POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. BELAGAVI BORDER DISPUTE
TAGS: GS-II-POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
THE CONTEXT:Recently, the Supreme Court adjourned the hearing on the state of Maharashtra’s plea in a border row with Karnataka, as Justice Aravind Kumar recused himself.
THE EXPLANATION:
When did the dispute begin?
- Maharashtra and Karnataka have sparred over the inclusion of some towns and villages along the state border ever since the State Reorganisation Act was passed by the Parliament in 1956.
- The Act was based on the findings of the Justice Fazal Ali Commission, which was appointed in 1953 and submitted its report two years later.
- On November 1, 1956, Mysore state – later renamed Karnataka – was formed, and differences between the state and the neighbouring Bombay state – later Maharashtra – erupted.
- Maharashtra was of the view that the northwestern district of Karnataka, Belagavi, should be part of the state, leading to a decade-long violent agitation and formation of Maharashtra Ekikaran Samithi (MES), which still holds sway in parts of the district and the eponymous city.
What was the Centre’s response?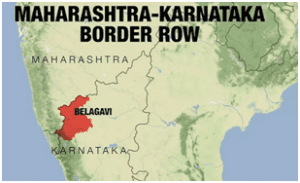
- Amid protests and pressure from Maharashtra, the Union government set up a commission under retired Supreme Court judge Justice Mehar chand Mahajan on October 25, 1966. S Nijalingappa was the Karnataka Chief Minister then and VP Nayak was his Maharashtra counterpart.
- The report was expected to be a binding document for both states and put an end to the dispute. The commission submitted its report in August 1967, where it recommended merging 264 towns and villages of Karnataka (including Nippani, Nandgad and Khanapur) with Maharashtra, and 247 villages of Maharashtra (including South Solapur and Akkalkot) with Karnataka.
Legal issues in court
- Maharashtra approached the Supreme Court in 2004, challenging the State Reorganisation Act. It demanded 865 villages and towns from five Karnataka districts to be merged with the state. The five districts are Belagavi, Karwar, Vijayapura, Kalaburagi and Bidar.
- However, almost two decades after the petition, its maintainability remains challenged. Karnataka has resorted to Article 3 of the Indian Constitution to argue that the Supreme Court does not have the jurisdiction to decide the borders of states, and only Parliament has the power to do so.
- Maharashtra has referred to Article 131 of the Constitution, which says that the Supreme Court has jurisdiction in cases related to disputes between the Union government and states.
ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
2. HUMAN COMPOSTING: A GREENER WAY TO DIE
TAGS: GS-III- ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, New York became the sixth state in the US to legalise human composting as a burial option.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Human composting, also known as natural organic reduction, is a process of transforming the human body into nutrient-rich soil that has emerged as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional burial or cremation.
- It has gained popularity, especially among the younger generation, for being an eco-friendly alternative to dispose of a corpse.
Process of human composting:
- The body is first washed and dressed in a biodegradable grown.
- It’s then placed in a closed vessel, usually measuring 8 feet by 4 feet, along with selected materials such as alfalfa, straw, and sawdust.
- The body is left to decompose for the next 30 days.
- To speed up the decay, oxygen is added to the vessel, which results in the unfolding of a process called “aerobic digestion”, in which microbes start to consume organic matter.
- Temperature inside the container is kept around 130 degrees Fahrenheit or 55 degrees Celsius to kill off contagions.
- By the time aerobic digestion is over, the body has been transformed into a soil-like material, containing nutrients, bones, and some medical devices — these are taken out from the compost pile and recycled.
- As the microbial activity comes to an end, the temperature inside the pile drops, marking the transformation from an active composite pile into the soil.
Concerns:
- The biggest opponent of this process has been the Catholic Church and called it an “unfortunate spiritual, emotional, and psychological distancing from the deceased.
- It has been believed that the ‘transformation’ of the remains would create an emotional distance rather than a reverence” for the remains.
- Even cremated remains must remain in a communal place befitting of the dignity inherent in the human body and its connection to the immortal soul.
GOVERNMENT SCHEMES
3. REVISION SERIES
PRADHAN MANTRI FASAL BIMA YOJANA
TAGS: GS-II-GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INTERVENTIONS
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) scheme was launched in India by Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers welfare, New Delhi from Kharif 2016 season onwards.
- National Insurance Company started participating in PMFBY from Rabi 2016 onwards and covered 8 States and 2 Union Territories during the past 5 seasons namely, Rabi 2016-17, Kharif & Rabi 2017 and Kharif & Rabi 2018 covering 70,27,637 farmers.
- Farmers share of premium is Rs. 453 crores and with subsidy from State/Central Govts RS.1909 Crores, gross Premium is Rs.2362 Crores for the 5 seasons together.
Objective of the Schemes
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) aims at supporting sustainable production in agriculture sector by way of:
- Providing financial support to farmers suffering crop loss/damage arising out of unforeseen events
- Stabilizing the income of farmers to ensure their continuance in farming
- Encouraging farmers to adopt innovative and modern agricultural practices
- Ensuring flow of credit to the agriculture sector which will contribute to food security, crop diversification and enhancing growth and competitiveness of agriculture sector besides protecting farmers from production risks.
Who can be covered?
- All farmers who have been sanctioned Seasonal Agricultural Operations (SAO) loans (Crop Loans) from Financial Institutions (FIs), i.e. loanee farmers, for the notified crop(s) season would be covered compulsorily.
- The Scheme is optional for non-loanee farmers.
- The insurance coverage will strictly be equivalent to sum insured/hectare, as defined in the Govt. notification or /and on National Crop Insurance Portal multiplied by sown area for notified crop.
Coverage of Crops
- Food crops (Cereals, Millets and Pulses),
- Oilseeds
- Annual Commercial / Annual Horticultural crops.
In addition for perennial crops, pilots for coverage can be taken for those perennial horticultural crops for which standard methodology for yield estimation is available.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
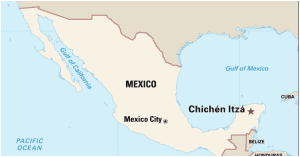
4. CHICHEN ITZA
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVES
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Archaeologists in Mexico have uncovered an intricately carved stone they believe was used as a scoreboard for pelota, a ball game played by the Maya hundreds of years ago.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The circular stone was found at the Chichen Itza archaeological site and is thought to be around 1,200 years old.
- At its centre are two players in elaborate headgear surrounded by hieroglyphic writing.
- Experts are now analysing the writing to decipher its possible meaning.
- The 40kg-stone (88lb) was found by archaeologist Lizbeth Beatriz Mendicut Pérez in an architectonic compound known as Casa Colorada (Red House).
- Casa Colorada is the best preserved of the buildings surrounding the main plaza in the pre-Columbian city of Chichen Itza.
- Experts believe the stone would have adorned an archway at the entrance to the compound during the late 800s or early 900s.
- It was found face down half a metre underground, where it is thought to have fallen when the archway collapsed.
5. EXERCISE COPE INDIA 23
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVES
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Exercise Cope India 23, a bilateral Air Exercise between the Indian Air Force (IAF) and the United States Air Force (USAF) is begins at Air Force Stations Arjan Singh (Panagarh), Kalaikunda and Agra.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The exercise aims to enhance mutual understanding between the two Air Forces and share their best practices.
- The first phase of exercise commenced on April 10, 2023. This phase of the exercise focused on air mobility and involved transport aircraft and Special Forces assets from both the Air Forces.
- Both sides fielded the C-130J and C-17 aircraft, with the USAF operating an MC-130J, as well. The exercise also included the presence of Japanese Air Self Defence Force aircrew, who participated in the capacity of observers.
US-India War Games Amid China Threat
- Meanwhile, India and United States Special Forces are also carrying out wargames with a focus on supporting fighter aircraft operations in forward areas. The war games came in view of an ongoing military standoff with China.
- The operations are likely to have focused on supporting the fighter aircraft operations including designating targets in frontline areas by laser so that the precision-guided bombs can reach their designated target accurately.




