1. ECONOMIC AND TECHNOLOGY COOPERATION AGREEMENT (ETCA)
TAG: GS 2: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE CONTEXT: India and Sri Lanka held the 12th round of negotiations on the Economic and Technology Cooperation Agreement (ETCA) in Colombo, Sri Lanka from 30th October 2023 to 1st November 2023.
EXPLANATION:
- The two countries had 11 rounds of bilateral talks from 2016 to 2018. Thereafter the negotiations were paused.
- During this round, both the sides took stock of the progress made till the 11th round.
- They engaged in discussions on various chapters including Trade in Goods, Technical Barriers to Trade, Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures, Trade in Services, Custom Procedure & Trade Facilitation, Rules of Origin etc.
- Both sides identified the areas of convergence and areas where they need to find creative solutions.
- Issues such as the quota on apparel and pepper and the procurement of pharmaceuticals were also discussed and both sides decided to continue the discussion and explore new options for resolution of the matter.
- On the proposed ETCA, both sides agreed on the need to build on progress made in past, while revisiting their positions wherever possible to reflect new developments.
- The conclusion of the negotiations is expected to open new opportunities for trade and economic cooperation for both countries.
- The India-Sri Lanka ETCA will be a pivotal move to further enhance bilateral trade between the two countries.
- Both sides acknowledged the huge potential in India and Sri Lanka trade partnership and the possibilities for enhanced economic relations in areas of mutual interest.
ECONOMIC AND TECHNOLOGY COOPERATION AGREEMENT (ETCA):
- In 1998, the India-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement was established.
- Subsequently, efforts were made to negotiate a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) to liberalize trade in services and investment, starting in the mid-2000s.
- The CEPA negotiations faced significant opposition within Sri Lanka, particularly from the business community, and they dragged on for nearly a decade.
- In light of the challenges with CEPA, India is now advocating for a new trade pact known as the Economic and Technological Cooperation Agreement (ETCA).
- ETCA is being negotiated as an extension of the existing Free Trade Agreement (FTA) between India and Sri Lanka.
- The key focus of the ETCA is to establish an agreement on trade in services and technological exchange, an objective that was not fully realized under CEPA.
- ETCA aims to enhance cooperation in technical areas, scientific expertise, and research among institutions.
- It seeks to raise the standards of goods and services to enable them to compete in the global market, as well as to improve opportunities for manpower training and human resource development.
- Investments under ETCA would be directed towards sectors such as oil farms in Trincomalee, renewable energy, infrastructure, and other new areas of business.
- India views ETCA as a means to participate in Sri Lanka’s post-war economic development by making Indian investments in specific sectors.
- The Sri Lankan government intends to leverage ETCA to become part of the Indian supply chain and benefit from India’s “Make in India” initiative, which aims to boost India’s manufacturing sector.
- ETCA will enable Indian manufacturers to establish factories in Sri Lanka and export their products to countries with which Sri Lanka has existing or planned Free Trade Agreements.
SOURCE: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1973859
2. AMENDMENTS IN THE GUIDELINES FOR THE APPOINTMENT OF STATE DGP
TAG: GS 2: POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
THE CONTEXT: The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) has recently amended its guidelines for the appointment of State Director General of Police (DGP).
EXPLANATION:
- The key changes include:
- Setting a minimum service requirement of at least six months left before retirement for consideration,
- Reducing the minimum service years requirement from 30 to 25 years, and
- Limiting the number of shortlisted officers to three, except in “exceptional circumstances.
AMENDMENTS AND THEIR ADVANTAGES:
PREVENTING FAVORITISM:
- The primary aim of these guideline amendments is to prevent States from appointing “favorite officers” who are on the verge of retirement in an attempt to extend their tenure.
- This is done to ensure that appointments are based on merit and not political considerations.
BYPASSING UPSC PROCESS:
- Several States have been appointing acting DGPs or officers with “full additional charge” rather than regular DGPs.
- This allows them to bypass the UPSC’s selection process.
- This has led to controversies and legal challenges in some cases, such as in Punjab.
IMPACT ON POLICE REFORMS:
- The issue of appointing DGPs is related to broader police reforms in the country.
- The Supreme Court’s 2006 verdict in the police reforms case led to the formulation of guidelines for DGP appointments by the UPSC.
- The recent guideline amendments seek to address loopholes and ensure that these reforms are effectively implemented.
CENTRAL DEPUTATION:
- Another significant change is that IPS officers on central deputation will not be considered for a State DGP’s post if the Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) informs the State government that it cannot release the officers.
- This is a step to clarify and enforce the process.
EXPERIENCE AND QUALIFICATIONS:
- The revised guidelines also specify the required experience areas for an IPS officer to lead a State police department, which includes various aspects of policing and central deputation in key agencies.
STATES’ CONCERNS:
- Some States have expressed concerns about the lack of adequate officers available for central deputation.
- States have resisted the Union government’s attempts to depute officers to the Center without State consent.
COMMITTEE COMPOSITION:
- The appointment of State DGPs involves a committee headed by the UPSC Chairman and includes other high-ranking officials.
- This ensures a structured and unbiased approach to the selection process.
3. NexCAR19
TAG: GS 3: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, Mumbai-based Immunoadoptive Cell Therapy Private Limited (ImmunoACT) announced the approval of India’s first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy Called NexCAR19 by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO).
EXPLANATION:
- ImmunoACT is an IIT Bombay-incubated company founded in 2018 and works on converting research into pharmaceutical products.
- CAR-T cell therapy cost around $400,000 or over Rs 3.3 crore and patients could avail of it in the United States.
- With this development, the therapy will be accessible at 20 Indian government and private hospitals treating cancer across major cities at around Rs 30-35 lakh per patient,
NexCAR19:
- It is an indigenously developed CD19-targeted CAR-T cell therapy.
- CD-19 is biomarker for B lymphocytes and can be utilised as a target for leukaemia immunotherapies.
- It will be used for treating relapsed-refractory B-cell lymphoma and leukaemia.
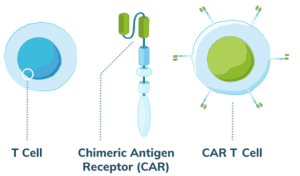
HOW DOES IT WORK?
- For CAR-T-cell therapy, a type of cancer immunotherapy treatment, blood is first drawn from the patient.
- Then, immune cells called T-cells are genetically modified in a laboratory and are injected back into the patient to enable the cells to locate and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
- Investigations were led by Dr Hasmukh Jain and Dr Gaurav Narula and their teams at Tata Memorial Hospital in Mumbai.
- It is a major breakthrough as the therapy is not available in India outside of clinical trials.
- The multi-centre Phase I and II clinical trials were conducted with 60 patients with r / r B-cell lymphomas and leukemia.
- The clinical data indicated a 70 per cent overall response rate.
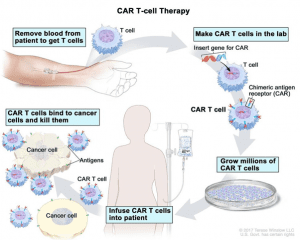
- Availability:
- The therapy is in the process of being introduced in various hospitals in India, including Tata Hospital, Nanavati, Fortis, and Jaslok, among others.
- The availability of CAR-T therapy is expected in a matter of weeks to a few months, depending on government approvals.
- Cost:
- Initially, the cost of CAR-T therapy in India is estimated to be in the range of Rs 30-40 lakh.
- However, the aim is to reduce the cost to Rs 10-20 lakh as technology matures and manufacturing processes improve.
- The cost of the therapy remains a concern for accessibility.
- Insurance Coverage:
-
- Typically, when a therapy is approved by regulatory agencies like CDSCO or DCGI, it should be covered by national insurance schemes and private insurance companies.
- However, the extent of coverage and accessibility to insurance may vary, and discussions with insurers and the government are planned to clarify this further.
SIDE EFFECTS:
- CAR T-cell therapy is generally accompanied by some side effects.
- One of them, according to the American Cancer Society, is cytokine release syndrome (CRS).
- It is when CAR T-cells multiply, they can release large amounts of chemicals called cytokines into the blood, which can ramp up the immune system.
- In comparison to other CAR T-cell therapies, the safety profile of CRS and the absence of neurotoxicity indicates a significant improvement.
- NexCAR19 has shown an excellent balance of efficacy and low toxicity, which is a significant advantage in clinical management (post-infusion) of the patients in our resource-constrained settings.
4. UNESCO CREATIVE CITIES NETWORK (UCCN)
TAG: GS 2: ART AND CULTURE
THE CONTEXT: Gwalior in Madhya Pradesh and Kozhikode in Kerala are among the 55 new cities which have joined the UNESCO Creative Cities Network.
EXPLANATION:
- On World Cities Day, UNESCO announced the addition of 55 new cities to the Creative Cities Network. These cities join the existing network of creative cities across the globe.
- Gwalior is recognized in the ‘Music’ category, while Kozhikode has been designated in the ‘Literature’ category. This recognition highlights their contributions to the fields of music and literature.
- UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) acknowledged these cities for their commitment to harnessing culture and creativity as part of their development strategies.
- These cities also demonstrate innovative practices in human-centered urban planning.
SIGNIFICANCE OF ADDITION OF GWALIOR AND KOZHIKODE:
- Seven Creative Fields:
- The UCCN comprises cities from seven creative fields, which include Crafts and Folk Art, Design, Film, Gastronomy, Literature, Media Arts, and Music.
- The addition of Gwalior and Kozhikode expands the network’s diversity.
- Urban Resilience and Development:
- UNESCO Director-General emphasized that cities in the Creative Cities Network are at the forefront of enhancing access to culture.
- UCCN Cities will leverage the power of creativity for urban resilience and development.
- Upcoming Policy Paper:
- UNESCO is set to release a policy paper titled “The added value of the UNESCO Creative Cities Network at local, national, and international level,”.
- It will showcase the role cities play in achieving the 2030 Agenda.
- The paper will demonstrate how UNESCO supports UCCN members through dialogue, peer-to-peer learning, and collaboration.
- Annual Conference:
-
- The newly designated Creative Cities are invited to participate in the 2024 UCCN Annual Conference to be held in Braga, Portugal.
- The theme for the conference is “Bringing Youth to the table for the next decade.”
UNESCO CREATIVE CITIES NETWORK (UCCN):
- It was created in 2004 to promote cooperation with and among cities that have identified creativity as a strategic factor for sustainable urban development.
- The cities which currently make up this network work together towards a common objective:
- placing creativity and cultural industries at the heart of their development plans at the local level and cooperating actively at the international level.
- By joining the Network, cities commit to sharing their best practices and developing partnerships involving the public and private sectors as well as civil society in order to:
- strengthen the creation, production, distribution and dissemination of cultural activities, goods and services;
- develop hubs of creativity and innovation and broaden opportunities for creators and professionals in the cultural sector;
- improve access to and participation in cultural life, in particular for marginalized or vulnerable groups and individuals;
- fully integrate culture and creativity into sustainable development plans.
INDIAN CITIES ON UCCN:
- Srinagar – Crafts and Folk Arts (2021)
- Mumbai – Film (2019).
- Hyderabad – Gastronomy (2019).
- Chennai- Creative city of Music (2017).
- Jaipur- Crafts and Folk Arts (2015).
- Varanasi- Creative city of Music (2015).
SOURCE: https://indianexpress.com/article/india/gwalior-kozhikode-unesco-creative-cities-network-9009592/
5. COMMITTEE OF PRIVILEGES
TAG: GS 2: POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
THE CONTEXT: A meeting of the Rajya Sabha’s privileges committee scheduled to take place in November to review the pending cases of breach of privilege against lawmakers.
EXPLANATION:
- The primary focus of this meeting is to review the pending cases of breach of privilege against lawmakers, particularly those involving the suspension of certain Members of Parliament (MPs) such as Raghav Chadha, Sanjay Singh, and Derek O’Brien.
- Background on Suspensions:
- Raghav Chadha, a 34-year-old AAP MP, was suspended during the monsoon session of Parliament over an alleged breach of privilege.
- This suspension was related to his inclusion of five Rajya Sabha MPs’ names in a select committee without their consent.
- Sanjay Singh was suspended for repeatedly violating the directives of the chair.
- Derek O’Brien faces at least three pending privilege notices.
- Supreme Court’s Recent Concerns:
- The timing of this meeting is significant as it comes shortly after the Supreme Court expressed concerns about the indefinite suspension of an MP, especially one from the Opposition.
- The court emphasized the importance of having diverse voices and representation in Parliament, indicating that excluding members of the Opposition is a serious concern for the constitutional court.
- Pending Cases:
-
- The meeting is expected to address cases involving suspended AAP lawmakers as well as Trinamool Congress (TMC) parliamentarian Derek O’Brien.
- These cases have been under consideration by the privileges committee.
COMMITTEE OF PRIVILEGES:
- This committee consists of 15 members in Lok Sabha (10 in case of Rajya Sabha) nominated by the Speaker (Chairman in case of Rajya Sabha).
- In the Rajya Sabha, the deputy chairperson heads the committee of privileges.
Powers and Functions:
- The committee examines every question involving a breach of privilege of the House or of the members or of any Committee thereof referred to it by the House or by the Speaker/Chairman.
- It also determines with reference to the facts of each case whether a breach of privilege is involved and makes suitable recommendations in its report.
- It also states the procedure to be followed by the House in giving effect to its recommendations.
- When a question of privilege is referred to the Committee by the House, the report of the Committee is presented to the House by the Chairman or, in his absence, by any member of the Committee.
- Where a question of privilege is referred to the Committee by the Speaker, the report of the Committee is presented to the Speaker who may pass final orders thereon or direct that it be laid on the Table of the House.
- The Speaker/Chairman may refer to the Committee any petition regarding the disqualification of a member on the ground of defection for making a preliminary inquiry and submitting a report to him.
- The procedure to be followed by the Committee in these cases is so far as may be the same as in applicable to questions of breach of privilege.


