THE CONTEXT: The Economic Research Department of the State Bank of India (SBI) recently published its study Debunking K-shaped recovery.
MORE ON THE NEWS:
- It is being widely debated that the post-pandemic recovery in India has been K-shaped. The debate over K-shaped recovery is also linked to widening inequality in the country.
- However, SBI research study claims to have “debunked” this belief. The report highlighted at a “conspiracy” against India and its growth.
WHAT IS K-SHAPED RECOVERY?
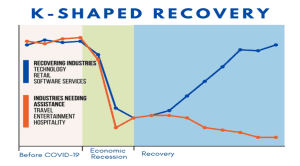
- A K-shaped recovery occurs when, following a recession, different parts of the economy recover at different rates, times, or magnitudes. It refers to a situation where some sectors of the economy revive after slowdown or recession while others don’t. It means not all sectors/parts of the economy are recovering.
- This is in contrast to an even, uniform recovery across sectors, industries, or groups of people.
- A K-shaped recovery leads to changes in the structure of the economy or the broader society as economic outcomes and relations are fundamentally changed before and after the recession.
- This type of recovery is called K-shaped because the path of different parts of the economy when charted together may diverge, resembling the two arms of the Roman letter “K.”
SBI REPORT’S ARGUMENTS
- Positive Emerging Patterns: It highlights patterns of income, savings, consumption, expenditure and policy measures aimed at public welfare.
- Parameters under Scrutiny: The report challenges traditional parameters used to assess economic well-being. It questions the use of old parameters like low two-wheeler sales or fragmented land holdings.
- New Considerations: It highlights patterns in income, savings, consumption, expenditure, and policy measures designed to empower the masses through technology-driven solutions, questioning the reliance on outdated indicators like 2-wheeler sales or land holdings.
- Rising Disposable Incomes in Non-Metro Areas: It cites data from Zomato as an example of rising disposable income in non-metro areas.
- Decrease in Inequality: It refers to the income tax data for FY22 to note that the Gini coefficient had declined significantly from 0.472 to 0.402 between FY14 and FY22.
It highlights that 36.3% of individual tax return filers belonging to the lowest income in FY14 have left the lowest income group and shifted upwards.
A DIFFERENT PERSPECTIVE
- Not representative: The research of SBI is not representative of the Indian economy, it also brings out a newly-destined ‘narrative’. It just focuses on the “privileged” formal sector that, going by various estimates, has recorded impressive growth.
- Contrasting Reports: In 2022, another report, “The State of Inequality in India,” commissioned by the Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister, highlighted rising inequality in the country. It noted that an individual earning a monthly wage of Rs 25,000 was among the top 10% of earners, underscoring the stark income disparities.
- High Welfare Spending indicated Economic distress: The government has been forced to extend the scheme of subsidized food grain to 800 million Indians.
- Tax Data does not reflect Broader Economy: Only a very small minority of people pay direct income tax. Hence, it is not reasonable to draw conclusions from tax data about broader inequality. Income tax data is nominal and is affected by overall inflation, thus making it unviable for drawing conclusions.
THE WAY FORWARD:
- Increase government spending: The government must spend where necessary to alleviate the concerns in the most troubled areas of the economy.
- Addressing debt issues: There is a need for a credible target for the country’s consolidated debt with the setting up of an independent fiscal council to put forward on the quality of the budget would be a great step.
- Include budgetary resources: Budgetary resources needs to be expanded through asset sales, including parts of government enterprises and surplus government land.
- Analysing data: The shape of economic recovery is not an exact science, but the predictions help governments, investors, and consumers alike in planning monetary policies and investments.
THE CONCLUSION:
The recent SBI research provides a unique perspective on India’s economic recovery and inequality but its focus on a limited sample from the formal sector raises concerns about its representativeness. There is a need to emphasis on more comprehensive understanding of the diverse economic landscape in India.
UPSC PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTION
Q. Do you agree that the Indian economy has recently experienced V-shaped recovery? Give reasons in support of your answer. (2021)
MAINS PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. ‘Recent SBI report has debunked the theory that India has experienced K-shaped economic recovery in the post-pandemic era’. Examine.
Spread the Word

Related posts
LESSONS FROM THE CHOLA EMPIRE TO THE CONTEMPORARY INDIA
FROM SEAFLOOR RUPTURE TO SAFER SHORES: RE-IMAGINING TSUNAMI RISK GOVERNANCE FOR INDIA
MANGROVE RESTORATION AND COASTAL SECURITY IN INDIA