THE CONTEXT: Historically, India has maintained a significant influence in the Maldives due to geographical proximity, shared cultural ties, and common interests in regional stability. However, the political leadership in Maldives has been see-sawing time and again either into the ‘India first’ faction, or the ‘India out’ faction. The current President-elect Mohamed Muizzu has again dispersed his inclination towards the ‘India out’ narrative, leaving ample space for India to ponder about future bilateral diplomacy. The following article attempts to analyse the contemporary India-Maldives relations along with prospects from the UPSC perspective.
CURRENT DEVELOPMENTS AFTER ELECTIONS
- 2023 elections: Mohamed Muizzu, alleged to favour China has been elected as President, thus raising concerns for India.
- Mohamed Muizzu had declared that if elected, he would follow the India first policy traditionally practiced by governments of Maldives, but will not allow the crossing of limits. Muizzu immediately contrasted his intent post electoral victory by saying, “We will send back foreign soldiers in the Maldives”. Although he didn’t name any country, this is said to point at Indian forces stationed in Maldives.
- Also, at the request of President-elect Muizzu, former President Solih agreed to shift former President Yameen from prison to house arrest. Mr. Yameen is serving a long sentence (11 years) for corruption. He is seen as Mr. Muizzu’s mentor. This is of significant concern to India as Mr. Yameen already promoted the ‘India out’ campaign.
WHY IS MALDIVES IMPORTANT FOR INDIA?
Strategic Location
- The Maldives is strategically located in the Indian Ocean, which is of immense geostrategic importance to India.
- It serves as a key maritime neighbor, and its proximity to important Indian ports in the southern states of India, such as Kerala and Tamil Nadu, makes it a critical component of India’s maritime security.
- Further, Maldives is crucial to secure free flow of trade in Indian Ocean region.
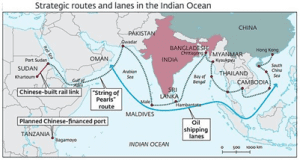
Maritime Security:
- The Maldives’ exclusive economic zone (EEZ) overlaps with important sea lanes of communication (SLOCs) used for the transportation of goods, energy resources, and military traffic.
- India and the Maldives cooperate closely to ensure the security of these vital SLOCs, which are crucial for India’s economic and strategic interests.
- 50% of India’s external trade and 80% of our energy imports transit through the Sea lanes of communication (SLOCs) in the vicinity of the Maldives.
Counter terrorism and Anti-Piracy
- The Maldives has faced challenges related to extremism and piracy in its waters. India collaborates with the Maldives in counter terrorism efforts and anti-piracy operations, which contribute to regional security in the Indian Ocean.
Regional Stability
- The stability and security of the Indian Ocean region are paramount for India. Any disturbances or conflicts in the region can directly impact India’s national security.
- The Maldives’ stability and cooperative relations with India contribute to regional peace and security.
- Also, Maldives holds an important place in countering the Chinese string of pearl’s policy in the Indian Ocean.
- With an estimated 70% of external debt owed to China it’s important for India to release Maldives from the possible debt-trap policy of China.
Cultural and People-to-People Ties
- India and the Maldives share historical, cultural, and linguistic ties. These people-to-people connections strengthen the diplomatic relationship and enhance mutual understanding.
- There is an estimated 25,000 Indian Nationals which makes up the second largest expatriate community in Maldives. Also, an estimated 6% of tourism in Maldives is supported by Indians.
Diplomatic Support
- The Maldives has historically supported India’s positions on various international issues.
- India’s partnership with the Maldives amplifies its influence in regional and global forums, reinforcing its diplomatic endeavors.
- For instance, both Nations are engaged through platforms like SAARC, SASEC, IORA and IONS. A friendly Maldives could possibly amplify India’s presence and position in these forums/groupings.
CHALLENGES TO INDIA-MALDIVES RELATIONS
India-Maldives relations, while important and historically friendly, have faced several challenges that have shaped the course of the bilateral relationship. Some of the key challenges include:
Political Instability and Leadership Changes
- The Maldives has witnessed periods of political instability, which have had repercussions on the bilateral relationship. Political transitions, including coups and resignations, have created uncertainties in the relationship.
- Historically, Maldives had an Executive Presidency system since 1968, transitioning to a multi-party democracy in 2008.
- No incumbent president has been re-elected since then, which is concerning for India this time.
- The Maldives has, at times, shifted its foreign policy orientation away from India (‘India out’), creating apprehensions about its strategic interests in the Indian Ocean region.
Concerns About Chinese Influence
- India is concerned about the growing influence of China in the Maldives, particularly through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) projects.
- India sees these projects as potentially leading to a debt trap and undermining its influence in the region.
Debt and Economic Sustainability
- The Maldives’ reliance on external loans and investments has raised concerns about debt sustainability. This includes both Indian and Chinese loans, potentially leading to financial vulnerabilities.
Radicalisation of youth
- A large number of Maldives citizens had joined violent extremist organisations such as the Islamic State (IS).
- There has been a steady rise in recruits joining jihadi groups in Pakistan over the last decade.
- There is now a greater risk that terrorist organisations based in Pakistan will use the Maldives as a staging ground for attacks on India and Indian assets.
Environmental Challenges
- Rising sea levels and the threat of climate change pose significant challenges for the Maldives. This affects its sustainability and economic prospects, which, in turn, can influence its relationship with India.
Slow rate of project completion
- India’s infrastructure projects are often delayed, like the Greater Malé Connectivity Project (GMCP). Also, the China centric government like that in the present further favour’s Chinese investments.The termination of the agreement with GMR for the modernization of the Ibrahim Nasir International Airport, followed by arbitration and the subsequent award of the project to a Chinese company, has strained India-Maldives relations.
HOW THE CURRENT ELECTION RESULTS CAN IMPACT THE BILATERAL RELATIONS?
- Developments spanning the past two decades have demonstrated China’s consistent expansion and strategic inroads into India’s neighboring regions. For India, risking the loss of goodwill in the Maldives could carry significant consequences, particularly in the context of China’s ‘String of Pearls’ strategy.
- This becomes more important, given the fact that the current president elect Mohamed Muizzu is already representing the ‘India out’ faction.
- This election result can significantly impact the prospects of ongoing infrastructure projects initiated by the previous Ibrahim Mohamed Solih government. These include projects like Maldives National Defence Forces Coast Guard ‘Ekatha Harbour’, initiated in May, 2023.
- This could also mean India’s ambition of enhancing its military position in Maldives may not fructify, in wake of a free hand to Chinese investments.
Despite the expected challenges stemming from the changing political landscape in the Maldives, it remains imperative for India to maintain its unwavering commitment to its priorities and sustain its endeavors for fostering progress in the archipelago nation. Therefore, the evolving situation in the Maldives should not be underestimated. Following the experience with Hambantota, India cannot afford to allow the establishment of a Chinese military base in the region.
THE WAY FORWARD:
Diplomatic Engagement
- Enhance Diplomatic Outreach: India should continue its robust diplomatic engagement with the Maldives, maintaining a constant dialogue at the highest levels. This ensures that both countries are aligned on regional and global issues.
- Multilateral Forums: Active participation in regional forums like the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) and initiatives such as the Quad allows India and the Maldives to collaborate on regional security, economic, and environmental issues. Further, India must amplify its supporting stance for Maldives in forums like G20 through its ‘Global South-South cooperation’ mandate.
Economic Cooperation
- Economic Projects: India should continue to support economic projects in the Maldives, focusing on critical infrastructure development, renewable energy, and tourism. These projects have a direct impact on the Maldives’ economy and can enhance mutual economic interests.
- Trade and Investment: Efforts should be made to boost trade between the two countries, promote Indian investments in the Maldives, and facilitate opportunities for Maldivian businesses in India.
Debt Sustainability and Economic Diversification
- Debt Management: India should support the Maldives in debt management, ensuring that investments do not lead to unsustainable debt burdens.
- Economic Diversification: The Maldives can diversify its economy to reduce dependence on a few sectors like tourism. India can provide expertise in areas such as agriculture, fisheries, and information technology.
Addressing China’s Role
- Balanced Engagement: India should encourage the Maldives to engage with multiple partners, including China, while maintaining transparency in all agreements and ensuring they are in line with the Maldives’ long-term interests.
- Debt Trap Mitigation: Both countries should work together to mitigate any potential debt trap risks associated with Chinese investments, ensuring that the Maldives retains its sovereignty.
THE CONCLUSION: India holds a significant place in the collective consciousness of its neighboring countries, often seen either as a generous benefactor or, in some cases, as an overbearing “big brother.” This dual perception makes India vulnerable to being either endorsed or criticized by political parties, sometimes as an emotive electoral topic and at times as a bargaining tool in negotiations, particularly when they are seeking support from another interested party like China. India must thus, work towards greater cooperative spirit towards every political faction in Maldives being in consonance with its ‘Neighbourhood first’ policy.
QUESTIONS
Q.1 “For India, Maldives is a first line of defence against terrorism, piracy on the high seas, and potential Chinese aggression in the Indian Ocean Region.” Critically examine.
Q.2 “While India has historically pushed for the ‘neighbourhood first’ policy, it has had limited success due to contrasting and unstable political leadership in Maldives.” Examine in the light of recent developments.
ADDITIONAL KNOWLEDGE
In the political landscape of the Maldives, two significant political factions have played prominent roles: the Maldivian Democratic Party (MDP) and the Progressive Party of Maldives (PPM). These two factions have had a substantial impact on the country’s political dynamics. Here’s an in-depth explanation of each faction:
1. Maldivian Democratic Party (MDP):
The Maldivian Democratic Party (MDP) is a prominent political party in the Maldives. It was founded in 2005 and has been at the forefront of the pro-democracy movement in the country. Key features and developments related to the MDP include:
- Foundation and Leadership: The MDP was founded by Mohamed Nasheed, who later became the Maldives’ first democratically elected President in 2008. Nasheed, a prominent advocate for democracy and climate change action, is a central figure in the MDP.
- Pro-Democracy Movement: The MDP played a crucial role in the movement for political reforms and the transition from an autocratic regime to a multi-party democracy. This movement led to the first democratic elections in 2008, which Nasheed won.
- Key Policy Initiatives: During its tenure in government, the MDP pursued various policy initiatives, including social welfare programs, healthcare reforms, and climate change advocacy. The Maldives, under the MDP’s leadership, gained international recognition for its efforts to address climate change and promote climate adaptation and mitigation.
- Challenges and Political Instability: The MDP-led government faced challenges, including opposition from the conservative and religious elements in the Maldivian society. Nasheed’s resignation in 2012 amid political turmoil and disputes over the judiciary further complicated the political landscape.
- International Relations: The MDP’s foreign policy orientation has been inclined towards India and democratic nations. Nasheed, during his presidency, sought support from India and the international community on issues of climate change, democracy, and human rights.
2. Progressive Party of Maldives (PPM):
The Progressive Party of Maldives (PPM) is another influential political faction in the Maldives. It was founded in 2011 and is associated with a more conservative and pro-establishment political outlook. Key features and developments related to the PPM include:
- Foundation and Leadership: The PPM was founded by Maumoon Abdul Gayoom, who served as the President of the Maldives for over three decades until 2008. He is a prominent figure in Maldivian politics and is known for his more conservative and authoritarian style of governance.
- Conservative Stance: The PPM has positioned itself as a conservative political party that promotes traditional values, cultural identity, and religious conservatism. It has often been seen as a counterforce to the more progressive MDP.
- Return of Maumoon Abdul Gayoom: After the transition to a multi-party democracy, Maumoon Abdul Gayoom returned to the political arena. He initially aligned with the MDP but later formed the PPM, creating a political division in the country.
- Role in the Political Landscape: The PPM has played a significant role in opposition politics, challenging the MDP’s policies and advocating for a more conservative approach in governance.
- Election Outcomes: The PPM’s candidate, Yameen Abdul Gayoom, won the presidential election in 2013. However, his tenure was marked by political controversies, including allegations of corruption and human rights abuses.
- International Relations: During Yameen’s presidency, the Maldives maintained diplomatic relations with various countries, including China, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. These relationships were seen as diversifying the Maldives’ foreign policy.
Both the MDP and the PPM represent distinct political ideologies and have contributed to the political diversity and complexity of the Maldives. Their interactions and the outcomes of elections and political developments have significantly influenced the country’s democratic journey and policy directions.
The Sinamale Bridge, also known as the China-Maldives Friendship Bridge, is a significant infrastructure project in the Maldives that connects the capital city of Malé with the nearby island of Hulhulé, where Velana International Airport is located. The bridge plays a pivotal role in enhancing connectivity, transportation, and economic development in the Maldives.
Key features and details of the Sinamale Bridge include:
- Purpose and Significance: The Sinamale Bridge was constructed with the primary aim of improving transportation links between Malé and Hulhulé, the two most populous islands in the Maldives. It addresses transportation challenges and facilitates the movement of people, goods, and services.
- Financing and Construction: The bridge project was financed and developed with support from the Chinese government and Chinese companies. It was a prominent example of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), which aims to promote economic and infrastructure connectivity between China and countries around the world.
- Inauguration: The Sinamale Bridge was officially opened in August 2018 and was seen as a significant achievement for the Maldives. It was inaugurated by then-President Abdulla Yameen Abdul Gayoom.
- Economic Impact: The bridge has had a profound economic impact on the Maldives by easing the movement of goods, reducing transportation costs, and enhancing connectivity to the main international airport. It has also improved tourism, trade, and logistics in the country.

The Sinamale Bridge represents a critical piece of infrastructure that has enhanced connectivity, transportation, and economic development in the Maldives. It also symbolizes the growing economic cooperation between the Maldives and China. However, it has been subject to discussions and debates regarding the financial implications of Chinese investments and debt sustainability in the country.
Spread the Word



