INDIAN POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. THE ONLINE GAMING MARKET IN INDIA, AND PROPOSED RULES TO REGULATE IT
THE CONTEXT: Recently, an inter-ministerial task force, set up by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) to propose contours of a national-level legislation to regulate online gaming, has proposed the creation of a central regulatory body for the sector, clearly defining what games of skill and chance are, and bringing online gaming under the purview of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002, among other things.
THE EXPLANATION:
The task force, set up by MeitY in May 2022, included the CEO of government think tank Niti Aayog, and secretaries of ministries including IT, Home, Finance, Information and Broadcasting, and Consumer Affairs, among others. The task force is understood to have prepared a final report of its recommendations and submitted it to the IT Ministry.
Why a central-level law?
- Online gaming so far has been a state subject, but state governments have said they find it extremely difficult to enforce certain rules like geo-blocking certain apps or websites within the territory of their state. Also, there is a concern that rules passed in one state are not applicable in another, which has caused inconsistency in how the online gaming industry is regulated in the country. State governments also do not have enough blocking powers like the Centre to issue blocking orders for offshore betting sites.
- Stakeholders have highlighted a number of societal concerns that can arise from the proliferation of online games in the country. There have been a number of reported incidents of people losing large sums of money on online games, leading to suicides in various parts of the country.
- Along with that, there is currently no regulatory framework to govern various aspects of online gaming companies such as having a grievance redressal mechanism, implementing player protection measures, protection of data and intellectual property rights, and prohibiting misleading advertisements.
- For online gaming businesses, the inconsistency has led to uncertainty. The thinking within the government is to have a nodal agency that will address all issues related to online gaming, including introducing a uniform law to determine what forms of online gaming are legally allowed.
How big is the online gaming market in India?
- The revenue of the Indian mobile gaming industry is expected to exceed $1.5 billion in 2022, and is estimated to reach $5 billion in 2025. The industry in the country grew at a CAGR of 38% between 2017-2020, as opposed to 8% in China and 10% in the US. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15% to reach Rs 153 billion in revenue by 2024. India’s percentage of new paying users (NPUs) in gaming has been the fastest growing in the world for two consecutive years, at 40% in 2020 and reaching 50% in 2021.
- According to a report by EY and FICCI, transaction-based games’ revenues grew 26% in India, with the number of paying gamers increasing by 17% from 80 million in 2020 to 95 million in 2021.
What are the recommendations of the task force?
- According to a source aware of the task force’s report, a central-level law for online gaming should apply to real money and free games of skill, including e-sports, online fantasy sports contests, and card games among others. Casual games with no real money element in the form of stakes may be kept outside the scope of such rules, unless they have a high number of users in India, or permit the publication or transmission of information in the nature of any inappropriate content like violence, nudity, addictive content or misleading content.
- It has also recommended creating a regulatory body for the online gaming industry, which will determine what qualifies as a game of skill or chance, and accordingly certify different gaming formats, seek compliance and enforcement.
- A three-tier dispute resolution mechanism, similar to that prescribed under the Information Technology Rules, 2021 for online streaming services, consisting of a grievance redressal system at the gaming platform level, self regulatory body of the industry, and an oversight committee led by the government should be put in place for online gaming.
- Any online gaming platform – domestic or foreign– offering real money online games to Indian users will need to be a legal entity incorporated under Indian law. These platforms will also be treated as ‘reporting entities’ under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002, and will be required to report suspicious transactions to the Financial Intelligence Unit-India.
Which ministry will be in charge of the regulation?
- The task force has suggested that MeitY may act as the nodal ministry to regulate online gaming, except for the e-sports category on which the Department of Sports can take the lead. The scope of the regulation by MeitY should only cover online gaming, that is, games of skill, and the issues of online betting and gambling being games of chance in nature should be excluded from its scope, the task force is learnt to have recommended.
- Certain other aspects of online gaming such as advertisements, code of ethics relating to content classifications etc. could be regulated by the Information and Broadcasting Ministry, while the Consumer Affairs Ministry can regulate the sector for unfair trade practices.
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2. BURKINA FASO MILITARY COUP
THE CONTEXT: The recent coup d’état resulted in the overthrowing of the Interim President Paul-Henri SandaogoDamiba and army Captain Ibrahim Traore taking over the government.
THE EXPLANATION:
- On September 30, 2022, the second coup took place in Burkina Faso this year, resulting dissolution of the traditional government and suspension of the constitution.
- The interim President Damiba was overthrown because of his alleged involvement in the African country’s
 Islamic insurgency.
Islamic insurgency. - Earlier this year, on January 24, Burkina Faso’s Army led by Damiba disposed President Roch Kabore, who held the office for more than 6 years. The coup came in response to several days of unrest in the country’s capital Ouagadougou.
- The civilian government was ousted for its inability to address deteriorating security situation and the inability to unite the country.
- Since 2015, Burkina Faso has been witnessing escalating violence mainly because of rebel fighters having close ties with extremist Islamic groups – al-Qaeda and the ISIL.
- The country has since become an epicentre for conflict in the Sahel, resulting in deaths of thousands of people and displacing 2 million others.
- The Damiba-led coup led to the suspension of Burkina Faso from Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS).
- After Damiba took over the government, there has been a 23 per cent increase in attacks from armed factions.
- The military government was able to control just 60 per cent of the country and the remaining territory was outside its control.
- The Damiba government was facing criticism because of its pro-France stance, amid the rising sentiments against the former colonizer.
- According to the UN, Burkina Faso is among the few West African nations facing “alarming levels” of hunger. It is currently witnessing the worst hunger crisis in 6 years, with over 630,000 individuals at the brink of starvation.
- Now, the military government led by Traore announced that a new interim leader (either civilian or military) will be appointed by the end of this year and it will honour the agreement with ECOWAS and oversee the return of civilian government by 2024.
DEFENCE AND SECURITY AFFAIRS
3. AATMANIRBHAR IN DEFENCE PRODUCTION
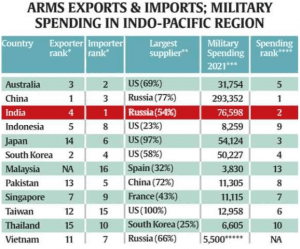
THE CONTEXT: According to a study released by the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), a widely respected independent resource on global security, India ranks fourth among 12 Indo-Pacific nations in self-reliant arms production capabilities
THE EXPLANATION:
- The study, which measures self-reliance until 2020, is based on three indicators of self reliance in each country:
- Arms procurement — imports, licensed and domestic production as a proportion of the government’s total procurement of major conventional arms.
- Arms industry — the study presents the five largest arms companies in each country, where data are available, ranked by sales of arms and military services in 2020 to both domestic and export customers;
- Uncrewed maritime vehicles, the sea equivalent of drones — covering both uncrewed surface vehicles (USVs) and uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs), meant to provide a qualitative understanding of how countries are engaging domestic research institutes and firms to produce such cutting edge systems.
- The study’s choice of maritime domain was because the Indo-Pacific region is a “maritime theatre”, and most of its flashpoints involve navies. The 12 countries in the study were selected because they have the highest military spending in the region — Australia, China, India, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Pakistan, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam.
- According to the study, understanding and determining the extent of self-reliance in the Indo-Pacific region, which has several ongoing flashpoints, is crucial for trust and confidence-building among states. This region has also seen a growing allocation by states for defence procurement. Eighteen arms manufacturing companies based in the region were ranked among the world’s largest arms companies in 2020.
- “[I]n a region where tensions among neighbours are rising, this report contributes to transparency with regards to levels of self-reliance in domestic arms production, allowing for an independent assessment of the region’s respective arms industries,” the study says.
- China was the world’s fifth largest arms importer in 2016-20. Its self-reliance policies, and its high economic growth in that period meant that the Chinese arms industry now increasingly fulfills the requirements of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA). Its high volume of imports in absolute terms accounts for only 8 per cent of total procurement for the period, the lowest share for any of the 12 governments studied in this report.
- China’s arms industry primarily involves nine large state-owned enterprises (SOEs). All eight companies for which data are available are in the top 100, with four in the top 10 in 2020. Four are dominant in the aerospace and aviation sectors, two in land systems, one in electronics, one in shipbuilding, and one in nuclear power.
- India is ranked as the second largest importer of arms for its armed forces in 2016-20. India is highly dependent on imports of complete foreign major arms, including many produced under licence or as components for its domestic production.
- Of India’s total volume of procurement in 2016–20, 84 per cent was of foreign origin. Domestic arms companies provide only 16 per cent of its total procurement. According to the study, the significant arms sales of local firms and the high level of licensed production push India to fourth position in the list.
- Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd, Indian Ordnance Factories, Bharat Electronics, Mazagaon Docks and Cochin Shipyard are among the major Indian arms servicing companies. Ashok Leyland, one of the largest suppliers of trucks to the Indian Army, is the only company ranked in the top 50 in the Indo-Pacific.
PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
4. SASTRA RAMANUJAN PRIZE FOR 2022
THE CONTEXT: The SASTRA Ramanujan Prize was recently bestowed to Yunqing Tang – an Assistant Professor at the University of California.
THE EXPLANATION
- The SASTRA Ramanujan Prize for 2022 was conferred to Yunqing Tang for her works in arithmetic and geometry of modular curves and Shimura varieties.
- Tang was recently involved in a joint research on modular equation in collaboration with Frank Calegari and Vesselin Dimitrov. This research is closely linked to Indian Mathematician Srinivasa Ramanujan’s work.
- Yunqing Tang is a Chinese-born Assistant Professor at the University of California, Berkeley.
- She completed her B.Sc in Peking University in 2011, after which she received her PhD in Harvard in 2016 under the guidance of Mark Kisin.
- SASTRA Ramanujan Prize will be conferred to Tang at the International Conference on Number Theory, which will be held from December 20 to 22 this year at SASTRA University
About SASTRA Ramanujan Prize
The prestigious award was instituted by the Shanmugha Arts, Science, Technology & Research Academy (SASTRA) in the year 2005. It includes a cash prize of 10,000 USD. The award recognizes individuals aging 32 and below who have made significant contributions in the field of mathematics that is broadly influenced by Srinivasa Ramanjuan. The first to receive this award was Manjul Bhargava and Kannan Soundararajan.
Who was Srinivasa Ramanujan?
- Srinivasa Ramanujan was an Indian mathematician who made major contributions to mathematics despite lacking formal training in the field. He made notable breakthroughs in mathematical analysis, infinite series, number theory and continued fractions. He solved mathematical problems that were previously thought to be unsolvable.
- Ramanujan was born on December 22, 1887 and passed away at the age of 32 on April 26, 1920. During his short life, Ramanujan compiled nearly 3,900 results, mostly identities and equations. Most notable of them are Ramanujan prime, the Ramanujan theta function, mock theta functions and partition formulae.
GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INTERVENTIONS
5. BHARAT SKILLS FORUM
THE CONTEXT: Bharat Skills Forum is a new feature of the Bharat skills learning platform.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The Bharat Skills Forum, which was added to the Bharat skills learning platform, enables sharing of books, videos, question banks, handwritten trainers’ and trainees’ notes, PDFs, scanned copies etc., in any language to interested learners.
- This new feature will act as a digital warehouse for skilling community by providing wide-range of digital content.
What is Bharat skills platform?
- Launched in 2019, the Bharat skills is an online training platform that provides skills concerning Industrial Training Institutes (ITI) ecosystems.
- It is the central digital repository for skills that provides easy access to digital study materials such as e-books, question banks, learning videos etc., as well as updated curriculum for courses provided under the Craft Instructor Training Scheme (CITS), Craftsmen Training Scheme (CTS) and Apprenticeship Training Scheme (ATS). It provides unique centralized, scalable and thriving assistance ecosystem with the help of industrial partners.
- Through this, students and teachers can learn skills related to Industrial Revolution 4.0 to meet the demands of the industry. Currently, the content in this platform is developed by the National Instructional Media Institute (NIMI) and Directorate General of Training (DGT).
About Directorate General of Training (DGT)
- The Directorate General of Training (DGT) comes under the aegis of the Union Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE). It is government agency involved in providing vocational training for Indian youth under the Skill India Programme – the flagship scheme of the Indian government.
- It has a network of around 15,000 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs), National Skills Training Institutes, National Skills Training Institutes for Women and other central training institutes. These institutes provide training to over 24 lakh students each year, catering to the industrial demands on skilled workforce.
- They play an important role in providing skilled manpower for various sectors of the Indian economy.
MISCELLANEOUS
6. THE NOBEL PEACE PRIZE WINNERS FOR 2022
THE CONTEXT: The Nobel Peace Prize for 2022 has been awarded to human rights advocate Ales Bialiatski from Belarus, the Russian human rights organisation Memorial, and the Ukrainian human rights organisation Center for Civil Liberties, the Norwegian Nobel Committee announced.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The laureates represent civil society in their home countries, said the committee, “They have for many years
 promoted the right to criticise power and protect the fundamental rights of citizens. They have made an outstanding effort to document war crimes, human right abuses and the abuse of power. Together they demonstrate the significance of civil society for peace and democracy”.
promoted the right to criticise power and protect the fundamental rights of citizens. They have made an outstanding effort to document war crimes, human right abuses and the abuse of power. Together they demonstrate the significance of civil society for peace and democracy”. - With the awardees being from Belarus, Ukraine, and Russia, an implicit message has been sent about the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine. “The Norwegian Nobel Committee wishes to honour three outstanding champions of human rights, democracy and peaceful co-existence in the neighbour countries Belarus, Russia and Ukraine”,
- The three prize winners: Belarus’s Ales Bialiatski
- According to the website, “Ales Bialiatski was one of the initiators of the democracy movement that emerged in Belarus in the mid-1980s.” Before 1991, when the former Soviet Union fell and independent countries emerged, many countries in Central Asia and Europe saw pro-independence movements. Belarus President Alexander Lukashenko has been in power since 1994 – when the post first came into being.
- Bialiatski is also credited with founding the organisation Viasna (Spring) in 1996 in response to the controversial constitutional amendments that gave the president dictatorial powers. Over time, Viasna evolved into a “broad-based human rights organisation that documented and protested against the authorities’ use of torture against political prisoners”.
- Having been imprisoned earlier for three years, he was arrested most recently after the large-scale demonstrations against the regime in 2020 and is still detained without trial. In 2020, he was one of the three recipients of the Right Livelihood Award by the Swedish Right Livelihood Foundation, sometimes referred to as the “Alternative Nobel”.
Russian human rights organisation, Memorial
The committee said the organisation was established in 1987, “by human rights activists in the former Soviet Union who wanted to ensure that the victims of the communist regime’s oppression would never be forgotten.” Nobel Peace Prize laureate Andrei Sakharov, who won the prize in 1954, and human rights advocate Svetlana Gannushkina were among the organisation’s founders. “Memorial is based on the notion that confronting past crimes is essential in preventing new ones”.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION OF THE DAY
Q1. There has been a recent proposal to establish International Dark Sky Reserve in India. In which of the following state/U.T is it proposed to be located?
a) Maharashtra
b) Pondicherry
c) Chandigarh
d) Ladakh
Answer: D
Explanation:
- Ladakh government along with the IIA (Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru) and India’s Scientific Ministries is laying the groundwork to have Hanle declared as an International Dark Sky Reserve by the International Dark-Sky Association (IDSA).
- A Dark Sky Reserve is public or private land with a distinguished nocturnal environment and starry nights that has been developed responsibly to prevent light pollution.
- Since 1988, the U.S.-based nonprofit IDSA has been advocating the cause of minimizing light pollution and certifies places where night skies are least polluted as International Dark Sky Reserves or sanctuaries. Between 2001 and January 2022, there have been 195 sites recognised as International Dark Sky Places globally, the IDSA said.
- The IIA already manages the Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) complex at Hanle, Ladakh.
- Here, scientists have been carrying out astronomical observations using the existing gamma ray, an infrared and an optical telescope to study exoplanets, galaxies and stars through the pristine skies of Hanle.

 promoted the right to criticise power and protect the fundamental rights of citizens. They have made an outstanding effort to document war crimes, human right abuses and the abuse of power. Together they demonstrate the significance of civil society for peace and democracy”.
promoted the right to criticise power and protect the fundamental rights of citizens. They have made an outstanding effort to document war crimes, human right abuses and the abuse of power. Together they demonstrate the significance of civil society for peace and democracy”.


