TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has released captivating images of the Sun captured by the Aditya-L1 mission during a significant May solar storm.
EXPLANATION:
- These images are set to enhance our understanding of various solar phenomena and their impact on space weather.
- Between May 8 and 15, the Sun experienced several intense solar flares, classified as X-class and M-class, erupting from the active region AR13664.
- These flares were associated with significant CMEs observed during May 8 and 9.
- During this period, two key remote sensing instruments on Aditya-L1, the Solar Ultra Violet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) and the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), were in baking and calibration modes, respectively, and could not observe the events on May 10-11.
- However, both instruments resumed their observational duties by May 14.
Captured Images and Their Significance
- SUIT Payload Observations
- On June 10, ISRO released six images of the Sun taken by the SUIT payload at different wavelengths, acquired on May 17.
- These images are crucial for multiple areas of solar research:
- Studying Solar Flares: Detailed observations of solar flares help understand their mechanisms and energy release processes.
- Energy Distribution: Analysis of the images provides insights into the distribution of energy across different solar regions.
- Sunspots: Observing sunspots helps predict solar activity and its potential impact on space weather.
- Space Weather Prediction: The data aids in forecasting space weather conditions that can affect satellite operations and communications on Earth.
- Monitoring UV Radiation: By covering a wide wavelength range, the observations help monitor the UV radiation emitted by the Sun.
- Long-term Solar Variations: The images contribute to the study of long-term changes in solar activity.
- VELC Payload Observations
- The VELC payload made significant observations using one of its spectroscopic channels for the emission line at 5303 Angstroms.
- Raster scans of the solar corona were performed on May 14 to capture coronal activities in this spectral line.



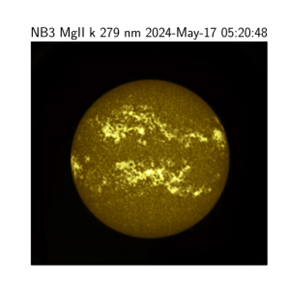
Images captured by SUIT and VELC instruments (Aditya-L1 mission) shows dynamic activities of the Sun during May 2024
Additional Observations
- Apart from SUIT and VELC, other instruments on Aditya-L1 also captured the solar storm events:
- SoLEXS and HEL1OS: These remote sensing payloads recorded the events between May 8 and 9.
- ASPEX and MAG: These in-situ payloads captured data on May 10 and 11 during the mission’s passage through the Sun-Earth L1 point (L1).
- ISRO’s observations were complemented by data from other missions and ground-based facilities:
- Chandrayaan-2 Spacecraft
- XPoSat
- Udaipur Solar Observatory-Physical Research Laboratory
Aditya-L1 mission
- Aditya-L1 is a coronagraphy spacecraft designed and developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to study the solar atmosphere.
- It is India’s first dedicated solar mission.
- The spacecraft will be orbiting at about 1.5 million km from Earth in a halo orbit around the L1 Lagrange point between the Earth and the Sun.
- It is studying the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, known as the corona, to understand its structure, dynamics, and the mechanisms behind its heating to millions of degrees.
- It is investigating the impact of solar activities on the Earth’s climate, weather, and space environment, including potential disruptions to communication and navigation systems.
- They are collecting data on solar storms, solar flares, and other solar phenomena that can affect space weather and terrestrial technologies.




