Table of Contents
GEOGRAPHY: NATURAL RESOURCES
1. NEW LITHIUM RESERVES
TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-I-GEOGRAPHY
THE CONTEXT: India’s Ministry of Mines recently announced that 5.9 million tonnes of lithium reserves have been found for the first time in the country in Jammu and Kashmir.
THE EXPLANATION:
- It is a soft, silvery-white metal that heads group 1, the alkali metals group, of the periodic table of the elements.
Features: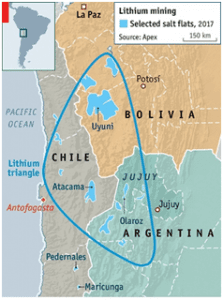
- It has the lowest density of all metals.
- It is the lightest of the solid elements.
- It reacts vigorously with water.
- It has a body-centered cubic crystal structure.
- Occurrence:
- Lithium does not occur as a metal in nature but is found combined in small amounts in igneous rocks.
- Lithium is found in brine deposits and as salts in mineral springs. Its concentration in seawater is 0.1 part per million (ppm).
- Major Reserves: Lithium reserves are concentrated in the lithium triangle in South America – Argentina, Bolivia & Chile, with 50% of the deposits concentrated in these regions.
FIG: LITHIUM TRIANGLE
Uses:
- Lithium is important in rechargeable batteries for mobile phones, laptops, digital cameras, and electric vehicles.
- It is also used in some non-rechargeable batteries for things like heart pacemakers, toys, and clocks.
- Lithium metal is made into alloys with aluminium and magnesium, improving their strength and making them lighter.
- Lithium oxide is used in special glasses and glass ceramics.
- Lithium stearate is used as an all-purpose and high-temperature lubricant.
- Lithium carbonate is used in drugs to treat manic depression.
INDIAN POLITY
2. MODES OF LOSING INDIAN CITIZENSHIP
TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-II- POLITY
THE CONTEXT: Over 16 lakh Indians have renounced their Indian citizenship since 2011, including 2,25,620 people last year, the highest during the period, while the lowest of 85,256 was in 2020, according to government data.
THE EXPLANATION:
Modes of losing Indian Citizenship:
- The Citizenship Act 1955 lays down the three modes by which an Indian citizen, whether a citizen at the commencement of the Constitution or subsequent to it, may lose their citizenship. These are,
By Renunciation:
- An Indian Citizen of full age and capacity can renounce his Indian citizenship by making a declaration to that effect and having it registered.
- But if such a declaration is made during any war in which India is engaged, the registration shall be withheld until the Central Government otherwise directs.
- When a male person renounces his citizenship, every minor child of him ceases to be an Indian citizen.
- Such a child may, however, resume Indian citizenship if he makes a declaration to that effect within a year of his attaining full age, i.e. 18 years.
By Termination:
- If a citizen of India voluntarily acquires citizenship of another country, then the citizenship of India gets terminated.
- This provision does not apply during times of war.
- If any question arises as to whether, when, or how any person has acquired the citizenship of another country, it is to be determined by such authority and in such manner as may be prescribed by the rules.
By Deprivation:
- It is a compulsory termination of citizenship of India.
- A citizen of India by naturalization, registration, domicile and residence may be deprived of his citizenship by order of the Central Government if it is satisfied that:
- The citizen has obtained the citizenship by means of fraud, false representation, or concealment of any material fact;
- The citizen has shown disloyalty to the Constitution of India;
- The citizen has unlawfully traded or communicated with the enemy during a war;
- The citizen has, within five years after registration or neutralization, been imprisoned in any country for two years;
- The citizen has been ordinarily resident out of India for seven years.
ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
3. THANE CREEK
TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-III-ENVIRONMENT
THE CONTEXT: A seven-km undersea tunnel will be constructed for the Mumbai-Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail Corridor project in a bid to save about 12 hectares of mangrove forests in Maharashtra’s Thane creek.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Thane creek:
- It is an inlet along the shoreline of the Arabian Sea that isolates the city of Mumbai from the Indian mainland.
- The east bank lies in the Thane and Navi Mumbai districts, while the west bank is in the Greater Mumbai district.
- It is Asia’s largest creek, with a length of 26 km.
- Thane Creek is fed by numerous freshwater sources (of which Ulhas river is the largest), making the water brackish.
- The creek is covered with mangroves on both sides.
- Thane Creek is a very important wintering ground for waterbirds. It supports over 1,00,000 birds during winter, including the iconic flamingos.
- A major part of the creek has been declared a bird sanctuary called Thane Creek Flamingo Bird Sanctuary (TCFS).

Thane Creek Flamingo Bird Sanctuary (TCFS):
- TCFS also referred to as the Airoli Flamingo Sanctuary, is the first flamingo sanctuary in India located along the western bank of the Thane creek.
- It encompasses more than 1600 hectares of mudflats, mangroves, and water bodies.
- The area was declared a flamingo sanctuary in 2015 and is home to substantial bird life – both residential and migratory.
- TCFS was declared a Ramsar site by the International Wetlands Convention in 2022.
- Flora: Avicennia marina, Rhizophora mucronata, Acanthus ilicifolius, Aeluropus lagopoides, Sesuvium protulacastrumetc.
- Fauna: Over 205 species of birds have been reported from this area, including Lesser Flamingo, Greater Flamingo, Asian Openbill, White Stork, Pied Avocet, Eastern Golden Plover, etc.
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
4. SMALL SATELLITE LAUNCH VEHICLE (SSLV-D2)
TAGS: PRELIMS- GS-III- SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE CONTEXT: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched the second edition of the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV-D2) from the first launch pad of Satish Dhawan space centre at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
THE EXPLANATION:
About the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle:
- The new vehicle was developed to capture the emerging small and microsatellite commercial market.
- The SSLV caters to the launch of up to 500 kg satellites to low earth orbits on a ‘launch-on-demand’ basis.
- The launch vehicle uses three solid stages followed by a liquid-fuel-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) to place satellites in orbit
- The rocket provides low-cost access to space, offers low turn-around time and flexibility in accommodating multiple satellites, and demands minimal launch infrastructure.
- It placed the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) earth observation satellite EOS-07 and two co-passenger satellites — Janus-1 and AzaadiSat2
What is Janus-1?
- Janus-1 is a technology demonstrator satellite built by United States-based Antaris and its Indian partners XDLinks and Ananth Technologies.
- It weighs only 10.2 kg and is a six-unit cube satellite with five payloads on board — two from Singapore, and one each from Kenya, Australia, and Indonesia.
What is AzaadiSat2?
- The payloads have been built by 750 girl students from across India.
- The payloads include: LoRa amateur radio, a sensor to measure radiation levels in space, and sensors to measure the health of the satellite such as temperature, reset count, and inertial data.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
5. ASBESTOS
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: Brazil has sunk a decommissioned aircraft carrier despite the presence of asbestos and toxic materials in Atlantic, many environmental groups claiming the former French ship was packed with toxic materials.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Asbestos:
- It is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral.
- Asbestos is a group of six naturally occurring minerals made up of heat-resistant fibers.
- It consists of flexible fibers resistant to heat, electricity and corrosion.
- Asbestos is an excellent electrical insulator and is highly fire-resistant, so for much of the 20th century it was very commonly used across the world as a building material.
- Construction materials contained asbestos because it is an effective insulator.
- Asbestos in cloth, paper, cement, plastic and other materials makes them stronger.
- Asbestos mainly comes from Russia, Kazakhstan and China.
- The toxic mineral was once mined throughout North America.
- Asbestos has been used on ships as both a fire retardant and an insulator to protect sailors from the constant and jarring vibrations of ships’ engines.
Health Effects
- It is known to be a highly toxic material and a carcinogen.
- Inhaled or swallowed asbestos fibers can become trapped in the respiratory or digestive systems of the body, accumulating over time.
- Repeated exposure can cause inflammation and damage the DNA.
- The following illnesses have been associated with asbestos exposure: lung cancer, COPD, mesothelioma and asbestosis.

