TAG: GS 2: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: For the first time since its inception, the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) announced its ‘Vision for Regional Security’ at a ceremony held in its headquarters in Riyadh.
EXPLANATION:
Key highlights of the Vision for Regional Security:
- It is based on the principles of shared destiny and indivisible security of the member states and any threat to one is a threat to all.
- Emphasises joint efforts to avoid use of force and prioritise dialogue and negotiation to resolve their differences.
- Urges member states to combat terrorism, extremism, and money laundering.
- It urges member states to support international and regional efforts on non-proliferation and make the region free of weapons of mass destruction.
- Activate Arab Peace Initiative to reach a just resolution of Palestinian cause in accordance with 2-state solution.
- Climate change, water and food security, energy security, defending economic resources, and creating investment opportunities have also been prioritised.
Significance of the ‘Vision for Regional Security’
- It represents a call to action for all parties to collaborate towards a secure and prosperous future.
- It offers an opportunity to member states to resolve historical regional conflicts such as Palestinian problem, etc.
The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC):
- The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf also known as the Gulf Cooperation Council is a regional, intergovernmental, political, and economic union comprising Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.
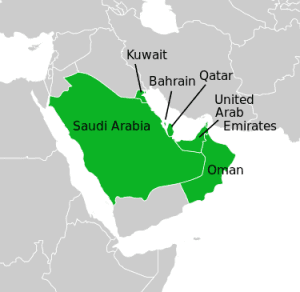
- The council’s main headquarters is located in Riyadh, the capital of Saudi Arabia.
- The Charter of the GCC was signed on 25 May 1981, formally establishing the institution.
- All current member states are monarchies, including three constitutional monarchies (Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain), two absolute monarchies (Saudi Arabia and Oman), and one federal monarchy (the United Arab Emirates, which is composed of seven member states, each of which is an absolute monarchy with its own emir).




