ENVIRONMENT & ECOLOGY
1. OMORGUS KHANDESH
TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-III-ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, a scientist from the Zoological Survey of India, Western Regional Centre (WRC), Pune discovered a new beetle species.
THE EXPLANATION:
- OmorgusKhandesh is necrophagous and is, therefore, also called a keratin beetle. During the decomposition of a body, blowflies are amongst the first ones to arrive in the early stages. Meanwhile, the final successional stage is with the arrival of the keratin feeders, thus their importance in forensic science.
- The beetles of this group are sometimes called hide beetles as they tend to cover their body under the soil and hide. They are not photogenic; they are usually black or grey and encrusted in dirt. Their bumpy appearance is distinct, with short, dense setae all over the body.
- The new species is morphologically most similar to Omorgusrimulosus. The latter is redescribed and illustrated to enable accurate recognition of both species in the new paper.
- OmorgusKhandesh is mainly associated with bird and mammal nests or burrows and the details of their life histories are poorly known. They feign death upon being disturbed and become motionless.
- “The keratin beetles are less studied in the Oriental region generally and India particularly as compared to the other part of the world.
- “Hence, the authors have tried to give the catalogue of the subgenus Omorgus with details on their type depositories, synonyms, chresonomy and known geographical distributions.

ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
2. MARGINAL COST OF FUNDS-BASED LENDING RATE (MCLR)
TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-III-ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the State Bank of India, Bank of Baroda and Indian Overseas Bank have raised their marginal cost of fund-based lending rates (MCLR) by up to 15 basis points.
THE EXPLANATION:
Marginal cost of funds-based lending rate:
- It is the minimum interest rate below which no bank is permitted to lend money.
- It is determined by banks internally, depending upon the loan repayment time.
- The Reserve Bank of India introduced the MCLR methodology for fixing interest rates on 1 April 2016.
- It replaced the base rate structure, which had been in place since July 2010.
- The rate is determined internally by the bank depending on the period left for the repayment of a loan.
- MCLR is calculated based on four components Marginal cost of fund, Negative carry on account of cash reserve ratio, Operating costs, Tenor premium.
What is the difference between MCLR and base rate?
- MCLR is an advanced version of the base rate.
- The base rate is based on the average cost of funds, but MCLR is based on the marginal or incremental cost of money.
- MCLR depends on the repo rates changed by RBI while Base Rate does not depend on the repo rates changed by RBI.
3. INVESTOR EDUCATION AND PROTECTION FUND AUTHORITY (IEPFA)
TAGS:PRELIMS- GS-III- ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
THE CONTEXT: The Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA), will organise a State Level Conference on Financial Literacy in Amrit Kaal – Empowering Investors in association with the Department of Tourism in Aizawl.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority:
- It was established in 2016 under the Companies Act, of 2013.
- The Authority is entrusted with;
- The responsibility of administration of the Investor Education Protection Fund (IEPF).
- Make refunds of shares, unclaimed dividends, matured deposits/debentures etc. to investors and promote awareness among investors.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Corporate Affairs
About the Investor Education Protection Fund (IEPF).
- It has been established under Section 205C of the Companies Act, 1956 by way of the Companies (Amendment) Act, 1999.
- The following amounts that remained unpaid and unclaimed for a period of seven years from the date they became due for payment are credited to the Fund:
o Amounts in the unpaid dividend accounts of the companies
o The application money received by companies for allotment of any securities and due for refund
o Matured deposits with companies
o Matured debentures with companies
o Grants and donations are given to the fund by the Central Government, State Governments, companies or any other institutions for the purposes of the Fund
o The interest or other income received out of the investments made from the fund.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
4. SHINKU LA TUNNEL
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: The Union Cabinet recently approved the construction of the tunnel. With the Atal Tunnel and the completion of the Shinku La Tunnel in 2025, the Nimmu – Padum – Darcha road shall be accessed all through the year.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Shinku La or Shingo La is a mountain pass located on the border between HP and Ladakh. It is at an altitude of 5,091 metres. In 2016, the Border Road Organization built a road to the pass.
- However, the road couldn’t be accessed during winter and large-wheeled vehicles couldn’t pass through. Following this, in 2020, GoI planned to build a 13.5 km tunnel in the pass.
Significance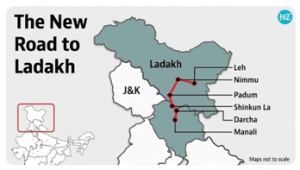
- The tunnel will help to boost the Zanskar valley economy. It reduces the travel time between HP and Ladakh.
- Currently, one has to travel 101 km on the Manali-Leh road and then take the Darcha road to enter the Zanskar region. With the tunnel, you can drive to Darcha via Padum.
- The toughest hurdle is the 15-20 feet of snowfall the region received during winter. Almost all roads are closed during this season. The Shinku La Tunnel is to make the Zanskar valley accessible 365 days.
Project Yojak
- The Shinku La tunnel is a part of Project Yojak. This project is implemented by BRO. The main objective of the project is to make sure Manali – Leh route is accessible all through the year.
5. STUDY ON THWAITES GLACIER
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: The recent study on Doomsday Glacier, also called the Thwaites Glacier says that the weak spots in the glacier are increasing. More and more warm water is seeping into the glacier. There is a threat of massive sea rise. If the glacier melts the sea level will increase by more than half a metre.
THE EXPLANATION: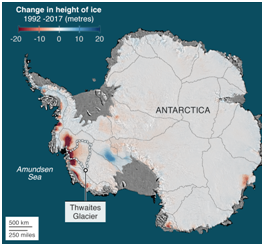
- The study was conducted by the International Thwaites Glacier Collaboration. It is one of the biggest studies conducted on the glacier so far. More than 13 scientists participated in the study from the UK, the US, and different other countries. They spent more than six weeks coming to this conclusion.
Findings
- Terraces in the glaciers are increasing. These openings are causing the sideways melt of the glacier. Terraces are leading the warm water to the crevasses and increasing the melting further.
What are Glacier Terraces?
- It is a long segment of a glacier. It is formed due to the stripping of soft strata from hard strata. In India, the glacial terraces are addressed as Karewas. They are found in Kashmir valley.
Glacial Crevasses - They are deep cracks in glaciers. Their sizes range from a few inches to more than 40 feet. They are formed due to shear stress. Say two big ice masses are moving. Friction develops resulting in shear stress. This leads to breakings in the faces.


