Day-561
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
DAILY MCQ
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
1. Consider the following pairs:
Shifting cultivation – Practised in the region
1. Milpa – Indonesia
2. Ladang – Central America
3. Jhuming – North Eastern India
4. Taungya – Sri Lanka
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Primitive subsistence agriculture or shifting cultivation is widely practised by many tribes in the tropics, especially in Africa, south and Central America and South East Asia.
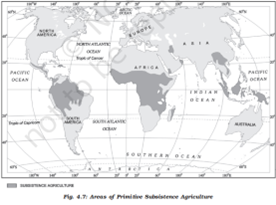
The vegetation is usually cleared by fire, and the ashes add to the fertility of the soil. Shifting cultivation is thus, also called slash and burn agriculture.
The cultivated patches are very small and cultivation is done with very primitive tools such as sticks and hoes.
After sometime (3 to 5 years) the soil looses its fertility and the farmer shifts to another parts and clears other patch of the forest for cultivation.
The farmer may return to the earlier patch after sometime.
One of the major problems of shifting cultivation is that the cycle of jhum becomes less and less due to loss of fertility in different parcels.
It is prevalent in tropical region in different names:
Jhuming in North eastern states of India
Milpa in central America and Mexico
Ladang in Indonesia and Malaysia
Taungya in Myanmar
Chena in Sri Lanka
Caigin in the PhilippinesIncorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Primitive subsistence agriculture or shifting cultivation is widely practised by many tribes in the tropics, especially in Africa, south and Central America and South East Asia.

The vegetation is usually cleared by fire, and the ashes add to the fertility of the soil. Shifting cultivation is thus, also called slash and burn agriculture.
The cultivated patches are very small and cultivation is done with very primitive tools such as sticks and hoes.
After sometime (3 to 5 years) the soil looses its fertility and the farmer shifts to another parts and clears other patch of the forest for cultivation.
The farmer may return to the earlier patch after sometime.
One of the major problems of shifting cultivation is that the cycle of jhum becomes less and less due to loss of fertility in different parcels.
It is prevalent in tropical region in different names:
Jhuming in North eastern states of India
Milpa in central America and Mexico
Ladang in Indonesia and Malaysia
Taungya in Myanmar
Chena in Sri Lanka
Caigin in the Philippines -
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2. In the context of mining activities in India, consider the following pairs:
Iron ore mines – States
1. Gurumahisani – West Bengal
2. Noamundi – Jharkhand
3. Badampahar – Odisha
4. Dalli-Rajhara – Rajasthan
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?Correct
Answer: B
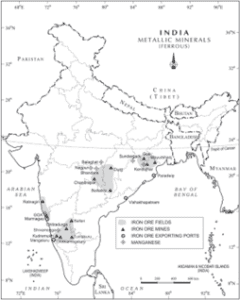
Explanation: India is endowed with fairly abundant resources of iron ore. It has the largest reserve of iron ore in Asia. The two main types of ore found in our country are haematite and magnetite. The iron ore mines occur in close proximity to the coal fields in the northeastern plateau region of the country which adds to their advantage.
About 95 per cent of total reserves of iron ore are located in the States of Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka, Goa, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
Pair 1 is matched incorrectly and Pair 3 is matched correctly: In Odisha, iron ore occurs in a series of hill ranges in Sundergarh, Mayurbhanj and Jhar.
The important mines are Gurumahisani, Sulaipet, Badampahar (Mayurbhaj), Kiruburu (Kendujhar) and Bonai (Sundergarh).
Pair 2 is matched correctly: Jharkhand has some of the oldest iron ore mines and most of the iron and steel plants are located around them. Most of the important mines such as Noamundi and Gua are located in Poorbi and Pashchimi Singhbhum districts.
Pair 4 is matched incorrectly: Dalli-Rajhara mines are in Chhattisgarh.

Additional Information
Apart from these sources, iron ore is extracted from following sources also:
In Chattisgarh major iron ore mining areas are Durg, Dantewara and Bailadila. Dalli, and Rajhara in Durg are the important mines of iron ore in the country.
In Karnataka, iron ore deposits occur in Sandur -Hospet area of Ballari district, Baba Budan hills and Kudremukh in Chikkamagaluru district and parts of Shivamogga, Chitradurg and Tumakuru districts.
The districts of Chandrapur, Bhandara and Ratnagiri in Maharashtra, Karimnagar and Warangal district of Telangana, Kurnool, Cuddapah and Anantapur districts of Andhra Pradesh, Salem and Nilgiris districts of Tamil Nadu are other iron mining regions.
Goa has also emerged as an important producer of iron ore.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation: India is endowed with fairly abundant resources of iron ore. It has the largest reserve of iron ore in Asia. The two main types of ore found in our country are haematite and magnetite. The iron ore mines occur in close proximity to the coal fields in the northeastern plateau region of the country which adds to their advantage.
About 95 per cent of total reserves of iron ore are located in the States of Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka, Goa, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
Pair 1 is matched incorrectly and Pair 3 is matched correctly: In Odisha, iron ore occurs in a series of hill ranges in Sundergarh, Mayurbhanj and Jhar.
The important mines are Gurumahisani, Sulaipet, Badampahar (Mayurbhaj), Kiruburu (Kendujhar) and Bonai (Sundergarh).
Pair 2 is matched correctly: Jharkhand has some of the oldest iron ore mines and most of the iron and steel plants are located around them. Most of the important mines such as Noamundi and Gua are located in Poorbi and Pashchimi Singhbhum districts.
Pair 4 is matched incorrectly: Dalli-Rajhara mines are in Chhattisgarh.


Additional Information
Apart from these sources, iron ore is extracted from following sources also:
In Chattisgarh major iron ore mining areas are Durg, Dantewara and Bailadila. Dalli, and Rajhara in Durg are the important mines of iron ore in the country.
In Karnataka, iron ore deposits occur in Sandur -Hospet area of Ballari district, Baba Budan hills and Kudremukh in Chikkamagaluru district and parts of Shivamogga, Chitradurg and Tumakuru districts.
The districts of Chandrapur, Bhandara and Ratnagiri in Maharashtra, Karimnagar and Warangal district of Telangana, Kurnool, Cuddapah and Anantapur districts of Andhra Pradesh, Salem and Nilgiris districts of Tamil Nadu are other iron mining regions.
Goa has also emerged as an important producer of iron ore. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
3. Lachin Corridor, seen in the news recently, is related to which one of the following?
Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
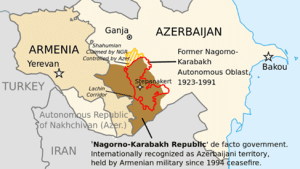
The Lachin corridor is a mountain road in Azerbaijan that links Armenia and Nagorno-Karabakh.
Being the only road between these two territories, it is considered a humanitarian corridor or “lifeline” to the Armenian population of Nagorno-Karabakh.
The corridor is in the Lachin District of Azerbaijan, but is ostensibly under the control of a Russian peacekeeping force as provided for in the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh armistice agreement.


 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Lachin corridor is a mountain road in Azerbaijan that links Armenia and Nagorno-Karabakh.
Being the only road between these two territories, it is considered a humanitarian corridor or “lifeline” to the Armenian population of Nagorno-Karabakh.
The corridor is in the Lachin District of Azerbaijan, but is ostensibly under the control of a Russian peacekeeping force as provided for in the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh armistice agreement.



-
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
4. Consider the following peninsular rivers:
1. Subarnarekha
2. Sharavati
3. Brahmani
4. Pennar
How many of the rivers given above flow from east to west?Correct
Answer: A
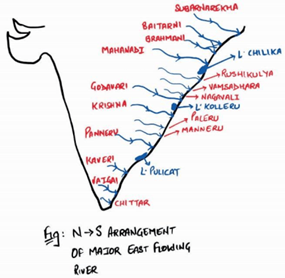
Explanation: Only Sharavati River flows towards the west. All other are east flowing rivers given here.
The Western Ghats, which run close to the western coast, serve as a water divide between the major Peninsular Rivers, which discharge their water into the Bay of Bengal, and the small rivulets joining the Arabian Sea.
Most of the major Peninsular Rivers except Narmada and Tapi flow from west to east.


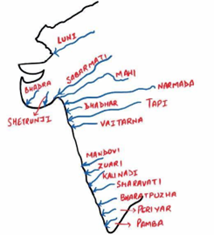
The rivers flowing towards the Arabian Sea have short courses.
The Sharavati is one such river, which originates in the Shimoga district of Karnataka and drains a catchment area of 2,209 sq. km. The total length of the river is around 128 km, and it joins the Arabian Sea at Honnavar in Uttara Kannada district. On its way, the Sharavati forms the Jog Falls, where the river falls from a height of 253 metres.
There are a number of small rivers that join the Bay of Bengal. The Subarnrekha, the Baitarni, the Brahmani, the Vamsadhara, the Pennar, the Palar, and the Vaigai are important east flowing rivers.


 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation: Only Sharavati River flows towards the west. All other are east flowing rivers given here.
The Western Ghats, which run close to the western coast, serve as a water divide between the major Peninsular Rivers, which discharge their water into the Bay of Bengal, and the small rivulets joining the Arabian Sea.
Most of the major Peninsular Rivers except Narmada and Tapi flow from west to east.



The rivers flowing towards the Arabian Sea have short courses.
The Sharavati is one such river, which originates in the Shimoga district of Karnataka and drains a catchment area of 2,209 sq. km. The total length of the river is around 128 km, and it joins the Arabian Sea at Honnavar in Uttara Kannada district. On its way, the Sharavati forms the Jog Falls, where the river falls from a height of 253 metres.
There are a number of small rivers that join the Bay of Bengal. The Subarnrekha, the Baitarni, the Brahmani, the Vamsadhara, the Pennar, the Palar, and the Vaigai are important east flowing rivers.



-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
5. Consider the following regions:
1. Mumbai-Pune region
2. Vishakhapatnam-Guntur region
3. Chhotanagpur region
4. Ambala-Amritsar region
How many of the above regions are the major industrial regions in India?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation:
Industries are not evenly distributed in the country. They tend to concentrate on certain locations because of the favorable locational factors.


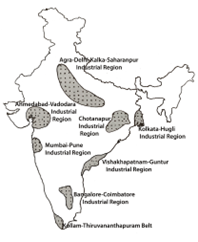
Major industrial regions of the country are given below (8):
Mumbai-Pune Region
Hugli Region
Bengaluru-Tamil Nadu Region
Gujarat Region
Chotanagpur Region
Vishakhapatnam-Guntur Region
Gurugram-Delhi-Meerut Region, and
Kollam-Thiruvananthapuram Region
Minor Industrial Regions (13):
Ambala-Amritsar
Saharanpur-Muzzaffarnagar-Bijnor
Indore-Dewas-Ujjain
Jaipur-Ajmer
Kolhapur-South Kannada
Northern Malabar
Middle Malabar
Adilabad-Nizamabad
Allahabad-Varanasi-Mirzapur
Bhojpur-Munger
Bilaspur-Korba
Durg-Raipur
Brahmaputra ValleyIncorrect
Answer: C
Explanation:
Industries are not evenly distributed in the country. They tend to concentrate on certain locations because of the favorable locational factors.



Major industrial regions of the country are given below (8):
Mumbai-Pune Region
Hugli Region
Bengaluru-Tamil Nadu Region
Gujarat Region
Chotanagpur Region
Vishakhapatnam-Guntur Region
Gurugram-Delhi-Meerut Region, and
Kollam-Thiruvananthapuram Region
Minor Industrial Regions (13):
Ambala-Amritsar
Saharanpur-Muzzaffarnagar-Bijnor
Indore-Dewas-Ujjain
Jaipur-Ajmer
Kolhapur-South Kannada
Northern Malabar
Middle Malabar
Adilabad-Nizamabad
Allahabad-Varanasi-Mirzapur
Bhojpur-Munger
Bilaspur-Korba
Durg-Raipur
Brahmaputra Valley




