Day-629
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
1. Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Jharkhand, Odisha, and Chhattisgarh account for almost 70% of the total known coal reserves in India.
Statement-II: The main areas of Gondwana rocks in the peninsular India are along the Damodar Valley, Mahanadi river valley and in a series of troughs along the Godavari.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
Gondwana System:
● The Gondwana System derives its name Gonds, the most primitive people of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
● They are deposits laid down in synclinal troughs on ancient plateau surface.
● As the sediments accumulated, the loaded troughs subsided.
● Fresh water and sediments accumulated in these trough and terrestrial plants and animals thrived.
● This has happened since the Permian period (250 million years ago).
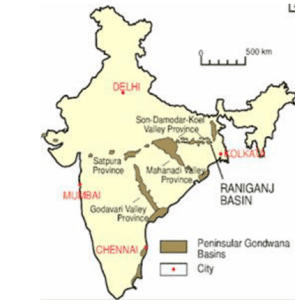
Gondwana Coal:
● Gondwana rocks contain nearly 98 per cent of India’s coal reserves.
● Gondwana coal is much younger than the Carboniferous coal and hence its carbon content is low.
● They have rich deposits of iron ore, copper, uranium and antimony also.
● Sandstones, slates and conglomerates are used as building materials.
Distribution of Gondwana rocks:Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation: Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
Gondwana System:
● The Gondwana System derives its name Gonds, the most primitive people of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
● They are deposits laid down in synclinal troughs on ancient plateau surface.
● As the sediments accumulated, the loaded troughs subsided.
● Fresh water and sediments accumulated in these trough and terrestrial plants and animals thrived.
● This has happened since the Permian period (250 million years ago).

Gondwana Coal:
● Gondwana rocks contain nearly 98 per cent of India’s coal reserves.
● Gondwana coal is much younger than the Carboniferous coal and hence its carbon content is low.
● They have rich deposits of iron ore, copper, uranium and antimony also.
● Sandstones, slates and conglomerates are used as building materials.
Distribution of Gondwana rocks: -
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2. Consider the following trees:
1. White Cedar
2. Magnolia
3. Hollock
4. Kail
5. Rosewood
How many of the above are semi-evergreen trees found in India?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation: White Cedar, Hallock and Kail are examples of the semi evergreen trees found in India.
On the basis of certain common features such as predominant vegetation type and climatic regions, Indian forests can be divided into the following groups:
Types of Forests:
I. Tropical Evergreen and Semi Evergreen forests
II. Tropical Deciduous forests
III. Tropical Thorn forests
IV. Montane forests
V. Littoral and Swamp forests
Tropical Evergreen and Semi Evergreen Forests
Tropical Evergreen Forests:
● These forests are found in the western slope of the Western Ghats, hills of the northeastern region and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
● They are found in warm and humid areas with an annual precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22 degree C.
● In these forests, trees reach great heights up to 60 m or above. There is no definite time for trees to shed their leaves, flowering and fruition. As such these forests appear green all the year round. Species found in these forests include rosewood, mahogony, aini, ebony, etc.

Semi Evergreen Forests:
● The semi evergreen forests are found in the less rainy parts of these regions.
● Such forests have a mixture of evergreen and moist deciduous trees. The undergrowing climbers provide an evergreen character to these forests.
● Main species are white cedar, hollock and kail.
Note: Magnolia, Laurel, Cinchona and Wattle are the examples of the Southern Mountain Forests.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation: White Cedar, Hallock and Kail are examples of the semi evergreen trees found in India.
On the basis of certain common features such as predominant vegetation type and climatic regions, Indian forests can be divided into the following groups:
Types of Forests:
I. Tropical Evergreen and Semi Evergreen forests
II. Tropical Deciduous forests
III. Tropical Thorn forests
IV. Montane forests
V. Littoral and Swamp forests
Tropical Evergreen and Semi Evergreen Forests
Tropical Evergreen Forests:
● These forests are found in the western slope of the Western Ghats, hills of the northeastern region and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
● They are found in warm and humid areas with an annual precipitation of over 200 cm and mean annual temperature above 22 degree C.
● In these forests, trees reach great heights up to 60 m or above. There is no definite time for trees to shed their leaves, flowering and fruition. As such these forests appear green all the year round. Species found in these forests include rosewood, mahogony, aini, ebony, etc.


Semi Evergreen Forests:
● The semi evergreen forests are found in the less rainy parts of these regions.
● Such forests have a mixture of evergreen and moist deciduous trees. The undergrowing climbers provide an evergreen character to these forests.
● Main species are white cedar, hollock and kail.
Note: Magnolia, Laurel, Cinchona and Wattle are the examples of the Southern Mountain Forests. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
3. Consider the following statements:
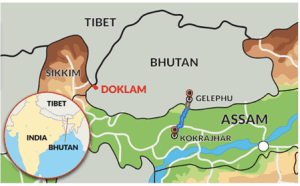
1. Bairabi-Sairang railway line project will connect Arunachal Pradesh with the rest of the country.
2. Kokrajhar-Gelephu railway line project will connect Assam with Mizoram.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation: None of the statements is correct
Statement 1 is incorrect:
About Bairabi-Sairang railway line project:
● The Northeast Frontier Railway (NFR) zone of Indian Railways has been given responsibility for the execution of the project, which will connect Mizoram, one of the eight northeastern states of India, with other parts of the country.
● In addition to enhancing connectivity, the project will also boost tourism in the state, leading to the generation of employment for localities.
Connectivity to neighbouring countries:
● The railway project will play a pivotal role in the development of Mizoram, which is known for its scenic beauty, rich culture and biodiversity, and ease the transportation system for the residents of the states, who are mostly dependent on roads and airways.
● In addition to the development of the state, the project will also enhance its connectivity with neighbouring countries, Myanmar and Bangladesh, as part of the Trans-Asian Railway network and the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
Kokrajhar-Gelephu railway line project:
● It aims to connect Kokrajhar in Assam, India, to Gelephu in Bhutan, enhancing trade and connectivity between the two countries.
● It holds strategic importance, offering an alternative transportation route and boosting cross-border trade and economic cooperation.
● The project involves significant infrastructure development and requires environmental and social impact assessments.


 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation: None of the statements is correct
Statement 1 is incorrect:
About Bairabi-Sairang railway line project:
● The Northeast Frontier Railway (NFR) zone of Indian Railways has been given responsibility for the execution of the project, which will connect Mizoram, one of the eight northeastern states of India, with other parts of the country.
● In addition to enhancing connectivity, the project will also boost tourism in the state, leading to the generation of employment for localities.
Connectivity to neighbouring countries:
● The railway project will play a pivotal role in the development of Mizoram, which is known for its scenic beauty, rich culture and biodiversity, and ease the transportation system for the residents of the states, who are mostly dependent on roads and airways.
● In addition to the development of the state, the project will also enhance its connectivity with neighbouring countries, Myanmar and Bangladesh, as part of the Trans-Asian Railway network and the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
Kokrajhar-Gelephu railway line project:
● It aims to connect Kokrajhar in Assam, India, to Gelephu in Bhutan, enhancing trade and connectivity between the two countries.
● It holds strategic importance, offering an alternative transportation route and boosting cross-border trade and economic cooperation.
● The project involves significant infrastructure development and requires environmental and social impact assessments.



-
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
4. Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Western cyclonic disturbance causes rainfall in Punjab, Haryana, Delhi and western Uttar Pradesh.
Statement-II: The easterly jet stream plays an important role in bringing the winter rains in Northern India.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation: Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
Statement-II is incorrect:
Western Cyclonic Disturbance:
● The western cyclonic disturbances which enter the Indian subcontinent from the west and the northwest during the winter months, originate over the Mediterranean Sea and are brought into India by the westerly jet stream.
Statement-I is incorrect:
● In northwestern India, some weak temperate cyclones from the Mediterranean Sea cause rainfall in Punjab, Haryana, Delhi and western Uttar Pradesh.
● Although the amount is meagre, it is highly beneficial for rabi crops.
● The precipitation is in the form of snowfall in the lower Himalayas.
● It is this snow that sustains the flow of water in the Himalayan rivers during the summer months.
● The precipitation goes on decreasing from west to east in the plains and from north to south in the mountains.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation: Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
Statement-II is incorrect:
Western Cyclonic Disturbance:
● The western cyclonic disturbances which enter the Indian subcontinent from the west and the northwest during the winter months, originate over the Mediterranean Sea and are brought into India by the westerly jet stream.
Statement-I is incorrect:
● In northwestern India, some weak temperate cyclones from the Mediterranean Sea cause rainfall in Punjab, Haryana, Delhi and western Uttar Pradesh.
● Although the amount is meagre, it is highly beneficial for rabi crops.
● The precipitation is in the form of snowfall in the lower Himalayas.
● It is this snow that sustains the flow of water in the Himalayan rivers during the summer months.
● The precipitation goes on decreasing from west to east in the plains and from north to south in the mountains. -
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
5. Consider the following statements:
1. Heatwave is declared when the departure from normal temperature is by 4.5 to 6.4 degrees Celsius.
2. The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) considers severe heat waves when the actual maximum temperature is more than 45 degrees Celsius.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation: Statement 1 is correct
Statement 1 is correct
What is a heatwave?
● The IMD says heatwave is considered when the maximum temperature of a station touches at least 40 degrees Celsius or more for plains, 37 degrees Celsius or more for coastal regions and at least 30 degrees Celsius or more for hilly regions.
What are the criteria?
● Heatwave is declared when the departure from normal temperature is by 4.5 to 6.4 degrees Celsius.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● A severe heatwave is when the departure from normal is more than 6.4 degrees Celsius.
● For plains, based on actual maximum temperature, IMD considers heat waves when actual maximum temperature is more than 45 degrees Celsius and severe heat waves when it is more than 47 degrees Celsius.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation: Statement 1 is correct
Statement 1 is correct
What is a heatwave?
● The IMD says heatwave is considered when the maximum temperature of a station touches at least 40 degrees Celsius or more for plains, 37 degrees Celsius or more for coastal regions and at least 30 degrees Celsius or more for hilly regions.
What are the criteria?
● Heatwave is declared when the departure from normal temperature is by 4.5 to 6.4 degrees Celsius.
Statement 2 is incorrect:
● A severe heatwave is when the departure from normal is more than 6.4 degrees Celsius.
● For plains, based on actual maximum temperature, IMD considers heat waves when actual maximum temperature is more than 45 degrees Celsius and severe heat waves when it is more than 47 degrees Celsius.




