the Corynebacterium diphtheria bacteria results in diphtheria.
Types :There are 2 types of diphtheria:
1. Respiratory: Respiratory diphtheria affects the nose, throat, and tonsils,
2. Cutaneous: while cutaneous diphtheria affects the skin.
Transmission:
-
- It can spread from person to person, usually through respiratory droplets, like from coughing or sneezing.
- People can also get sick from touching infected open sores or ulcers.
- The bacteria can also infect the skin, causing open sores or ulcers. However, diphtheria skin infections rarely result in severe disease.
- Although diphtheria can be treated with medications, in advanced stages, the bacterial infection can damage the heart, kidneys and nervous system.
Symptoms:
- Typical symptoms of the infection include a sore throat, fever, swollen neck glands and weakness.
- Within 2–3 from infection, the dead tissue in the respiratory tract forms a thick, grey coating that can cover tissues in the nose, tonsils and throat, making it hard to breathe and swallow.
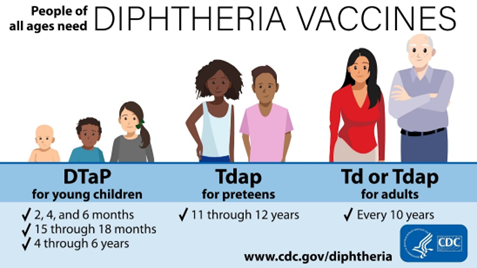
- Immunisation is the best prevention against it, with the full schedule requiring seven doses between 0-16 years.
- Three doses are given before the child turns one, a booster Diphtheria, Pertussis and Tetanus (DPT) shot when the child is two, a fifth dose when the child turns six, and one each in years 10 and 16.
Impact:
- The primary infection is in the throat and upper airways. Produces a toxin affecting other organs.
- One type of diphtheria affects the throat and sometimes the tonsils.
Treatments:
- Neutralization of unbound toxin with Diphtheria Antitoxin (DAT)
- Antibiotics to prevent further bacterial growth.
- Monitoring and supportive care to prevent and treat complications, e.g. airway obstruction, myocarditis.
Prevalence:
- Data from 2023-24 states that almost 84% of diphtheria cases in India were reported from 10 states
-
- Kerala, Assam, Delhi, Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, Nagaland, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and West Bengal.
- According to the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, 93.5% of Indian children in the one-year age bracket were immunised in 2023-24 while Punjab’s numbers stood at 93.96%.
Spread the Word




