Day-680
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
1. Consider the following statements about earthquake waves:
1. Surface waves are produced due to interaction of body waves with surface rocks.
2. Deep focus earthquakes produce stronger surface waves as compared to shallow focus earthquakes.
3. Most of the shaking felt from an earthquake is due to the Rayleigh wave.
How many of the above statements are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation: Only Statement 2 is incorrect
Statement 1 is correct:
Types of Earthquake Waves/Seismic Waves-
● Earthquake waves are basically of two types — Body Waves and Surface Waves
Body Waves:
● Body waves are generated due to the release of energy at the focus and move in all directions travelling through the body of the earth. Hence, the name body waves.
● Body waves are of two types-
⮚ Primary Waves (P-Waves)
⮚ Secondary Waves (S-Waves)
Surface Waves:
● Surface waves are those waves that travel on the surface of the earth.
● The destruction caused by earthquakes is primarily done by these waves.
● They are of two types-
⮚ Rayleigh Waves
⮚ Love Waves
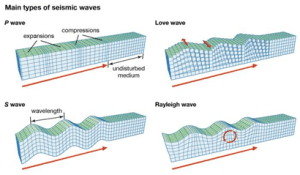
Relation between the Body Waves and the Surface Waves-
● Body waves are the reason for the generation of surface waves.
● Surface waves are generally produced when body waves reach the earth’s surface and interact with surface rocks, setting up complex wave patterns.
● The Body waves interact with the surface rocks and generate a new set of waves called surface waves.
● Particle motion of surface waves (amplitude) is larger than that of body waves, so surface waves are the most destructive among the earthquake waves.
● They are slowest among the earthquake waves and are recorded last on the seismograph.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
Earthquake based on the depth of focus-
● The focus (or hypocenter) of an earthquake is the point within the earth where the rupture begins.
● Earthquakes can be classified by depth as follows:
⮚ Shallow earthquake(less than 70 km deep)
⮚ Intermediate earthquake(70-300 km deep)
⮚ Deep earthquake (greater than 300 km deep). However, generally an earthquake with a depth of more than 70 km is termed a deep earthquake.
Deep focus earthquakes generally do not produce stronger surface waves compared to shallow focus earthquakes. The reasons may be:
● Energy dissipation: Deep focus earthquakes release their energy deep within the earth. As the seismic waves travel toward the surface, the energy dissipates, meaning it loses strength over distance. This results in weaker surface waves by the time they reach the earth’s surface.
● Generation of Surface Waves: Surface waves are generated when body waves (P-waves and S-waves) interact with the Earth’s surface.
⮚ In shallow focus earthquakes, this interaction is more direct, allowing for greater surface wave generation.
⮚ In contrast, deep focus earthquakes have less energy reaching the surface, leading to weaker or fewer surface waves.
● Hence, the shallow focus earthquakes are more likely to produce stronger surface waves due to their proximity to the earth’s surface, while deep focus earthquakes tend to generate less intense surface waves because the energy dissipates as it travels from deep within the earth to the surface.
● This makes shallow focus earthquakes generally more destructive in terms of surface-level impact and damage.
Statement 3 is correct:
The shaking of earth by an earthquake is largely dependent on the type of wave interacting with the earth surface. This can be explained by understanding the particle motion under various kinds of waves as given below.
Body Waves: P-waves and S-waves
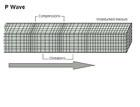
P-Waves:
● The first kind of body wave is the P wave or Primary wave.
● The particle motion of P waves is parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave.
● This is the fastest of seismic waves.
● The P wave can move through solid rock and fluids, like water or the liquid layers of the earth.
● It pushes and pulls the rock as it moves through; just like sound waves push and pull the air.
● Sometimes animals can hear the P waves of an earthquake. Usually, we only feel the bump and rattle of these waves.

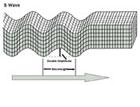
S-Waves:
● The second kind of body wave is the S-wave or Secondary wave.
● The particle motion of the wave is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
● An S wave is slower than the P wave and can only travel through solid rock.
● This wave moves rock up and down, or side-to-side.
● The arrow shows the direction that the wave is moving.
Surface Waves: They are of two types-


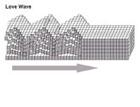
Love Waves:
● Named after A.E.H. Love, a British mathematician who worked out the mathematical model for this kind of wave in 1911.
● It’s the fastest surface wave and moves the ground from side-to-side.
● The arrow shows the direction that the wave is moving.


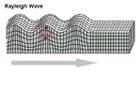
Rayleigh Waves:
● The other kind of surface wave is the Rayleigh wave.
● A Rayleigh wave rolls along the ground just like a wave rolls across a lake or an ocean.
● Because it rolls, it moves the ground up and down, and side-to-side in the same direction that the wave is moving.
● Most of the shaking felt from an earthquake is due to the Rayleigh wave, which can be much larger than the other waves.


 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation: Only Statement 2 is incorrect
Statement 1 is correct:
Types of Earthquake Waves/Seismic Waves-
● Earthquake waves are basically of two types — Body Waves and Surface Waves
Body Waves:
● Body waves are generated due to the release of energy at the focus and move in all directions travelling through the body of the earth. Hence, the name body waves.
● Body waves are of two types-
⮚ Primary Waves (P-Waves)
⮚ Secondary Waves (S-Waves)
Surface Waves:
● Surface waves are those waves that travel on the surface of the earth.
● The destruction caused by earthquakes is primarily done by these waves.
● They are of two types-
⮚ Rayleigh Waves
⮚ Love Waves

Relation between the Body Waves and the Surface Waves-
● Body waves are the reason for the generation of surface waves.
● Surface waves are generally produced when body waves reach the earth’s surface and interact with surface rocks, setting up complex wave patterns.
● The Body waves interact with the surface rocks and generate a new set of waves called surface waves.
● Particle motion of surface waves (amplitude) is larger than that of body waves, so surface waves are the most destructive among the earthquake waves.
● They are slowest among the earthquake waves and are recorded last on the seismograph.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
Earthquake based on the depth of focus-
● The focus (or hypocenter) of an earthquake is the point within the earth where the rupture begins.
● Earthquakes can be classified by depth as follows:
⮚ Shallow earthquake(less than 70 km deep)
⮚ Intermediate earthquake(70-300 km deep)
⮚ Deep earthquake (greater than 300 km deep). However, generally an earthquake with a depth of more than 70 km is termed a deep earthquake.
Deep focus earthquakes generally do not produce stronger surface waves compared to shallow focus earthquakes. The reasons may be:
● Energy dissipation: Deep focus earthquakes release their energy deep within the earth. As the seismic waves travel toward the surface, the energy dissipates, meaning it loses strength over distance. This results in weaker surface waves by the time they reach the earth’s surface.
● Generation of Surface Waves: Surface waves are generated when body waves (P-waves and S-waves) interact with the Earth’s surface.
⮚ In shallow focus earthquakes, this interaction is more direct, allowing for greater surface wave generation.
⮚ In contrast, deep focus earthquakes have less energy reaching the surface, leading to weaker or fewer surface waves.
● Hence, the shallow focus earthquakes are more likely to produce stronger surface waves due to their proximity to the earth’s surface, while deep focus earthquakes tend to generate less intense surface waves because the energy dissipates as it travels from deep within the earth to the surface.
● This makes shallow focus earthquakes generally more destructive in terms of surface-level impact and damage.
Statement 3 is correct:
The shaking of earth by an earthquake is largely dependent on the type of wave interacting with the earth surface. This can be explained by understanding the particle motion under various kinds of waves as given below.
Body Waves: P-waves and S-waves
P-Waves:
● The first kind of body wave is the P wave or Primary wave.
● The particle motion of P waves is parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave.
● This is the fastest of seismic waves.
● The P wave can move through solid rock and fluids, like water or the liquid layers of the earth.
● It pushes and pulls the rock as it moves through; just like sound waves push and pull the air.
● Sometimes animals can hear the P waves of an earthquake. Usually, we only feel the bump and rattle of these waves.


S-Waves:
● The second kind of body wave is the S-wave or Secondary wave.
● The particle motion of the wave is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
● An S wave is slower than the P wave and can only travel through solid rock.
● This wave moves rock up and down, or side-to-side.
● The arrow shows the direction that the wave is moving.
Surface Waves: They are of two types-



Love Waves:
● Named after A.E.H. Love, a British mathematician who worked out the mathematical model for this kind of wave in 1911.
● It’s the fastest surface wave and moves the ground from side-to-side.
● The arrow shows the direction that the wave is moving.



Rayleigh Waves:
● The other kind of surface wave is the Rayleigh wave.
● A Rayleigh wave rolls along the ground just like a wave rolls across a lake or an ocean.
● Because it rolls, it moves the ground up and down, and side-to-side in the same direction that the wave is moving.
● Most of the shaking felt from an earthquake is due to the Rayleigh wave, which can be much larger than the other waves.



-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2. Consider the following statements:
Statement – I: Glaciers have more erosional power as compared to rivers.
Statement – II: The kinetic energy of rivers is more than glaciers.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
Glaciers:
● Masses of ice moving as sheets over the land are called glaciers.
Statement-I is correct:
Glaciers typically have greater erosional power compared to rivers. Following reasons can justify this as follow:
● Massive force of gravity: Glaciers are large bodies of dense ice, often accumulating over long periods. Their immense weight allows them to exert significant pressure on the underlying rock and soil, enhancing their ability to erode.
● Abrasion and plucking: Glaciers erode primarily through two processes: plucking and abrasion.The material plucked from the land by glaciers (usually large-sized angular blocks and fragments) get dragged along the floors or sides of the valleys and cause great damage through abrasion and plucking.
● Slow and consistent movement: The movement of glaciers is slow unlike water flow. The movement could be a few centimetres to a few metres a day or even less or more.
● Large volume of material: Glaciers can carry enormous quantities of rock, sediment, and debris, resulting in significant geomorphological changes. This debris adds to the glacier’s abrasive power, allowing it to carve deep valleys and fjords.
● Long-term impact: Glaciers often persist for thousands of years, providing a long-term erosional force. In contrast, river erosion can be more episodic and influenced by weather and climate patterns.
Statement-II is correct but it is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
The kinetic energy refers to the energy that an object possesses due to its motion.
The kinetic energy of rivers is generally more than that of glaciers due to the following reasons:
● Speed of flow of the rivers: Rivers typically have a much higher flow speed compared to glaciers.
⮚ Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the square of the velocity of an object.
⮚ Even though glaciers have more mass, their flow is slow, often measured in centimetres to meters per day, while rivers can flow at speeds ranging from meters per second to several tens of meters per second during floods.
⮚ This higher velocity contributes to greater kinetic energy in rivers.
● Faster conversion of gravitational energy into kinetic energy: Rivers generate kinetic energy as they flow downhill due to gravity.
⮚ This energy is continuously renewed by the water cycle, with rivers flowing from higher to lower elevations.
⮚ This gravitational energy is converted into kinetic energy as the river flows.
⮚ In contrast, glaciers flow due to gravity but at much slower rates, resulting in lower kinetic energy relative to their mass.
While glaciers have a high erosional capacity due to their sheer mass and pressure, rivers possess greater kinetic energy due to their faster flow speed and dynamic nature, allowing them to transport and erode material more rapidly.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
Glaciers:
● Masses of ice moving as sheets over the land are called glaciers.
Statement-I is correct:
Glaciers typically have greater erosional power compared to rivers. Following reasons can justify this as follow:
● Massive force of gravity: Glaciers are large bodies of dense ice, often accumulating over long periods. Their immense weight allows them to exert significant pressure on the underlying rock and soil, enhancing their ability to erode.
● Abrasion and plucking: Glaciers erode primarily through two processes: plucking and abrasion.The material plucked from the land by glaciers (usually large-sized angular blocks and fragments) get dragged along the floors or sides of the valleys and cause great damage through abrasion and plucking.
● Slow and consistent movement: The movement of glaciers is slow unlike water flow. The movement could be a few centimetres to a few metres a day or even less or more.
● Large volume of material: Glaciers can carry enormous quantities of rock, sediment, and debris, resulting in significant geomorphological changes. This debris adds to the glacier’s abrasive power, allowing it to carve deep valleys and fjords.
● Long-term impact: Glaciers often persist for thousands of years, providing a long-term erosional force. In contrast, river erosion can be more episodic and influenced by weather and climate patterns.
Statement-II is correct but it is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
The kinetic energy refers to the energy that an object possesses due to its motion.
The kinetic energy of rivers is generally more than that of glaciers due to the following reasons:
● Speed of flow of the rivers: Rivers typically have a much higher flow speed compared to glaciers.
⮚ Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the square of the velocity of an object.
⮚ Even though glaciers have more mass, their flow is slow, often measured in centimetres to meters per day, while rivers can flow at speeds ranging from meters per second to several tens of meters per second during floods.
⮚ This higher velocity contributes to greater kinetic energy in rivers.
● Faster conversion of gravitational energy into kinetic energy: Rivers generate kinetic energy as they flow downhill due to gravity.
⮚ This energy is continuously renewed by the water cycle, with rivers flowing from higher to lower elevations.
⮚ This gravitational energy is converted into kinetic energy as the river flows.
⮚ In contrast, glaciers flow due to gravity but at much slower rates, resulting in lower kinetic energy relative to their mass.
While glaciers have a high erosional capacity due to their sheer mass and pressure, rivers possess greater kinetic energy due to their faster flow speed and dynamic nature, allowing them to transport and erode material more rapidly. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
3. Consider the following statements:
Statement – I: The eastern coast of India has several depositional landforms formed by sea waves.
Statement – II: The eastern coast of India is an example of an emergent coast.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
● The eastern coast of India features several depositional landforms formed by sea waves and associated coastal processes.
Characteristics of the eastern coast of India:
● Wide continental shelf: The eastern coast of India has a relatively wide continental shelf, providing a gentle slope and a broad area for sediment deposition. This characteristic favours the formation of depositional landforms.
⮚ East coast of India is an emergent coast that’s why it is a low, smooth and gently sloping sedimentary coast.(While western coast of India is a submergent coast)
⮚ When waves break over a gently sloping sedimentary coast, the bottom sediments get churned and move readily, building bars, barrier bars, spits and lagoons.
⮚ Lagoons would eventually turn into a swamp which would subsequently turn into a coastal plain.
● Gentle sea wave action: The eastern coast experiences relatively moderate wave action compared to the western coast, reducing the rate of erosion and promoting sediment deposition.
Types of depositional landforms formed along the eastern coast of India due to above characteristics:
● Beaches:They are created by the accumulation of sand and other sediments along the shoreline.
● Sandbars and spits: Sandbars are elongated ridges of sand formed by wave action offshore.
⮚ Spits are narrow strips of land extending from the mainland into the sea, created by longshore drift.
● Barrier islands: Barrier islands are narrow, elongated landforms parallel to the coast, often separated by a body of water like a lagoon.
⮚ They form when sediment accumulates due to wave action, creating protective barriers against sea waves.
⮚ Example – The islands along the Sundarbans In West Bengal are examples of barrier islands formed by sediment deposition from the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta.
● Deltas: Deltas are depositional landforms created at the mouths of rivers as they enter a larger body of water, depositing sediments in a fan-like shape.
⮚ The eastern coast has major deltas like the Sunderbans Delta (Ganges-Brahmaputra), the Godavari Delta, and the Krishna Delta, all resulting from substantial sediment deposition.
These conditions make the eastern coast of India a region rich in depositional landforms shaped by sea waves and sediment supply from major rivers.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
● The eastern coast of India features several depositional landforms formed by sea waves and associated coastal processes.
Characteristics of the eastern coast of India:
● Wide continental shelf: The eastern coast of India has a relatively wide continental shelf, providing a gentle slope and a broad area for sediment deposition. This characteristic favours the formation of depositional landforms.
⮚ East coast of India is an emergent coast that’s why it is a low, smooth and gently sloping sedimentary coast.(While western coast of India is a submergent coast)
⮚ When waves break over a gently sloping sedimentary coast, the bottom sediments get churned and move readily, building bars, barrier bars, spits and lagoons.
⮚ Lagoons would eventually turn into a swamp which would subsequently turn into a coastal plain.
● Gentle sea wave action: The eastern coast experiences relatively moderate wave action compared to the western coast, reducing the rate of erosion and promoting sediment deposition.
Types of depositional landforms formed along the eastern coast of India due to above characteristics:
● Beaches:They are created by the accumulation of sand and other sediments along the shoreline.
● Sandbars and spits: Sandbars are elongated ridges of sand formed by wave action offshore.
⮚ Spits are narrow strips of land extending from the mainland into the sea, created by longshore drift.
● Barrier islands: Barrier islands are narrow, elongated landforms parallel to the coast, often separated by a body of water like a lagoon.
⮚ They form when sediment accumulates due to wave action, creating protective barriers against sea waves.
⮚ Example – The islands along the Sundarbans In West Bengal are examples of barrier islands formed by sediment deposition from the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta.
● Deltas: Deltas are depositional landforms created at the mouths of rivers as they enter a larger body of water, depositing sediments in a fan-like shape.
⮚ The eastern coast has major deltas like the Sunderbans Delta (Ganges-Brahmaputra), the Godavari Delta, and the Krishna Delta, all resulting from substantial sediment deposition.
These conditions make the eastern coast of India a region rich in depositional landforms shaped by sea waves and sediment supply from major rivers. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
4. Consider the following statements:
Statement – I: The average annual temperature of the northern hemisphere is more than that of the southern hemisphere.
Statement – II: The northern hemisphere has more land surface as compared to the ocean surface.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
Statement-I is correct:
In earth’s present-day climate, the annually-averaged surface air temperature in the northern hemisphere (NH) is 1.5°C higher than in the southern hemisphere (SH).
Causes:
● The main reason can be attributed to the variation in the land-ocean mix in two hemispheres.
● Specific heat: The specific heat of water is much greater than the land which means more heat is required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by 1 degree Celsius than one gram of land. (Specific heat is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of substance by one degree Celsius).
● Since the land surface is more in the northern hemisphere, this results into
⮚ Differences in seasonal insolation: There is more evaporation from the seas and the oceans and hence more heat is spent in this process with the result oceans get less insolation than land surface.
⮚ The larger area of tropical land in the NH: Heat is concentrated at the place where insolation is received and there is a very slow process of redistribution of heat by conduction because the land surface is static. On the other hand, heat is redistributed in water bodies by sea waves, ocean currents etc.
Other factors contributing to relatively higher average annual temperatures in northern hemisphere include –
● Albedo differences between the earth’s polar regions: The reflection of insolation by water is far more than that of land surface.
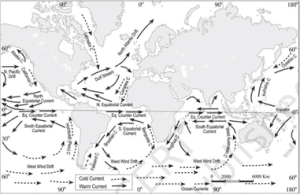
● Northward heat transport by the ocean circulation: Number of warm ocean currents in the northern hemisphere is more as compared to the southern hemisphere. While, the oceans of the southern hemisphere are surrounded by cold currents in large numbers.


 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
Statement-I is correct:
In earth’s present-day climate, the annually-averaged surface air temperature in the northern hemisphere (NH) is 1.5°C higher than in the southern hemisphere (SH).
Causes:
● The main reason can be attributed to the variation in the land-ocean mix in two hemispheres.
● Specific heat: The specific heat of water is much greater than the land which means more heat is required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by 1 degree Celsius than one gram of land. (Specific heat is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of substance by one degree Celsius).
● Since the land surface is more in the northern hemisphere, this results into
⮚ Differences in seasonal insolation: There is more evaporation from the seas and the oceans and hence more heat is spent in this process with the result oceans get less insolation than land surface.
⮚ The larger area of tropical land in the NH: Heat is concentrated at the place where insolation is received and there is a very slow process of redistribution of heat by conduction because the land surface is static. On the other hand, heat is redistributed in water bodies by sea waves, ocean currents etc.
Other factors contributing to relatively higher average annual temperatures in northern hemisphere include –
● Albedo differences between the earth’s polar regions: The reflection of insolation by water is far more than that of land surface.
● Northward heat transport by the ocean circulation: Number of warm ocean currents in the northern hemisphere is more as compared to the southern hemisphere. While, the oceans of the southern hemisphere are surrounded by cold currents in large numbers.



-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
5. Consider the following pairs:
Peninsula – Countries
1. Sinai Peninsula – Israel
2. Baja California Peninsula – USA
3. Anatolian Peninsula – Turkey
How many of the pairs given above are correctly matched?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation: Only Pair 3 is matched correctly
Pair 1 is matched incorrectly:
● The Sinai Peninsula is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia.
● It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa.


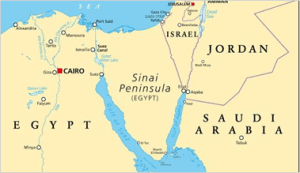
● In news: Sinai Peninsula has been in news due to the ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas. Huge population of southern Gaza has gathered itself near the Rafah crossing (shown in map above) which opens up to the Egyptian land of Sinai Peninsula.
Pair 2 is matched incorrectly:
● The Baja California peninsula is a peninsula in northwestern Mexico.
● It separates the Gulf of California from the Pacific Ocean.
● The peninsula is separated from mainland Mexico by the Gulf of California and the Colorado River.
● There are four main desert areas on the peninsula: the San Felipe Desert, the Central Coast Desert, the Vizcaíno Desert, and the Magdalena Plain Desert.


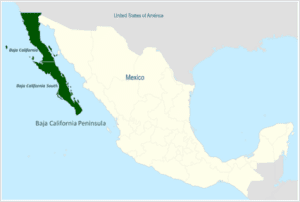
● In news: Baja California peninsula was in news due to the landfall of a powerful Hurricane named Hillary in August 2023.
Pair 3 is matched correctly:
● Anatolia Peninsula also known as Asia Minor is a large peninsula located in West Asia and a region of Turkey.
● The Peninsula is bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the north-west, and the Black Sea to the north.


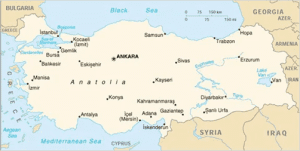
● Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus strait and the Dardanelles strait, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in the Balkan peninsula of Southeastern Europe.
● In news: The Anatolian Peninsula is one of the most tectonically sensitive plates in the whole West Asian region. A massive earthquake also occurred here in 2023.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation: Only Pair 3 is matched correctly
Pair 1 is matched incorrectly:
● The Sinai Peninsula is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia.
● It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa.



● In news: Sinai Peninsula has been in news due to the ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas. Huge population of southern Gaza has gathered itself near the Rafah crossing (shown in map above) which opens up to the Egyptian land of Sinai Peninsula.
Pair 2 is matched incorrectly:
● The Baja California peninsula is a peninsula in northwestern Mexico.
● It separates the Gulf of California from the Pacific Ocean.
● The peninsula is separated from mainland Mexico by the Gulf of California and the Colorado River.
● There are four main desert areas on the peninsula: the San Felipe Desert, the Central Coast Desert, the Vizcaíno Desert, and the Magdalena Plain Desert.



● In news: Baja California peninsula was in news due to the landfall of a powerful Hurricane named Hillary in August 2023.
Pair 3 is matched correctly:
● Anatolia Peninsula also known as Asia Minor is a large peninsula located in West Asia and a region of Turkey.
● The Peninsula is bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the north-west, and the Black Sea to the north.



● Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus strait and the Dardanelles strait, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in the Balkan peninsula of Southeastern Europe.
● In news: The Anatolian Peninsula is one of the most tectonically sensitive plates in the whole West Asian region. A massive earthquake also occurred here in 2023.




