TAG: GS 1: GEOGRAPHY
THE CONTEXT: The occurrence of extreme weather events in distant locations like Mumbai and Dubai on April 16, 2024, underscores the influence of a vast anticyclone spanning the northern Indian Ocean.
EXPLANATION:
- This meteorological phenomenon, characterized by high atmospheric pressure and descending air masses, exerts profound effects on regional weather patterns, exacerbating conditions such as floods and heatwaves on its periphery.
Mumbai’s Humid Heatwave
- In Mumbai, the Konkan coast of India experienced a stifling humid heatwave, with temperatures soaring to unprecedented levels.
- An independent weather forecaster noted a significant temperature rise of 4.7°C within 24 hours, culminating in a scorching maximum temperature of 39°C on April 16.
- Moreover, elevated humidity levels compounded the discomfort, contributing to a wet bulb temperature of 29.3°C, surpassing the threshold for perceived heat.
Factors Driving Mumbai’s Heatwave
- The intensification of Mumbai’s heatwave can be attributed to various factors, including the influence of the anticyclone.
- By inhibiting the flow of cooling sea breezes, the anticyclone disrupted nocturnal temperature regulation, leading to elevated night temperatures.
- Additionally, the transition from El Niño to La Niña, coupled with warming trends in West Asia and the Arabian Sea, contributed to a pronounced heat buildup, exacerbating thermal discomfort among residents.
Implications for Public Health and Safety
- The escalation of heat-related risks underscores the importance of timely and effective public health interventions.
- While wet bulb temperature serves as a critical metric for assessing heat stress, communicating heat advisories and implementing mitigation measures are imperative for safeguarding vulnerable populations.
- Strategies such as establishing hydration centers, offering free public transportation, and disseminating early warnings can mitigate the adverse impacts of heatwaves.
Dubai’s Deluge and Flooding
- Conversely, Dubai experienced an unprecedented deluge characterized by torrential rainfall, inundating major thoroughfares and infrastructure.
- The city bore witness to an astonishing accumulation of rainfall, surpassing the annual average in a single day.
- Furthermore, neighboring Emirates like Sharjah and Abu Dhabi grappled with excessive precipitation, marking a historic event in the region’s meteorological record.
Anticyclone’s Role in Extreme Rainfall
- The expansive anticyclone spanning the northern Indian Ocean played a pivotal role in exacerbating the rainfall event over Dubai and surrounding areas.
- By impeding the progression of weather systems, the anticyclone fostered conditions conducive to intense precipitation and thunderstorms on its fringes.
- Additionally, interactions between the anticyclone and a western disturbance over West Asia likely amplified the severity of the storm system, exacerbating rainfall intensity.
Contributing Factors and Controversies
- While the anticyclone served as a primary driver of extreme weather, other factors contributed to the complexity of the meteorological event.
- Cloud seeding operations conducted by the National Centre of Meteorology of the UAE and the presence of excessive dust in the region may have accentuated rainfall intensity.
- However, discerning the precise contributions of natural and anthropogenic influences remains a subject of debate and scrutiny.
Impacts and Preparedness Measures
- The inundation of Dubai and neighboring regions underscores the vulnerability of urban infrastructure to extreme weather events.
- As cities confront the escalating risks of climate change, enhancing preparedness and resilience measures becomes paramount.
- From improving drainage systems to bolstering emergency response capabilities, proactive interventions are essential for mitigating the socio-economic impacts of flooding and safeguarding public safety.
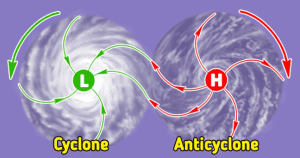
Anticyclone:
- An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure.
- It rotates clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counter clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere (opposite to a cyclone).
- Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure.