THE CONTEXT: Recently, Indian Ocean Rim Association’s (IORA) Council of Ministers (COM) held in Colombo, Sri Lanka on October 11, 2023 that was attended by foreign ministers and senior officials of the 23-nation grouping of countries.
HIGHLIGHT OF IORA 2023 CONFERENCE
- The theme of Indian Ocean Rim Association’s (IORA) Council of Ministers (COM) is ‘Reinforcing Indian Ocean Identity’.
- Sri Lanka took charge as Chair from Bangladesh, and India is Vice-Chair, meaning that the troika of IORA is within the South Asian region.
- The conference witnessed the signing of three agreements on bilateral cooperation:
-
- Indian assistance for housing projects
- Modernising school
- A new joint project between the Indian National Dairy Development Board, Amul cooperative and the Sri Lankan Cargill Group to increase milk production in Sri Lanka.
ABOUT INDIAN OCEAN RIM ASSOCIATION’S (IORA)
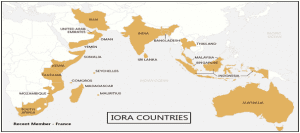
- The Indian Ocean Rim Association includes 23 countries from Africa, West Asia, South Asia, South East Asia, Australia and littoral states situated in and around the Indian Ocean.
- IORA’s apex body is the Council of Foreign Ministers, which meets once a year and moves by rotation through members every two years.
- IORA’s membership includes 23 countries: Australia, Bangladesh, the Comoros, France, India, Indonesia, Iran, Kenya, Madagascar, Malaysia, the Maldives, Mauritius, Mozambique, Oman, Seychelles, Singapore, Somalia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Thailand, the UAE and Yemen.
- It also has 11 dialogue partners: China, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Germany, Italy, Japan, South Korea, Russia, Türkiye, the U.K. and the U.S.
HOW WAS IT FORMED?
- Its genesis came from a speech of Nelson Mandela in Delhi in 1995 when he was invited as the guest for Republic Day. He said that India and South Africa should explore “the concept of an Indian Ocean Rim of socioeconomic cooperation and other peaceful endeavours” that could help developing countries within other multilateral institutions.
- IORA was formed in 1997 in Mauritius and named initially as Indian Ocean Region-Association for Regional Cooperation.
WHY DOES THE INDIAN OCEAN REGION MATTER?
- A third of the world’s population i.e 2.6 billion people live in the region, and 80% of global oil trade, 50% of the world’s containerised cargo and 33% of its bulk cargo passes through it.
- The region produces a combined total of $1 trillion in goods and services, and intra-IORA trade is estimated at around $800 billion.
- There is a need of maintaining the Indian Ocean as a “free, open and inclusive space” for maintaining sovereignty and territorial integrity. It can help in countering China and countering unviable projects or unsustainable debt” to countries in the Indian Ocean Region.
WHAT DOES IORA FOCUS ON?
- According to its charter, the IORA’s seven priority areas are
-
- Maritime safety and security
- Trade and investment facilitation
- Fisheries management
- Disaster risk management
- Academic
- Science and technology
- Tourism and cultural exchanges
- Gender empowerment.
- The IORA also runs a special fund in addition, disbursing $80,000-$150,000 for project grants to members, and has a particular focus on climate change.
- IORA has special focus on strategic issues and the importance of keeping a free and open sea lane, guarding against piracy.
WHY IORA MATTERS TO INDIA?
- Challenges in other regional organizations: India’s other regional organisations, like SAARC and BIMSTEC, face their own challenges. While the QUAD has made progress it remains largely U.S.-led, along with military allies Australia and Japan.
- Countering China: As, China is actively trying to rope in India’s neighbours with groupings like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China-Indian Ocean Region Forum on Development Cooperation which exclude India. IORA can play a significant role in countering China.
- Avoid big power rivalries: IORA membership is based on consensus, hence it remains a safe space for India and other countries of the region to keep out the constant challenge of big-power rivalries.
- Excludes Pakistan: Pakistan has not been admitted to the grouping since it first applied in 2001, on the basis that it has not extended MFN (most favoured nation) status to India. This makes the IORA a less contentious space for India as well, compared to groupings like the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO).
THE CONCLUSION: For ensuring a free, open, and inclusive rules-based Indian Ocean region for the benefit of all the countries of the region, there is a need to strengthen and utilize the maximum potential of the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS:
Q.1 Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD)’ is the transforming itself into a trade bloc from a military alliance, in present times – Discuss. (2020)
Q.2 The newly tri-nation partnership AUKUS is aimed at countering China’s ambitions in the Indo-Pacific region. Is it going to supersede the existing partnerships in the region? Discuss the strength and impact of AUKUS in the present scenario. (2021)
MAINS PRACTICE QUESTIONS:
Q.1 Discuss the importance of IORA in maintaining ‘’free, open and prosperous” Indian Ocean Region.
Q.2 Critically examine the aims and objectives of IORA. What importance does it hold for India?
Spread the Word



