ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY & CLIMATE CHANGE
1. WHAT IS THE KALASA-BANDURI NALA PROJECT?
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: Recently,Karnataka Chief Minister Basavaraj Bommai told the Legislative Assembly that the government had received clearance from the Centre for two Detailed Project Reports (DPRs) on the Kalasa-Banduri Nala on the Mahadayi. It has escalated its long-standing dispute on the issue with neighbouring Goa.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Kalasa Banduri Nala project: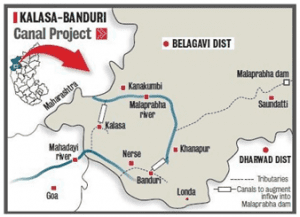
- The Kalasa Banduri Nala project aims to divert water from Mahadayi to satisfy the drinking water needs of Belagavi, Dharwad, Bagalkot and Gadag districts.
- Though the project was first proposed in the early 1980s, it has remained on paper owing to a dispute between Karnataka, Goa and Maharashtra.
- As per plans, barrages are to be built against Kalasa and Banduri streams — tributaries of Mahadayi — and water diverted towards Karnataka’s parched districts.
- Mahadayi originates inside the Bhimgad Wildlife Sanctuary in the Belagavi district of Karnataka and flows into the Arabian Sea in Goa.
What did the Tribunal say?
- A Tribunal was set up by the UPA government in November 2010.
- The Tribunal in 2018 awarded 13.42 TMC water from Mahadayi river basin to Karnataka, 1.33 TMC to Maharashtra and 24 TMC to Goa.
- In Karnataka’s share, 5.5 TMC was to meet drinking water needs and 8.02 TMC was for hydro-electricity generation.
- Of the 5.5 TMC, 3.8 TMC was to be diverted to Malaprabha basin through Kalasa and Banduri Nalas (canals).
- This was notified by the Central government in February 2020.
2. INDIA’S FIRST GREEN HYDROGEN BLENDING PROJECT
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: NTPC Limited and Gujarat Gas Limited (GGL) have commissioned India’s first green hydrogen blending project in the piped natural gas (PNG) network of NTPC Kawas township, Surat.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is Green Hydrogen?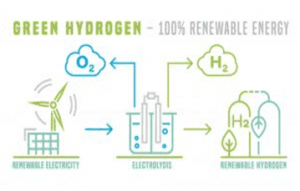
- Green hydrogen is produced through the electrolysis of water, using electricity generated from renewable sources such as solar or wind power. This process splits water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, with the hydrogen being captured and stored for use as a fuel. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere.
- The main advantage of green hydrogen is that it is a clean, renewable fuel that can be used to power a variety of applications, including transportation and electricity generation.
- It also has the potential to play a significant role in the decarbonization of the energy sector, as it can be used to replace fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Benefits of Green Hydrogen Blending
- The green hydrogen blending project in Surat is being carried out with the approval of the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB). The regulatory body has given permission for a 5% vol./vol. blending of green hydrogen with PNG to start with, with the blending level to be gradually increased to reach 20%.
- The addition of green hydrogen to the natural gas network has a number of benefits. First and foremost, it reduces CO2 emissions while maintaining the same net heating content. This is an important step in the fight against climate change and will help India reduce its hydrocarbon import bill while also bringing in foreign exchange through the export of green hydrogen and green chemicals to the rest of the world.
- In addition, the use of green hydrogen in the energy sector has the potential to create new job opportunities and boost economic growth. It can also improve energy security by reducing the country’s reliance on imported fossil fuels.
- The commissioning of India’s first green hydrogen blending project is a major milestone that puts the country at the forefront of the global hydrogen economy. It is a testament to the hard work and dedication of NTPC and GGL, who have been able to achieve this feat in record time.
- The project serves as a model for other countries to follow and demonstrates the potential for green hydrogen to play a key role in the decarbonization of the energy sector. It is hoped that this project will pave the way for the wider adoption of green hydrogen in India and help the country transition to a more sustainable and cleaner energy future.
GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INTERVENTION
3. RISE- RISING INDIA THROUGH SPIRITUAL EMPOWERMENT
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE-GS-III- GOVERNMENT INTERVENTIONS
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the President of India participated in the launch of the National Campaign on ‘RISE- Rising India Through Spiritual Empowerment’, organized by Brahma Kumaris at Mount Abu, Rajasthan.
THE EXPLANATION:
President’s Personal Connection with Brahma Kumaris
- In her address to the gathering, the President spoke of her personal connection with the Brahma Kumaris Institution. She explained that she had learned the method of Raja Yoga, which emphasizes inner spiritual power rather than external physical conveniences and events. This helped her to find light and enthusiasm during a time when she felt surrounded by darkness and lacked hope.
Objectives of RISE
- The National Campaign on ‘RISE- Rising India Through Spiritual Empowerment’ is aimed at spiritually empowering Indian nationals in order to fulfill the dream of a “Golden India.” Brahma Kumaris believes that self-transformation leads to world transformation, and that the journey of a million transformations will create a domino effect, ultimately leading to the rebuilding of the nation.
Methodology
- To achieve these goals, a range of lectures, workshops, short courses, youth camps, and fests will be conducted nationwide to create awareness and transformation among youth. Additionally, Brahma Kumaris will collaborate on various projects that provide opportunities for young people to participate in activities of social and humanitarian concern.
Key Areas
- The National Campaign on ‘RISE- Rising India Through Spiritual Empowerment’ will focus on a range of areas, including lectures, workshops, short courses, youth camps, and fests nationwide to create awareness and transformation among youth. Additionally, the campaign will involve collaboration on projects that offer opportunities for young people to engage in social and humanitarian activities.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
4. DIEBACK DISEASE
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT:Recently, Dieback disease hits neem trees in Telangana.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Dieback Disease:
- The dieback disease was first reported in the country during the 1990s near Dehradun in Uttarakhand, while it was first noticed in Telangana in 2019.
- The dieback disease is mainly caused by the fungi Phomopsis azadirachtae.
- The dieback disease affects leaves, twigs and the inflorescence of neem trees of all ages and it causes almost 100% loss of fruit production in severely infected trees.
- The dieback is a fungal disease but the neem trees are sometimes hit by insect infestation and the combination of both increases its impact.
- The disease posing a threat to the neem trees has been identified as twig blight and dieback disease in Telangana, and it has reappeared in the state this year on a massive scale.
- The appearance of symptoms starts with the onset of the rainy season and becomes progressively severe in the later part of the rainy season and early winter.
5. WORLD BRAILLE DAY: JANUARY 4
TAGS: PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
THE CONTEXT: Every year, the World Braille Day is celebrated on January 4 by the United Nations and several other international organizations. The day is celebrated to create awareness of the importance of Braille as a means of communication in the realization of human rights for the blind.
THE EXPLANATION:
Why is World Braille Day celebrated on January 4?
- The celebration of World Braille Day on January 4 is in honor of Louis Braille, the inventor of the Braille system. Braille was born in France on January 4, 1809, and it was his development of the system that has allowed blind individuals to read and write, increasing their independence and access to education and employment opportunities.
When was the first World Braille Day celebrated?
The first World Braille Day was celebrated in 2019.
What is Braille?
- Braille is a system of representing alphabetic and numerical symbols using six raised dots. The dots are arranged in a grid, with different combinations of dots representing different letters, numbers, and symbols. This allows blind individuals to read and write by feeling the raised dots with their fingers.
Who invented Braille?
- Braille was invented by Louis Braille in the 19th century in France. As a young boy, Braille was blinded in an accident and struggled to find ways to continue his education. He eventually developed the Braille system as a way for blind individuals to read and write, and it has since become the primary means of communication for the blind community around the world.
Braille Language in India
- In India, the Braille system has been in use for many years, with the country adopting uniform Braille codes for different languages in 1951. India also established the Central Braille Plant in Dehradun and the Central Braille Press in 1954, which produce simple Braille equipment such as slates and styluses.
Steps Taken by the Government of India to Support People with Disabilities
- The Government of India has taken several steps to support people with disabilities, including enacting the Persons with Disabilities Act in 1995. This act provides a special category called “low vision” in addition to the category of “blind,” and meets the stipulations of the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities.
- India has also accepted several United Nations resolutions on disabled people, including observing the International Year of Disabled Persons in 1981 and the UN Decade for the Disabled from 1983 to 1992.
- Additionally, India has observed the Asia-Pacific Decade for the Disabled declared by the Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP), a regional think-tank that provides analysis on social, economic, and environmental dynamics in the region.




