TAG: GS-3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT:
In recent years, John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton’s groundbreaking contributions to developing artificial neural networks have won them the Nobel Prize in Physics.
EXPLANATION:
Way in the news:
Nobel Prize-2024 in Physics recognised John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton for their groundbreaking work in artificial neural networks.
- These scientists, who made significant contributions in the 1980s, laid the foundation for today’s AI revolution.
- Their research is only now being fully realized as the capabilities of machine learning and AI continue to advance rapidly.

- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools have become a key part of modern life, enabling users to access information, create multimedia, and analyze large data sets in ways that were unthinkable just a few years ago.
- AI is transforming the way people work and live, with applications ranging from everyday tasks on computers and phones to complex problem-solving in scientific fields.
What is an Artificial Neural Network?
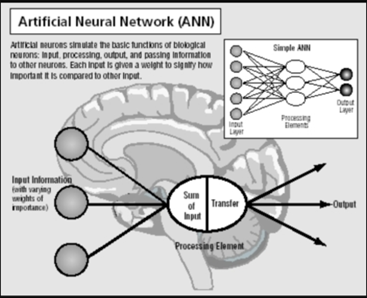
- It is a vital subset of machine learning that helps computer scientists in their work on complex tasks, such as, strategizing, making predictions, and recognizing trends.
- It is a computational model that mimics the way nerve cells work in the human brain.
- It is designed to simulate the way the human brain analyses and processes information.
- It is not like other machine learning algorithms that crunch numbers or organise data, it is an algorithm that learns from experience and repeated tasks performed by its users.
- It is also known as a Neural Network. Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) is a computational model based on the functions and structure of biological neural networks.
- Information that runs through the network affects the structure of the artificial neural network due to the fact that a neural network learns, or changes based on the input and output.
- Neural Network are fed massive volumes of data in the beginning phases. In most cases, training is done by providing input and informing the network about what should be the output.
- Many smartphone makers, for example, have recently integrated facial recognition technology.
How it mimics the human brain:
- Hopfield’s key contribution was the development of neural networks that mimic the functioning of the human brain.
- His work in the 1980s allowed machines to “remember” and “learn” by building neural networks similar to the nerve cells in the brain.
- This breakthrough helped enable pattern recognition, which powers modern technologies like facial recognition and image enhancement tools.
How Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) Work?
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are algorithms that allow computers to learn and remember while processing data. They essentially imitate the way human brains work. Neural networks comprise interconnected artificial neurons divided into an inner layer (or layers), hidden layer/s, and outer layer/s. The inner layer receives the data, hidden layer processes it, and outer layer transmits the result. The number of inner and hidden layers depends on the complexity of the problem.
Signification How Real-world impact of Artificial intelligence (AI):
- This innovation led to the development of deep neural networks, which are crucial for today’s AI systems like voice assistants, image recognition, and self-driving cars.
- Hinton’s work gained global recognition when his team’s algorithm, Alex Net, demonstrated superior image recognition at the 2012 ImageNet competition.
- This marked a turning point in the AI field, solidifying the potential of deep learning. Today, AI is used across industries, from astronomy to healthcare, for analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying significant patterns.
- Geoffrey Hinton expanded on Hopfield’s work, introducing deep learning techniques. His method, known as backpropagation, allowed neural networks to learn from their mistakes and improve accuracy.
- Both Hopfield and Hinton have left an indelible mark on AI and computer science.
Spread the Word




