Day-504
Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
To attempt the Quiz, simply click on START Button.
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
2 points1. The term ‘Epigenetics’ is commonly seen in the news. Which of the following statements best describes this term?
Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
With good measure, scientists might be able to change our rate of aging to live longer and healthier lives. Researchers know that some people age faster than others and have been trying to concisely measure the internal physiological changes that lead to deteriorating health with age. Researchers have since developed several measures that can more reliably predict health outcomes based on epigenetics.
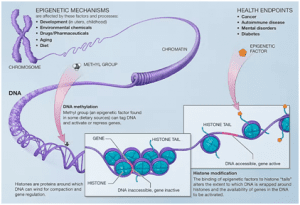
● Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression that do not involve changes to the underlying DNA sequence – a change in phenotype without a change in genotype – which in turn affects how cells read the genes. Epigenetic change is a regular and natural occurrence but can also be influenced by several factors including age, the environment/lifestyle, and disease state.
● Epigenetic modifications can manifest as commonly as the manner in which cells terminally differentiate to end up as skin cells, liver cells, brain cells, etc. Or, epigenetic change can have more damaging effects that can result in diseases like cancer.
● New and ongoing research is continuously uncovering the role of epigenetics in a variety of human disorders and fatal diseases.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
With good measure, scientists might be able to change our rate of aging to live longer and healthier lives. Researchers know that some people age faster than others and have been trying to concisely measure the internal physiological changes that lead to deteriorating health with age. Researchers have since developed several measures that can more reliably predict health outcomes based on epigenetics.
● Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression that do not involve changes to the underlying DNA sequence – a change in phenotype without a change in genotype – which in turn affects how cells read the genes. Epigenetic change is a regular and natural occurrence but can also be influenced by several factors including age, the environment/lifestyle, and disease state.
● Epigenetic modifications can manifest as commonly as the manner in which cells terminally differentiate to end up as skin cells, liver cells, brain cells, etc. Or, epigenetic change can have more damaging effects that can result in diseases like cancer.
● New and ongoing research is continuously uncovering the role of epigenetics in a variety of human disorders and fatal diseases.

-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
2 points2. In the context of space technology, consider the following statements:
1. Satellites in a polar orbit do not have to pass the north and south pole precisely.
2. Sun-synchronous orbit is a particular type of polar orbit.
3. Satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) must always orbit along the earth’s equator.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: A
Explanation:
An orbit is the curved path that an object in space (such as a star, planet, moon, asteroid or spacecraft) takes around another object due to gravity.
● Geostationary orbit (GEO): Satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO) circle Earth above the equator from west to east following Earth’s rotation – taking 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds – by travelling at exactly the same rate as Earth. This makes satellites in GEO appear to be ‘stationary’ over a fixed position. In order to perfectly match Earth’s rotation, the speed of GEO satellites should be about 3 km per second at an altitude of 35 786 km. GEO is used by satellites that need to stay constantly above one particular place over Earth, such as telecommunication satellites. Satellites in Geostationary orbit must always orbit along the earth’s equator. Hence, statement 3 is incorrect.
● Low Earth orbit (LEO): A low Earth orbit (LEO) is, as the name suggests, an orbit that is relatively close to Earth’s surface. It is normally at an altitude of less than 1000 km but could be as low as 160 km above Earth – which is low compared to other orbits, but still very far above Earth’s surface. Unlike satellites in GEO that must always orbit along Earth’s equator, LEO satellites do not always have to follow a particular path around Earth in the same way – their plane can be tilted. This means there are more available routes for satellites in LEO, which is one of the reasons why LEO is a very commonly used orbit. Polar orbit: Satellites in polar orbits usually travel past Earth from north to south rather than from west to east, passing roughly over Earth’s poles. Satellites in a polar orbit do not have to pass the North and South Pole precisely; even a deviation within 20 to 30 degrees is still classed as a polar orbit. Polar orbits are a type of low Earth orbit, as they are at low altitudes between 200 to 1000 km. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
● Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO): It is a particular kind of polar orbit. Satellites in SSO, travelling over the polar regions, are synchronous with the Sun. This means they are synchronised to always be in the same ‘fixed’ position relative to the Sun. This means that the satellite always visits the same spot at the same local time, for example, passing the city of Delhi every day at noon exactly. Hence, statement 2 is correct.Incorrect
Answer: A
Explanation:
An orbit is the curved path that an object in space (such as a star, planet, moon, asteroid or spacecraft) takes around another object due to gravity.
● Geostationary orbit (GEO): Satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO) circle Earth above the equator from west to east following Earth’s rotation – taking 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds – by travelling at exactly the same rate as Earth. This makes satellites in GEO appear to be ‘stationary’ over a fixed position. In order to perfectly match Earth’s rotation, the speed of GEO satellites should be about 3 km per second at an altitude of 35 786 km. GEO is used by satellites that need to stay constantly above one particular place over Earth, such as telecommunication satellites. Satellites in Geostationary orbit must always orbit along the earth’s equator. Hence, statement 3 is incorrect.
● Low Earth orbit (LEO): A low Earth orbit (LEO) is, as the name suggests, an orbit that is relatively close to Earth’s surface. It is normally at an altitude of less than 1000 km but could be as low as 160 km above Earth – which is low compared to other orbits, but still very far above Earth’s surface. Unlike satellites in GEO that must always orbit along Earth’s equator, LEO satellites do not always have to follow a particular path around Earth in the same way – their plane can be tilted. This means there are more available routes for satellites in LEO, which is one of the reasons why LEO is a very commonly used orbit. Polar orbit: Satellites in polar orbits usually travel past Earth from north to south rather than from west to east, passing roughly over Earth’s poles. Satellites in a polar orbit do not have to pass the North and South Pole precisely; even a deviation within 20 to 30 degrees is still classed as a polar orbit. Polar orbits are a type of low Earth orbit, as they are at low altitudes between 200 to 1000 km. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
● Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO): It is a particular kind of polar orbit. Satellites in SSO, travelling over the polar regions, are synchronous with the Sun. This means they are synchronised to always be in the same ‘fixed’ position relative to the Sun. This means that the satellite always visits the same spot at the same local time, for example, passing the city of Delhi every day at noon exactly. Hence, statement 2 is correct. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
2 points3. Isotopes have identical chemical properties, yet have very different nuclear properties. Which among the following are the applications of radioactive isotopes?
1. Treatment of cancer
2. Fuel in nuclear reactors
3. Treatment of Goitre
4. Source of electric power in spacecraft
Select the correct answer using the code given below:Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
The difficult stories we hear when it comes to cancer treatment, like patients discontinuing treatment or not wanting treatment owing to the side effects, will be a thing of the past if Theronostics (diagnosis + therapeutics) is adopted. Theronostics in nuclear medicine aids in clearly recognising and destroying advanced cancer without affecting the health tissues. It uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radioactive isotopes or radioisotopes: one radioisotope to identify (diagnose) and a second radioisotope to deliver therapy to treat any metastatic tumours, where cancer is advanced or hasn’t responded to other conventional treatments.
● A major characteristic of an atom is its atomic number, which is defined as the number of protons. The chemical properties of an atom are determined by its atomic number. The total number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in an atom is the atomic mass number. Atoms with the same atomic number but with different atomic masses are called isotopes. Isotopes have identical chemical properties, yet have very different nuclear properties. For example, there are three isotopes of hydrogen. Two of these isotopes are stable (not radioactive), but tritium (one proton and two neutrons) is unstable. Most elements have stable isotopes.
● Radioactive isotopes can also be created for many elements. An isotope of uranium (Uranium-235) is used as a fuel in nuclear reactors. An isotope of cobalt (Cobalt-60) is used in the treatment of cancer. An isotope of iodine (Iodine-131) is used in the treatment of Goitre.
● The use of radioactive isotopes as compact sources of electrical power—e.g., plutonium-238 in spacecraft. In such cases, the heat produced in the decay of the radioactive isotope is converted into electricity by means of thermoelectric junction circuits or related devices.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
The difficult stories we hear when it comes to cancer treatment, like patients discontinuing treatment or not wanting treatment owing to the side effects, will be a thing of the past if Theronostics (diagnosis + therapeutics) is adopted. Theronostics in nuclear medicine aids in clearly recognising and destroying advanced cancer without affecting the health tissues. It uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radioactive isotopes or radioisotopes: one radioisotope to identify (diagnose) and a second radioisotope to deliver therapy to treat any metastatic tumours, where cancer is advanced or hasn’t responded to other conventional treatments.
● A major characteristic of an atom is its atomic number, which is defined as the number of protons. The chemical properties of an atom are determined by its atomic number. The total number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in an atom is the atomic mass number. Atoms with the same atomic number but with different atomic masses are called isotopes. Isotopes have identical chemical properties, yet have very different nuclear properties. For example, there are three isotopes of hydrogen. Two of these isotopes are stable (not radioactive), but tritium (one proton and two neutrons) is unstable. Most elements have stable isotopes.
● Radioactive isotopes can also be created for many elements. An isotope of uranium (Uranium-235) is used as a fuel in nuclear reactors. An isotope of cobalt (Cobalt-60) is used in the treatment of cancer. An isotope of iodine (Iodine-131) is used in the treatment of Goitre.
● The use of radioactive isotopes as compact sources of electrical power—e.g., plutonium-238 in spacecraft. In such cases, the heat produced in the decay of the radioactive isotope is converted into electricity by means of thermoelectric junction circuits or related devices. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
2 points4. Consider the following statements:
1. Lymphatic filariasis (LF) is a viral disease caused by culex mosquitoes.
2. The Union Health Ministry has launched the Sarva Dawa Sevan campaign to eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?Correct
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare launched the nationwide Sarva Dawa Sevan or Mass Drug Administration (MDA) campaign to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (LF).
● Aim is to eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis by 2027, three years ahead of the global target.
● Health workers will go door-to-door to administer anti-filaria medicine in 10 filaria affected States.
● Focus will be on High-burden districts in Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Karnataka, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, and Andhra Pradesh.
● Intensive monitoring at block level to be focused upon along with daily analyses of coverage and monitoring reports at all governance levels.
● India has ramped up efforts to eliminate lymphatic filariasis (LF), a vector-borne disease caused by culex mosquitoes that leads to disabilities, well ahead of the global targets to safeguard communities from disabilities, as well as from social- and economic insecurity.Incorrect
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare launched the nationwide Sarva Dawa Sevan or Mass Drug Administration (MDA) campaign to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (LF).
● Aim is to eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis by 2027, three years ahead of the global target.
● Health workers will go door-to-door to administer anti-filaria medicine in 10 filaria affected States.
● Focus will be on High-burden districts in Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Karnataka, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, and Andhra Pradesh.
● Intensive monitoring at block level to be focused upon along with daily analyses of coverage and monitoring reports at all governance levels.
● India has ramped up efforts to eliminate lymphatic filariasis (LF), a vector-borne disease caused by culex mosquitoes that leads to disabilities, well ahead of the global targets to safeguard communities from disabilities, as well as from social- and economic insecurity. -
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
2 points5. The Geological Survey of India (GSI) recently discovered huge reserves of lithium deposits in Jammu. The GSI operates under which of the following ministries?
Correct
Answer: D
Explanation:
The Geological Survey of India (GSI) recently said it has discovered in Jammu and Kashmir the country’s first deposits of lithium, a strategic metal used in batteries for electric vehicles, mobile phones and computers. The GSI has inferred an estimate of 5.9 million tonnes of lithium deposits in Reasi district of Jammu which, scientists said, if verified, would make it the world’s second-largest reserve after Chile’s 8 million tonnes.
A draft Bill, aimed at protecting India’s geological heritage that includes fossils, sedimentary rocks, natural structures, has raised alarm in India’s geo-sciences and palaeontology community.
• The draft Geo-heritage Sites and Geo-relics (Preservation and Maintenance) Bill, 2022, while deemed necessary by several researchers, vests powers entirely in the Geological Survey of India (GSI), a 170-year-old organisation that comes under the Ministry of Mines.
• Provisions of the Bill give it the power to declare sites as having ‘geo-heritage’ value, take possession of relics (fossils, rocks) that rest in private hands, prohibit construction 100 meters around such a site, penalise with fines up to ₹5 lakh and possibly imprisonment vandalism, defacement, and violations of directives of a site by the Director General of the GSI.Incorrect
Answer: D
Explanation:
The Geological Survey of India (GSI) recently said it has discovered in Jammu and Kashmir the country’s first deposits of lithium, a strategic metal used in batteries for electric vehicles, mobile phones and computers. The GSI has inferred an estimate of 5.9 million tonnes of lithium deposits in Reasi district of Jammu which, scientists said, if verified, would make it the world’s second-largest reserve after Chile’s 8 million tonnes.
A draft Bill, aimed at protecting India’s geological heritage that includes fossils, sedimentary rocks, natural structures, has raised alarm in India’s geo-sciences and palaeontology community.
• The draft Geo-heritage Sites and Geo-relics (Preservation and Maintenance) Bill, 2022, while deemed necessary by several researchers, vests powers entirely in the Geological Survey of India (GSI), a 170-year-old organisation that comes under the Ministry of Mines.
• Provisions of the Bill give it the power to declare sites as having ‘geo-heritage’ value, take possession of relics (fossils, rocks) that rest in private hands, prohibit construction 100 meters around such a site, penalise with fines up to ₹5 lakh and possibly imprisonment vandalism, defacement, and violations of directives of a site by the Director General of the GSI.




