ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
1. SUHELWA WILDLIFE SANCTUARY
TAGS: GS-III-ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: In the recently released report on the tiger census in the country, it is said that Suhelwa Wildlife Sanctuary is a new area where photographic evidence of tigers has been recorded for the first time.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Located in Shravasti, Balrampur and Gonda districts of Uttar Pradesh, Suhelwa was declared a Wildlife Sanctuary in 1988
- Occupying an area of 452 sq km, the sanctuary is covered with Sal, Sheesham, Khair, Sagaun (Teak), Asna, Jamun, Haldu, Phaldu, Dhamina, Jhingan and Bahera trees. The fauna found in the sanctuary includes Leopard, Tiger, Bear, Wildcat, Wild Boar and various birds.
- Sohelwa Wild Life Division is situated on the Indo-Nepal International Border.
- Fauna:Different types of mammals are found here viz. Leopard, Bear, Wolf, Hyena, Jackal, Wild Boar, Sambhar, Spotted Deer, Neelgaya, Barking Deer along with Monkeys of different types.
- Flora:In this Wild Life Sanctuary the main tree species are Sal, Asna, Khair, Teak etc. With these speciese Black Sheesham, Jamun, Haldu, Faldu, Zigna, Harra, Bahera, Rohani are other important species. The Sanctuary area is very rich in medicinal plants.
2. THE INTERNATIONAL BIG CATS ALLIANCE
THE CONTEXT: The Prime Minister of India recently launched the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) during an event commemorating 50 years of Project Tiger in Mysuru, Karnataka.
Aims and Objectives:
- The IBCA aims to conserve the planet’s seven big cats: Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Cheetah, Jaguar, and Puma.
- India has extensive experience in big cat conservation, from the ongoing efforts for tigers, lions, snow leopards, and leopards to the recent translocation of the Cheetah to restore this extinct species to its natural habitat.
- The Alliance will expand its reach to 97 range countries, covering the natural habitats of these big cats, and strengthen global cooperation and efforts for their conservation.
- Big Cats as Mascots for Sustainable Development: The big cats can serve as mascots for sustainable development and livelihood security. Through the IBCA, India and other big cat range countries can promote environmental resilience and climate change mitigation.

Significance:
- The importance of conserving big cats and their habitats could secure crucial natural ecosystems, provide water and food security for millions, and support the livelihoods of forest communities.
- The Alliance will enhance global efforts and partnerships on big cat conservation while creating a platform for knowledge convergence, best practices, and support for existing species-specific intergovernmental platforms. It will also provide direct assistance to recovery efforts in potential range habitats.
- The initiative aims to ensure natural ecosystems continue to thrive and become central to economic and development policies in the “Amrit Kaal.”
The Seven Big Cats:
TIGER(PANTHERA TIGRIS)
SIZE:75-300 KG | STATUS: ENDANGERED
Tiger is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus Panthera.It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily preys on ungulates, such as deer and wild boar. Tigers are the largest cat species and is both flagship and Umbrella species. It is the national animal of India, Bangladesh, Malaysia, and South Korea.
LION (PANTHERA LEO)
SIZE: 100-250 KG | STATUS: VULNERABLE
Native to Africa and Asia, the lion is the most social cat, and lives in groups called ‘prides”. They prefer open forests such as males have a prominent mane. The widely recognised of animal symbols-from the pillar of Ashoka to the main entrance of Buckingham Palace.
CHEETAH (ACINONYXJUBATUS)
SIZE:20-70 KG|STATUS: VULNERABLE
The fastest land mammal and it is the only cat without retractable claws-the grip helps it accelerate faster than a sports car (0-100km/hr in 3 secs). They are not aggressive towards humans; they have been tamed since the Sumerian era. They don’t breed well in captivity-females play hard to get. Cheetahs are not big; they hunt during the day to avoid competing with other big cats.
JAGUAR (PANTHERA ONCA)
SIZE: 50-110 KG | STATUS: NEAR THREATENED
The largest cat in the America’s, the jaguar has the strongest bite the leopard was force of all wild cats, enabling it to bite wild cats and the most scrubland, and adult directly through the all animals” for its “grace cannot roar, and has the skull of its prey. Melanistic(black) animal, its range is the lion is among the most jaguars are common, most adaptable of all big for balance while hunt- and are often called black panthers. Jaguar was a powerful motif in the Mayan civilisations.
COUGAR (PUMA CONCOLOR)
SIZE:40-100 KG | STATUS:LEAST CONCERN
The Cougar is the second-largest cat in the Americas: jaguar is largest. Cougars are also called mountain lion/panther across their range from the Canadian Yukon to Southern Andes.
LEOPARD (PANTHERA PARDUS)
SIZE:30-90KG | STATUS: VULNERABLE
Leopards are similar in appearance to the jaguar with a rosette patterned coat, described by Jim Corbett as “the most beautiful of movement and beauty of colouring”. The cats, they occupy diverse habitats at all altitudes across Africa and Asia. Like black jaguars. melanistic leopards are called black panthers.
SNOW LEOPARD (PANTHERA UNCIA)
SIZE:25-55KG | STATUS: VULNERABLE
Snow Leopards known as Ghost of the mountains. This Smokey-grey cat lives above the snow line in Central and South Asia. The most elusive of big cats, it longest tail of all which comes in handy for balance while hunting along cliffs, and also gives warmth when wrapped around the body. The snow leopard is the state animal of Ladakh and Himachal.
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
3. RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY
TAGS: GS-III-SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, Scientists have developed a new low-cost substrate that can increase the sensitivity of Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) — a vital analytical and sensing tool for detecting molecules. It can aid rapid detection of toxic pollutants present in water, food, etc.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) has emerged as a vital analytical and sensing tool for detecting molecules. When molecules near the noble metal nanoparticles of gold, silver, platinum, etc., their Raman signals will substantially increase, which can help detect trace amounts of analyte molecules.
- However, as noble metals are expensive, have poor uniformity, and cannot be reused, there is a quest for alternative SERS active substrates involving non-noble metals. In this regard, semiconductor oxides have emerged as promising materials for the fabrication of SERS substrates.
What is Raman Spectroscopy?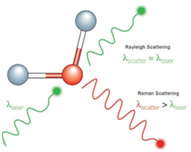
- Raman Spectroscopy is a non-destructive chemical analysis technique which provides detailed information about chemical structure, phase and polymorphy, crystallinity and molecular interactions. It is based upon the interaction of light with the chemical bonds within a material.
- Raman is a light scattering technique, whereby a molecule scatters incident light from a high intensity laser light source. Most of the scattered light is at the same wavelength (or color) as the laser source and does not provide useful information – this is called Rayleigh Scatter.
- However a small amount of light (typically 0.0000001%) is scattered at different wavelengths (or colors), which depend on the chemical structure of the analyte – this is called Raman Scatter.
4. JUICE MISSION
THE CONTEXT: The JUpiter ICy moons Explorer (JUICE) is a mission by the European Space Agency (ESA) set to launch on April 13, 2023, from the European Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana.
THE EXPLANATION:
Science Goals of JUICE
- The primary focus of JUICE’s science goals is the Jupiter system, with a particular emphasis on Ganymede as a planetary body and potential habitat.
- The mission objectives for Ganymede include the characterization of the ocean layers and detection of putative subsurface water reservoirs, topographical, geological, and compositional mapping of the surface, studying the physical properties of the icy crusts, characterizing the internal mass distribution, dynamics, and evolution of the interiors, investigating the exosphere, and studying Ganymede’s intrinsic magnetic field and its interactions with the Jovian magnetosphere.
- JUICE’s investigations on Europa will be focusing on the chemistry essential to life, including organic molecules. It will help in the understanding the formation of surface features and the composition of non-water-ice material.
Mission Profile and Launch Details
- After launch, JUICE will take 7 to 8 years to reach Jupiter, utilizing Earth and Venus gravity assists. During the journey, the spacecraft will undergo multiple tests to ensure it can withstand the harsh conditions of space.
- Upon arrival at Jupiter in 2031, JUICE will flyby Ganymede and Callisto to optimize its orbit around Jupiter. These flybys will also include a flyby of Europa. After studying Jupiter and its moons, JUICE will enter a highly elliptical orbit around Ganymede, which will evolve to a 5000 km circular orbit, and will then be lowered into a 500 km circular orbit. After it maps and conducts other investigations at this altitude, it will move to a 200 km circular orbit.
- The nominal mission length for JUICE is about 3 years, with the possibility of an extension of 200 or more days. It will conclude with an impact on the Ganymede’s surface.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVES
5. INTERNATIONAL PRIZE IN STATISTICS 2023
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVES
THE CONTEXT: The Indian-American statistician Calyampudi Radhakrishna Rao has been awarded the 2023 International Prize in Statistics, which is statistics’ equivalent of the Nobel Prize.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Rao, who is now 102 years old, is a ‘living legend’ whose work has influenced, in the words of the American Statistical Association, “not just statistics” but also “economics, genetics, anthropology, geology, national planning, demography, biometry, and medicine”.
About the Prize:
- The International Prize in Statistics is awarded every two years to an individual or team “for major achievements using statistics to advance science, technology and human welfare”. The International Prize in Statistics, along with the COPSS Presidents’ Award, are the two highest honours in the field of Statistics.
- The prize is modelled after the Nobel prizes, Abel Prize, Fields Medal and Turing Award and comes with a monetary award of $80,000. The award ceremony takes place during the World Statistics Congress.
The prize recognizes a single work or body of work, representing a powerful and original idea that had an impact in other disciplines or a practical effect on the world. The recipient must be alive when the prize is awarded.
Organisation:
The prize is awarded by the International Prize in Statistics Foundation, which comprises representatives of the following major learned societies:
- American Statistical Association
- International Biometric Society
- Institute of Mathematical Statistics
- International Statistical Institute
- Royal Statistical Society
In addition to recognizing the contributions of a statistician, the Foundation also aims at educating the public about statistical innovations and their impact on the world and gaining wider recognition for the field.
Spread the Word
