Day-514
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
To attempt the Quiz, simply click on START Button.
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
2 points1. With reference to the efforts to tackle the Covid-19 virus, consider the following statements:
1. The ZyCoV-D is the world’s first and India’s indigenously developed DNA based vaccine for COVID-19.
2. It is not to be administered in individuals below 18 years.
3. The vaccine has been developed in partnership with the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) under the ‘Mission COVID Suraksha’.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
● Statement 1 is correct: The ZyCoV-D is the world’s first and India’s indigenously developed DNA based vaccine for COVID-19.
● Statement 2 is incorrect: This 3 dose vaccine which when injected produces the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and elicits an immune response, which plays a vital role in protection from disease as well as viral clearance. It is to be administered in humans including children and adults 12 years and above.
● Statement 3 is correct: This vaccine has been developed in partnership with the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India under the ‘Mission COVID Suraksha’ and implemented by BIRAC, a PSU of DBT.
Vaccine Technology Centre (VTC), vaccine research centre of the Zydus group, Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), an autonomous institute of the DBT and Interactive Research School for Health Affairs (IRSHA), Pune, GCLP Lab set up under the DBT-National Biopharma Mission (NBM) also played a vital role in this success story. The plug and play technology on which the plasmid DNA platform is based can be easily adapted to deal with mutations in the virus, such as those already occurring.
What is DNA Vaccine?
● DNA Vaccines consist of a plasmid (circular DNA molecule) containing the gene from virus / bacteria, which stimulates the immune system upon delivery.
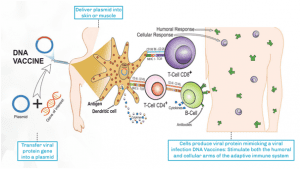
Global Status of DNA Vaccines
● Currently no DNA vaccines have been approved for use in humans.
● But many DNA vaccines are undergoing human clinical trials and some DNA vaccines have been approved by US regulatory agencies.
● DNA vaccines in human clinical trials:
○ DNA vaccines against cancer
○ DNA vaccines against HIV
● DNA vaccines approved by United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) for veterinary use:
○ Vaccine against West Nile Virus in horses
○ Melanoma vaccine for dogs
BENEFITS
Stability and Safety
● DNA Vaccines are non-infectious.
● Carries no potential toxicity from viral vectors.
● Non-replicating and non-integrating plasmid carrying the gene of interest making it very safe.Efficacy and Boosting
● Stimulate both the humoral and cellular arms of the adaptive immune system.
● DNA Vaccines pose minimal risk of anti-vector immunity.Rapid and Scalable Manufacturing
● Ease of manufacturing related to minimal biosafety requirements (BSL-1)
● Rapid development from concept to human use in 5 months
● Improved vaccine stability and lower cold chain requirementsCHALLENGES
● Relatively limited data on safety and efficacy in humans
● Risk of development of anti-nuclear antibodies
● Induction of Antibiotic Resistance
Hence, option B is correct.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
● Statement 1 is correct: The ZyCoV-D is the world’s first and India’s indigenously developed DNA based vaccine for COVID-19.
● Statement 2 is incorrect: This 3 dose vaccine which when injected produces the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and elicits an immune response, which plays a vital role in protection from disease as well as viral clearance. It is to be administered in humans including children and adults 12 years and above.
● Statement 3 is correct: This vaccine has been developed in partnership with the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India under the ‘Mission COVID Suraksha’ and implemented by BIRAC, a PSU of DBT.
Vaccine Technology Centre (VTC), vaccine research centre of the Zydus group, Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), an autonomous institute of the DBT and Interactive Research School for Health Affairs (IRSHA), Pune, GCLP Lab set up under the DBT-National Biopharma Mission (NBM) also played a vital role in this success story. The plug and play technology on which the plasmid DNA platform is based can be easily adapted to deal with mutations in the virus, such as those already occurring.
What is DNA Vaccine?
● DNA Vaccines consist of a plasmid (circular DNA molecule) containing the gene from virus / bacteria, which stimulates the immune system upon delivery.

Global Status of DNA Vaccines
● Currently no DNA vaccines have been approved for use in humans.
● But many DNA vaccines are undergoing human clinical trials and some DNA vaccines have been approved by US regulatory agencies.
● DNA vaccines in human clinical trials:
○ DNA vaccines against cancer
○ DNA vaccines against HIV
● DNA vaccines approved by United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) for veterinary use:
○ Vaccine against West Nile Virus in horses
○ Melanoma vaccine for dogs
BENEFITS
Stability and Safety
● DNA Vaccines are non-infectious.
● Carries no potential toxicity from viral vectors.
● Non-replicating and non-integrating plasmid carrying the gene of interest making it very safe.Efficacy and Boosting
● Stimulate both the humoral and cellular arms of the adaptive immune system.
● DNA Vaccines pose minimal risk of anti-vector immunity.Rapid and Scalable Manufacturing
● Ease of manufacturing related to minimal biosafety requirements (BSL-1)
● Rapid development from concept to human use in 5 months
● Improved vaccine stability and lower cold chain requirementsCHALLENGES
● Relatively limited data on safety and efficacy in humans
● Risk of development of anti-nuclear antibodies
● Induction of Antibiotic Resistance
Hence, option B is correct. -
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2 points2. With reference to Myeloma and Hybridoma cells, consider the following statements:
1. Myeloma cells are cancerous cells that can divide and replicate indefinitely.
2. Hybridoma cells are used to produce stem cells.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
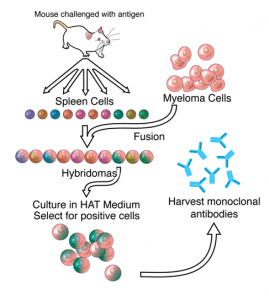
Myeloma and hybridoma cells are both types of cells that are used in biomedical research, but they have different origins and properties.
● Statement 1 is correct: Myeloma cells are cancerous cells that are derived from plasma cells, which are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies. Myeloma cells are immortalized, meaning that they can divide and replicate indefinitely in culture, which makes them useful for the production of large quantities of monoclonal antibodies.

● In contrast, hybridoma cells are created by fusing a normal antibody-producing B cell with a myeloma cell. The resulting hybridoma cell has the ability to produce large quantities of a single type of monoclonal antibody, while also retaining the ability to divide and replicate indefinitely.
● Therefore, hybridoma cells are a type of cell line that can be used to produce monoclonal antibodies in large quantities, while myeloma cells are not used directly in this application.
● Statement 2 is incorrect: Another major difference between these cells is that myeloma cells are cancerous cells that are often used to study cancer and to develop cancer treatments, while hybridoma cells are typically used in immunology and biomedical research to produce monoclonal antibodies that can be used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.Hence, option A is correct.
Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Myeloma and hybridoma cells are both types of cells that are used in biomedical research, but they have different origins and properties.
● Statement 1 is correct: Myeloma cells are cancerous cells that are derived from plasma cells, which are a type of white blood cell that produces antibodies. Myeloma cells are immortalized, meaning that they can divide and replicate indefinitely in culture, which makes them useful for the production of large quantities of monoclonal antibodies.


● In contrast, hybridoma cells are created by fusing a normal antibody-producing B cell with a myeloma cell. The resulting hybridoma cell has the ability to produce large quantities of a single type of monoclonal antibody, while also retaining the ability to divide and replicate indefinitely.
● Therefore, hybridoma cells are a type of cell line that can be used to produce monoclonal antibodies in large quantities, while myeloma cells are not used directly in this application.
● Statement 2 is incorrect: Another major difference between these cells is that myeloma cells are cancerous cells that are often used to study cancer and to develop cancer treatments, while hybridoma cells are typically used in immunology and biomedical research to produce monoclonal antibodies that can be used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.Hence, option A is correct.
-
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
2 points3. The National Institute of Ocean Technology is in the process of setting up a self powered desalination plant in Lakshadweep. Consider the following statements with reference to the process of desalination:
1. The most commonly used technology in a desalination plant is reverse osmosis.
2. Reverse osmosis is the process of a solvent diffusing through a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
Desalination is the process by which the dissolved mineral salts in water are removed. Currently, this process, applied to seawater, is one of the most used to obtain fresh water for human consumption or agricultural purposes.
● Statement 1 is correct: Reverse osmosis is the most used process and consumes less energy than the rest, as it is based on the use of semipermeable membranes that allow the water to pass, but not the salt. These membranes are made of ultra-thin polyamide, which can become contaminated with bacteria so the water must be treated.
● Statement 2 is incorrect: Osmosis is the process of a solvent diffusing through a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.Reverse osmosis is a water purification process that uses a semi-permeable membrane (synthetic lining) to filter out unwanted molecules and large particles such as contaminants and sediments like chlorine, salt, and dirt from drinking water. In addition to removing contaminants and sediments, reverse osmosis can also remove microorganisms – which you certainly do not want to drink. It gets water clean down to a molecular level, leaving only pure H2O behind.


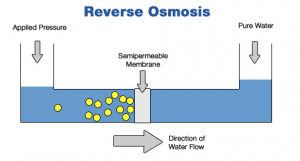
How Does Reverse Osmosis Work?
Before we go into the details of how reverse osmosis works, we should start by explaining how osmosis works. As you may remember from your high school chemistry class, osmosis is the process by which water passes through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one. In other words, the pure water passes through the filter to the contaminated water in order to equalize the concentrations – which is not what we want our drinking water to do. This movement generates osmotic pressure.In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome the osmotic pressure and push the water from high concentration of contaminants to low concentration of contaminants. This means it’s being forced in reverse and the contaminated water is trying to move into the pure water, but because it must pass through a filter first, the contaminants get trapped and only the pure water passes through; resulting in the cleanest possible drinking water – which is exactly what we want!


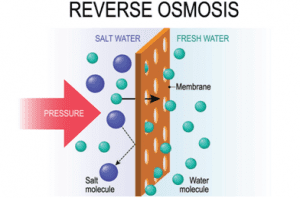
Reverse osmosis typically involves four stages of filtration: a sediment filter, pre-carbon block, reverse osmosis membrane, and post-carbon filter. The sediment filter removes the largest particles, like dirt, sand, and rust to prevent clogging of the subsequent filters. The pre-carbon filter uses activated carbon to prevent anything larger than a spec of flour from passing through as well as attracting and bonding with positively charged ions to prevent chemical compounds, like chlorine and chloramines, from passing through to the third filter. The reverse osmosis membrane then removes molecules heavier than water, such as sodium, high levels of lead, dissolved minerals, and fluoride. Finally, the post-carbon filter polishes the water.
Hence, option A is correct.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
Desalination is the process by which the dissolved mineral salts in water are removed. Currently, this process, applied to seawater, is one of the most used to obtain fresh water for human consumption or agricultural purposes.
● Statement 1 is correct: Reverse osmosis is the most used process and consumes less energy than the rest, as it is based on the use of semipermeable membranes that allow the water to pass, but not the salt. These membranes are made of ultra-thin polyamide, which can become contaminated with bacteria so the water must be treated.
● Statement 2 is incorrect: Osmosis is the process of a solvent diffusing through a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.Reverse osmosis is a water purification process that uses a semi-permeable membrane (synthetic lining) to filter out unwanted molecules and large particles such as contaminants and sediments like chlorine, salt, and dirt from drinking water. In addition to removing contaminants and sediments, reverse osmosis can also remove microorganisms – which you certainly do not want to drink. It gets water clean down to a molecular level, leaving only pure H2O behind.



How Does Reverse Osmosis Work?
Before we go into the details of how reverse osmosis works, we should start by explaining how osmosis works. As you may remember from your high school chemistry class, osmosis is the process by which water passes through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one. In other words, the pure water passes through the filter to the contaminated water in order to equalize the concentrations – which is not what we want our drinking water to do. This movement generates osmotic pressure.In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome the osmotic pressure and push the water from high concentration of contaminants to low concentration of contaminants. This means it’s being forced in reverse and the contaminated water is trying to move into the pure water, but because it must pass through a filter first, the contaminants get trapped and only the pure water passes through; resulting in the cleanest possible drinking water – which is exactly what we want!



Reverse osmosis typically involves four stages of filtration: a sediment filter, pre-carbon block, reverse osmosis membrane, and post-carbon filter. The sediment filter removes the largest particles, like dirt, sand, and rust to prevent clogging of the subsequent filters. The pre-carbon filter uses activated carbon to prevent anything larger than a spec of flour from passing through as well as attracting and bonding with positively charged ions to prevent chemical compounds, like chlorine and chloramines, from passing through to the third filter. The reverse osmosis membrane then removes molecules heavier than water, such as sodium, high levels of lead, dissolved minerals, and fluoride. Finally, the post-carbon filter polishes the water.
Hence, option A is correct. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
2 points4. With reference to the Internet of Things (IoT), consider the following statements:
1. The IoT can be used for making intelligent street lights that automatically turn off to conserve energy.
2. The IoT-based smart farming systems can help to monitor light, temperature, humidity and soil moisture of crop fields.
3. The IoT systems can be used for inventory management of pharmaceuticals and medical instruments.
Which of the above given statements is/are correct?Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
The Internet of Things (IoT) describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet. These devices range from ordinary household objects to sophisticated industrial tools.
Applications of Internet of Things (IoT):● Statement 1 is correct: The Internet of Things (IoT) may be used in urban planning to create smarter cities. One such application can be for making intelligent street lights that automatically turn off to conserve energy.
● Statement 2 is correct: In agriculture, IoT-based smart farming systems can help monitor, for instance, light, temperature, humidity and soil moisture of crop fields using connected sensors. IoT is also instrumental in automating irrigation systems.
● Statement 3 is correct: In healthcare, IoT offers many benefits, including the ability to monitor patients more closely using an analysis of the data that’s generated. Hospitals often use IoT systems to complete tasks such as inventory management for both pharmaceuticals and medical instruments.While the idea of IoT has been in existence for a long time, a collection of recent advances in a number of different technologies has made IoT possible:
● Access to low-cost, low-power sensor technology: Affordable and reliable sensors are making IoT technology possible for more manufacturers.
● Connectivity: A host of network protocols for the internet has made it easy to connect sensors to the cloud and to other “things” for efficient data transfer.
● Cloud computing platforms: The increase in the availability of cloud platforms enables both businesses and consumers to access the infrastructure they need to scale up without actually having to manage it all.
● Machine learning and analytics: With advances in machine learning and analytics, along with access to varied and vast amounts of data stored in the cloud, businesses can gather insights faster and more easily. The emergence of these allied technologies continues to push the boundaries of IoT and the data produced by IoT also feeds these technologies.
● Conversational artificial intelligence (AI): Advances in neural networks have brought natural-language processing (NLP) to IoT devices (such as digital personal assistants Alexa, Cortana, and Siri) and made them appealing, affordable, and viable for home use.
Hence, option D is correct.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
The Internet of Things (IoT) describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet. These devices range from ordinary household objects to sophisticated industrial tools.
Applications of Internet of Things (IoT):● Statement 1 is correct: The Internet of Things (IoT) may be used in urban planning to create smarter cities. One such application can be for making intelligent street lights that automatically turn off to conserve energy.
● Statement 2 is correct: In agriculture, IoT-based smart farming systems can help monitor, for instance, light, temperature, humidity and soil moisture of crop fields using connected sensors. IoT is also instrumental in automating irrigation systems.
● Statement 3 is correct: In healthcare, IoT offers many benefits, including the ability to monitor patients more closely using an analysis of the data that’s generated. Hospitals often use IoT systems to complete tasks such as inventory management for both pharmaceuticals and medical instruments.While the idea of IoT has been in existence for a long time, a collection of recent advances in a number of different technologies has made IoT possible:
● Access to low-cost, low-power sensor technology: Affordable and reliable sensors are making IoT technology possible for more manufacturers.
● Connectivity: A host of network protocols for the internet has made it easy to connect sensors to the cloud and to other “things” for efficient data transfer.
● Cloud computing platforms: The increase in the availability of cloud platforms enables both businesses and consumers to access the infrastructure they need to scale up without actually having to manage it all.
● Machine learning and analytics: With advances in machine learning and analytics, along with access to varied and vast amounts of data stored in the cloud, businesses can gather insights faster and more easily. The emergence of these allied technologies continues to push the boundaries of IoT and the data produced by IoT also feeds these technologies.
● Conversational artificial intelligence (AI): Advances in neural networks have brought natural-language processing (NLP) to IoT devices (such as digital personal assistants Alexa, Cortana, and Siri) and made them appealing, affordable, and viable for home use.
Hence, option D is correct. -
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
2 pointsWith reference to the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act 2010, consider the following statements:
1. The Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act 2010 is administered by the Science and Engineering Research Board.
2. Under this act, the civil liability for the nuclear damages lies primarily with the supplier.
3. The supplier’s liability cannot be more than that of the operator’s liability.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: C
Explanation:
The Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act 2010 has been enacted with a view to provide prompt compensation to the victims for damage caused by a nuclear incident through a no-fault liability regime. The Act was also meant to facilitate India becoming a State Party to the Convention on Supplementary Compensation for Nuclear Damage (CSC) 1997.
● Statement 1 is incorrect: Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act 2010 is administered by the Department of Atomic Energy.
● Statement 2 is incorrect: Under this act, the civil liability for the nuclear damages lies primarily with the operator.
● Statement 3 is correct: The supplier’s liability cannot be more than that of the operator’s liability.
Hence, option C is correct.Incorrect
Answer: C
Explanation:
The Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act 2010 has been enacted with a view to provide prompt compensation to the victims for damage caused by a nuclear incident through a no-fault liability regime. The Act was also meant to facilitate India becoming a State Party to the Convention on Supplementary Compensation for Nuclear Damage (CSC) 1997.
● Statement 1 is incorrect: Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act 2010 is administered by the Department of Atomic Energy.
● Statement 2 is incorrect: Under this act, the civil liability for the nuclear damages lies primarily with the operator.
● Statement 3 is correct: The supplier’s liability cannot be more than that of the operator’s liability.
Hence, option C is correct.




