1. ADITYA-L1 MISSION
TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: The High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS) payload, onboard the Aditya-L1 spacecraft, has captured the first glimpse of solar flares.
EXPLANATION:
- HEL1OS Payload:
- The High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS) payload onboard Aditya-L1 is the instrument responsible for capturing the first glimpse of solar flares.
- It marks an important milestone in India’s mission to study the Sun.
- The information collected is expected to contribute to our understanding of solar activity and its impact on space weather.
- The payload was developed by the Space Astronomy Group of the U. R. Rao Satellite Centre in Bengaluru, ISRO.
- Solar Flares:
- During its first observation period on October 29, HEL1OS recorded the impulsive phase of solar flares.
- Solar flares are sudden and intense bursts of energy and radiation from the Sun.
- The data captured is consistent with X-ray light curves provided by NOAA’s GOES satellites.
- Scientific Value:
- The HEL1OS instrument’s capabilities allow for monitoring the Sun’s high-energy X-ray activity with fast timing and high-resolution spectra.
- This data is essential for researchers to study the explosive energy release and electron acceleration during the impulsive phases of solar flares.
- Understanding these processes is crucial for space weather prediction and solar physics research.
- L1 Orbit:
- Aditya-L1 is scheduled to arrive at the L1 point in January 2024.
- Once there, the satellite will operate in an irregularly shaped orbit, allowing it to continuously monitor the Sun’s behavior from this vantage point.
- International Collaboration:
-
- The collaboration with NOAA’s GOES [National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites], indicating the valuable international partnerships in the field of space research and solar observations.
WHAT IS ADITYA L1 MISSION?
- Aditya L1 is the first space based Indian mission to study the Sun.
- The spacecraft shall be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, which is about 1.5 million km from the Earth.
- A satellite placed in the halo orbit around the L1 point has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any occultation/eclipses.
- This will provide a greater advantage of observing the solar activities and its effect on space weather in real time.
- The spacecraft carries seven payloads to observe the photosphere, chromosphere, and the outermost layers of the Sun (the corona) using electromagnetic and particle and magnetic field detectors.
- Using the special vantage point L1, four payloads directly view the Sun, and the remaining three payloads carry out in-situ studies of particles and fields at the Lagrange point L1.
- It will provide important scientific studies of the propagatory effect of solar dynamics in the interplanetary medium.
WHAT ARE THE OBJECTIVES OF ADITYA-L1 MISSION?
The major objectives of Aditya-L1 mission are:
- Study of Solar upper atmospheric (chromosphere and corona) dynamics.
- Study of chromospheric and coronal heating, physics of the partially ionized plasma, initiation of the coronal mass ejections, and flares.
- Observe the in-situ particle and plasma environment providing data for the study of particle dynamics from the Sun.
- Physics of solar corona and its heating mechanism.
- Diagnostics of the coronal and coronal loops plasma’s temperature, velocity, and density.
- Development, dynamics, and origin of Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs).
- Identify the sequence of processes that occur at multiple layers (chromosphere, base, and extended corona) which eventually leads to solar eruptive events.
- Magnetic field topology and magnetic field measurements in the solar corona.
- Drivers for space weather (origin, composition, and dynamics of solar wind.
ADITYA-L1 PAYLOADS:
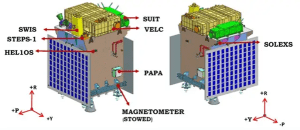
- The instruments of Aditya-L1 are tuned to observe the solar atmosphere mainly the chromosphere and corona.
- In-situ instruments will observe the local environment at L1.
- There are total seven payloads on-board with four of them carrying out remote sensing of the Sun and three of them carrying in-situ observation.
|
Type |
Sl. No. | Payload | Capability |
| Remote Sensing Payloads | 1 | Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) | Corona/Imaging & Spectroscopy |
| 2 | Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) | Photosphere and Chromosphere Imaging- Narrow & Broadband | |
| 3 | Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS) | Soft X-ray spectrometer: Sun-as-a-star observation | |
| 4 | High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS) | Hard X-ray spectrometer: Sun-as-a-star observation | |
| In-situ Payloads | |||
| 5 | Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX) | Solar wind/Particle Analyzer Protons & Heavier Ions with directions | |
| 6 | Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA) | Solar wind/Particle Analyzer Electrons & Heavier Ions with directions | |
| 7 | Advanced Tri-axial High Resolution Digital Magnetometers | In-situ magnetic field (Bx, By and Bz). |
2. SEMICONDUCTORS
TAG: GS 3: ECONOMY, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Approximately $8 billion out of the $10 billion allocated for the semiconductor manufacturing scheme remains unused.
EXPLANATION:
- The funds have been allocated by the Union government of India for encouraging domestic production of semiconductors under the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme.
- This underutilization of funds highlights a significant gap in the government’s efforts to promote semiconductor production in India.
- Incentives for Semiconductor Manufacturing:
- The government is providing incentives, including financial support, in high-tech areas such as semiconductor manufacturing.
- These incentives are intended to attract semiconductor makers to establish manufacturing facilities in India, with the goal of strengthening the country’s manufacturing base.
- Encouraging Korean Investors and Bilateral Trade Goals:
- The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade Secretary, Rajesh Kumar Singh said that India and Korea must aim to enhance bilateral trade to $50 billion by 2030.
- This goal suggests the desire for closer economic ties between the two countries.
- Korean investors have invested $5.6 billion in India since April 2000 and they can take advantage of the semiconductor PLI along with upcoming opportunities for investments in battery storage solutions.
- There is a call to upgrade and enhance the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) between India and Korea. Strengthening this economic partnership is seen as beneficial to both countries.
- Korean investors have a history of investing in India, and there is a call for them to consider utilizing the untapped incentives provided under the scheme.
- The importance of enhancing bilateral trade between India and Korea has been emphasized.
- Opportunities in Battery Storage Solutions:
-
- In addition to semiconductor manufacturing, there are upcoming investment opportunities in battery storage solutions.
- The Indian government is inviting investors, including Korean companies, to participate in the bid openings for over 20 gigawatt hours of storage and mobility battery capacity in India.
INDIA’S INITIATIVES IN SEMICONDUCTORS
1. INDIA SEMICONDUCTOR MISSION (ISM)
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) is a specialized and independent Business Division within the Digital India Corporation.
- It aims to build a vibrant semiconductor and display ecosystem.
- It aims to enable India’s emergence as a global hub for electronics manufacturing and design.
- The mission aims to serve as a focal point for the comprehensive and smooth development of Semiconductor in consultation with the Government ministries / departments / agencies, industry, and academia.
2. INDIA’S SEMICON PROGRAMME.
- The Union Cabinet had approved the comprehensive Semicon India programme with a financial outlay of INR 76,000 crore for the development of a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem in 2021.
- Semicon India Program aims to provide attractive incentive support to companies that are engaged in Silicon Semiconductor Fabs, Display Fabs, Compound Semiconductors, Silicon Photonics etc.
- The program will give an impetus to semiconductor and display manufacturing by facilitating capital support and technological collaborations.
3. CHIPS2 STARTUP (C2S) PROGRAMME
- An umbrella programme “Chips to Startup(C2S)” was in line with the objective and vision of National Policy on Electronics 2019 (NPE-2019).
- It aims at developing Specialized Manpower in VLSI/Embedded System Design domain.
- It also addresses each entity of the Electronics value chain via Specialized Manpower training, Creation of reusable IPs repository, Design of application-oriented Systems etc.
- The programme would be implemented at about 100 academic institutions/R&D organizations across the Country.
- Start-ups and MSMEs can also participate in the programme by submitting their proposals.
- Under the programme, the project would be initiated in following key areas:
- Energy & Environment
- Healthcare
- Agriculture
- Disaster Management
- Intelligent Transport System
- Emerging Technology etc.
CONCLUSION:
- There is a need for India to attract more investment in semiconductor manufacturing by utilizing the allocated funds effectively.
- The government is also actively seeking foreign investors, particularly from Korea, to participate in this scheme and tap into the incentives provided.
- The broader goal is to strengthen economic ties and bilateral trade between India and Korea and to encourage investment in high-tech sectors, including semiconductor manufacturing and battery storage solutions.
3. LANDSLIDE AT THE SUBANSIRI HYDRO PROJECT
TAG: GS 1: GEOGRAPHY
THE CONTEXT: A massive landslide occurred at the Subansiri hydro project on October 27, completely blocking the only functional diversion tunnel (DT).
EXPLANATION:
- This landslide at the NHPC’s 2,000-MW Subansiri hydro project, which is located along the Assam-Arunachal Pradesh border in India, has blocked the only operational diversion tunnel, affecting water flow in the river.
- The diversion tunnel number 1, which was the only one in use, was obstructed by the landslide, impacting water flow through the river.
- Fortunately, there have been no reports of human casualties resulting from the incident.
- Landslide warnings ignored:
- In April 2022, the Central Electricity Authority (CEA) warned that the Subansiri Lower Project was at risk of landslides.
- The CEA recommended that National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC) Ltd., the company responsible for building the dam, conduct a study to assess the risk of landslides.
- However, NHPC ignored this recommendation.
- Status of the Hydro Project:
- The Subansiri Lower Hydro Electric Project has faced multiple delays and setbacks since its inception.
- The project, with a capacity of 2,000 MW, has experienced revisions in its commissioning deadline and has been postponed several times.
- As of today, more than 90% of the total work on the project has been completed.
- Impact on River Flow:
- The main dam spillway is not yet ready, and the river was flowing through the diversion tunnel, making the landslide a critical issue.
- The landslide has significantly reduced the flow of the river downstream.
- The water level in the reservoir is gradually increasing due to the reduced flow, and measures are being taken to restore the normal river flow.
- Concerns for Aquatic Life:
- The reduced river flow has caused the river bed to dry up, leading to concerns about aquatic life.
- Locals report that people are walking on the dry river bed and catching fish, which poses a threat to aquatic life.
- This drastic change in river flow is noted as unusual and potentially harmful to the environment.
- Project Details and Cost:
-
- The Subansiri Lower Hydro Electric Project is a run-of-river scheme and is expected to generate approximately 7,500 million units of power annually.
- The cost of the project has escalated significantly from the initial estimate, reaching around Rs 20,000 crore in January 2020, up from the initial estimate of Rs 6,285 crore.
- NHPC began construction work on the project in January 2005 after obtaining forest clearance in October 2004.
CONCLUSION:
- The landslide at the Subansiri hydro project has caused a blockage in the diversion tunnel, affecting water flow in the river and raising concerns about its impact on aquatic life.
- The project has faced multiple delays and cost overruns, highlighting the challenges in implementing large-scale hydroelectric projects in the region.
4. AIR QUALITY INDEX (AQI)
TAG: GS 3: ECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT
THE CONTEXT: Air Quality Index (AQI) in North India, particularly in Delhi, has risen to “severe” levels.
POLLUTANTS, SOURCES, THEIR IMPACTS AND HEALTH IMPLICATIONS:
- PM 10 and PM 2.5:
- These are fine particulate matter (PM) particles with diameters smaller than 10 and 2.5 microns, respectively.
- Smaller particles (PM 2.5) can penetrate the circulatory system.
- It can lead to serious health issues such as asthma, heart attacks, bronchitis, and other respiratory problems.
- They are primarily emitted from factories, vehicles, construction activities, and road dust.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2):
- NO2 comes from the burning of fuel, especially from vehicles and power plants.
- Short-term exposure to high levels of NO2 can worsen respiratory diseases like asthma and lead to coughing and breathing difficulties.
- Long-term exposure can contribute to the development of asthma.
- Ozone (O3):
- While ozone in the upper atmosphere protects from UV rays, ground-level ozone is a significant air pollutant.
- It forms through the reaction of atmospheric pollutants in sunlight.
- Increased surface ozone levels are associated with an increased risk of hospital admissions for respiratory diseases and cardiovascular deaths.
- Sulphur Dioxide (SO2):
- SO2 primarily comes from the burning of fossil fuels by power plants and industrial facilities, as well as industrial processes and natural sources like volcanoes.
- SO2 exposure is harmful to the cardiovascular system and can lead to respiratory illnesses.
- High concentrations can harm plants and trees.
- Lead:
- Lead is a toxic metal that can be naturally occurring but becomes dangerous in high quantities.
- Environmental contamination primarily comes from mining, smelting, manufacturing, and recycling activities.
- Young children are particularly vulnerable to lead poisoning, which can lead to intellectual disability and behavioral disorders.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO):
- Carbon monoxide is a toxic, odorless, and colorless gas produced when carbon-containing fuels like wood, coal, and petrol are burned.
- High levels can lead to unconsciousness and death, while long-term exposure is linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
- The sources of these pollutants are mainly industrial activities, vehicular emissions, power plants, and natural sources like volcanoes.
- Recommendations: While the article focuses on the concerning air quality, it doesn’t provide specific recommendations or actions being taken to address the issue. However, it emphasizes the need for awareness and action to mitigate the impact of air pollution on public health.
- Air Quality Index (AQI):
-
- The AQI is a numerical measure used to convey the overall quality of air in a specific area.
- In this context, it is used to assess air quality in North India, with a focus on Delhi, where the AQI has reached severe levels.
INITIATIVES TAKEN FOR CONTROLLING AIR POLLUTION:
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR) Portal.
- Air Quality Index: AQI has been developed for eight pollutants viz. PM2.5, PM10, Ammonia, Lead, nitrogen oxides, sulphur dioxide, ozone, and carbon monoxide.
- Graded Response Action Plan (for Delhi).
- For Reducing Vehicular Pollution:
- BS-VI Vehicles,
- Push for Electric Vehicles (EVs),
- Odd-Even Policy as an emergency measure (for Delhi).
- New Commission for Air Quality Management
- Subsidy to farmers for buying Turbo Happy Seeder (THS) Machine for reducing stubble burning.
- National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP): Under NAMP, four air pollutants viz. SO2, NO2, PM10, and PM2.5 have been identified for regular monitoring at all locations.
WAY FORWARD
- Changing Approach:
- India needs to change its approach and bring out effective policies in order to improve air quality and reduce pollutants to levels considered acceptable by the World Health Organisation (WHO).
- Close Coordination Required:
-
- Curbing air pollution requires not only tackling its specific sources, but also close coordination across local and national jurisdictional boundaries.
- Regional cooperation can help implement cost-effective joint strategies that leverage the interdependent nature of air quality.
5. GLOBAL LANDSCAPE OF CLIMATE FINANCE 2023
TAG: GS 3: ECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT
THE CONTEXT: As per the Climate Policy Initiative’s (CPI) new report Global Landscape of Climate Finance 2023, Climate finance flows have doubled compared to previous years but have been unevenly distributed across geographies and sources.
HIGHLIGHTS OF THE REPORT:
- Global Climate Finance Growth:
- According to the report, the average annual flow of climate finance in 2021 and 2022 reached $1.3 trillion.
- This is a significant increase compared to the $653 billion recorded for 2019 and 2020.
- The growth is primarily attributed to an escalation in mitigation finance, which saw an increase of $439 billion from the previous two years.
- Uneven Distribution of Climate Finance:
- Climate finance has been unevenly distributed across sectors and geographies.
- Mitigation finance has primarily gone to renewable energy (44%) and transport (29%), with a strong presence of private financing.
- In contrast, sectors responsible for significant emissions like agriculture and industry received a smaller share of total mitigation and dual benefits finance.
- Adaptation finance reached a new high of $63 billion but still falls short of the estimated needs, which are projected to be $212 billion per year by 2030 for developing nations.
- Nearly all adaptation finance (98%) tracked in the report came from public sources.
- Geographic Concentration:
- Developed countries mobilized the majority of climate finance, with a significant contribution from the private sector.
- East Asia and the Pacific, the United States, Canada, and Western Europe accounted for 84% of all climate finance.
- China led in domestic resource mobilization for climate finance, contributing 51% of all domestic climate finance globally.
- Developing and low-income countries received a limited share of funds.
- The report pointed out the disparities in climate finance distribution, with the 10 countries most affected by climate change receiving a very small portion of total climate finance.
- Private Sector Contribution:
- Private actors contributed 49% of total climate finance, amounting to $625 billion.
- The report highlighted the rapid growth in private finance, driven in part by household spending, particularly from the sales of electric vehicles, which doubled from 2020 to 2021.
- Fiscal policies promoting low-carbon technologies played a role in this increase.
- Recommendations:
- The report suggests measures to enhance the scale and quality of climate finance, focusing on four categories:
- transforming the financial system,
- bridging climate and development needs,
- mobilizing domestic capital, and
- improving climate finance data.
- The report underscores the need to reduce the cost of capital barriers, particularly for developing and low-income countries, by reforming financial institutions and making concessional finance more accessible.
- The report suggests measures to enhance the scale and quality of climate finance, focusing on four categories:
- Global Climate Finance Needs:
-
- Despite the growth in climate finance, it is emphasized that the current scale represents only 1% of the global GDP.
- The report’s projections indicate that average estimated annual climate finance needs will increase to $9 trillion by 2030.
WAY FORWARD:
- Transforming the Financial System:
- This involves reducing the cost of capital barriers, particularly for developing and low-income countries.
- There is a call for reforming financial institutions to make concessional finance more accessible.
- Bridging Climate and Development Needs:
- The report highlights the need to bridge the gap between climate and development needs.
- This could involve strategies to align climate investments with broader sustainable development goals, ensuring that climate finance addresses poverty reduction and other social objectives.
- Mobilizing Domestic Capital:
- The report suggests mobilizing domestic capital for climate finance.
- This could involve promoting domestic investment in climate-friendly projects and industries to reduce dependence on international funds.
- Improving Climate Finance Data:
-
- Data collection and interpretation have improved over the years.
- The report underscores the importance of continuing to enhance the quality of climate finance data and information.
Climate Policy Initiative’s (CPI):
- The Climate Policy Initiative (CPI) is an independent, non-profit, international research organization that works to support governments, businesses, and financial institutions in driving economic growth while addressing climate change.
- It was founded in 2009 to support nations building low carbon economies to develop and implement effective climate, energy and land use policies.
- CPI provides analysis, advice, and solutions in the areas of climate finance, climate policy, and low-carbon development.
CPI’s work is focused on the following areas:
- Enabling capital:
- CPI helps to mobilize and allocate capital for low-carbon investments by developing innovative finance mechanisms, such as blended finance and risk management frameworks.
- Promoting green and sustainable finance:
- CPI monitors and evaluates climate finance flows and investments, providing insights into the effectiveness of different approaches and identifying opportunities for improvement.
- Enabling a just transition:
-
- CPI helps countries to develop and implement policies and strategies for a just transition to a low-carbon economy, ensuring that the transition is fair and equitable for all.


