THE INDIAN POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. ASSAM RECORDS MOST VIOLENT CRIMES: NCRB
THE CONTEXT: For the fifth consecutive year, Assam recorded the highest rate of crimes against women in 2021, according to the National Crime Record Bureau’s “Crime in India” report for last year.
THE EXPLANATION:
REPORT HIGHLIGHTS:
- The statistics also showed that Assam has maintained the trend of recording an increase in such crimes after a dip in the previous year.
- “But the crime rate of 76.6 cases per one lakh population – a little more than the 73.7 cases in 2020 – does not give the complete picture,” Assam police officers said.
- They attributed the figure to the high reporting and registration of cases, especially in crimes against women.
- The report places UP on top (56,083) in terms of actual number of cases registered in 2021, although the rate is lesser at 50.5 per cent. The other states that recorded the highest number of crimes against women include Rajasthan, Maharashtra, West Bengal and Odisha.
- Nagaland stood out with the lowest number of crimes against women registered in the past three years — 43 in 2019, 39 in 2020 and 54 in 2021. It also had the lowest crime rate against women for 2021 at 5.5 per cent.
- Among Union Territories, Delhi had the highest rate of crime against women in 2021 at 147.6 per cent. It also topped in absolute numbers of cases registered, recording an increase over the past three years from 13,395 in 2019 to 14,277 in 2021.
- The NCRB also collates data for crime against women in 19 cities across the country with a population of over 2 million.
- Among these cities, the 2021 data shows that Jaipur had the highest rate at over 194 per cent, followed by Delhi, Indore and Lucknow. Chennai and Coimbatore — both in Tamil Nadu — had the lowest rate.
- Cases of “murder with gangrape/rape”, for which the NCRB has maintained records since 2017, have remained steady — 284 cases in 2021, the same as in 2019. In 2020, there were 218 such incidents. The highest number of cases under the category were registered in 2018 with 291.
- The highest number of such cases took place last year in UP with 48, followed closely by Assam with 46. Bihar, Arunachal Pradesh, Goa, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland and Uttarakhand did not register any cases under this category last year.
- According to NCRB data, rape-murders make up less than 1 per cent of the total rapes in the country annually. In these cases, the NCRB data between 2017-2021 shows that UP, Assam, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra had the highest number of cases in the country annually for rape-murders for the period of 2017-2020.
- Over 28,000 women were abducted last year to be “compelled into marriage’’, including 12,000 minors, with the highest number recorded in UP (8,599) followed by Bihar (6,589), the NCRB report shows.
- Only 507 cases were registered in the country under the Domestic Violence Act in 2021 — 0.1 per cent of the total cases of crime against women. The highest number of cases (270) were filed in Kerala. Meanwhile, 6,589 cases of dowry deaths were registered last year with the highest number of such deaths registered in UP and Bihar.
VALUE ADDITION:
About NCRB:
- In 1986 (based on recommendations of the Tandon Committee, MHA Taskforce and National Police Commission (1977))
- It acts under the Ministry of Home Affairs and functions as a repository of information on crime and criminals so as to assist the investigators in linking crime to the perpetrators.
- NCRB looks after CCTNS (Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems) and Central Finger Print Bureau
- It released reports: Crimes in India, Prison Statistics in India and Accidental Deaths and Suicides in India.
2. JOURNALISTS, ACTIVISTS CONTINUE TO BE TARGETED IN J&K: AMNESTY
THE CONTEXT: Recently, Amnesty International said it had recorded at least 60 instances of crackdowns on journalists and human rights defenders in Jammu and Kashmir since the revocation of special status of the erstwhile State in August 2019.
THE EXPLANATION:
- In a report titled, We are being punished by the law: Three years since of abrogation of Article 370 in Jammu & Kashmir, Amnesty documented interrogations, travel bans and detentions of journalists and human rights defenders.
- “For three years now, civil society and media in Jammu and Kashmir have been subjected to a vicious crackdown by the Indian government, which is determined to stifle dissent using draconian laws, policies and unlawful practices in their arsenal,” said Aakar Patel, the chair of the board of Amnesty International India.
- Amnesty said it had found that at least six persons, including journalists, human rights activists and academics, had been prevented from travelling abroad despite having the requisite documents. At least 27 journalists had been detained and arrested since August 5, 2019.
- “Journalists including Fahad Shah, Aasif Sultan and Sajad Gul have been subjected to ‘revolving door’ arrests. In a continuing pattern, they have been arrested under one law, granted bail by the court, and then re-arrested almost immediately under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) – India’s primary anti-terror law in Jammu & Kashmir, keeping them perpetually detained”.
- The report reviewed 1,346 cases on the website of the Jammu and Kashmir High Court and found that by August 1, 2022, the number of writ petitions had increased by 32%, which it said indicated an increase in unlawful detention. “Amnesty International also reviewed the data published by National Crime Record Bureau and found that there has been a 12% increase in the use of UAPA in Jammu & Kashmir since 2019”.
VALUE ADDITION:
About the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act:
- Passed in 1967, the law aims at effective prevention of unlawful activities associations in India.
- The Act assigns absolute power to the central government, by way of which if the Centre deems an activity as unlawful then it may, by way of an Official Gazette, declare it so.
- It has death penalty and life imprisonment as highest punishments.
- Under UAPA, both Indian and foreign nationals can be charged.
- It will be applicable to the offenders in the same manner, even if crime is committed on a foreign land, outside India.
- Under the UAPA, the investigating agency can file a charge sheet in maximum 180 days after the arrests and the duration can be extended further after intimating the court.
As per amendments of 2019:
- The Act empowers the Director General of National Investigation Agency (NIA) to grant approval of seizure or attachment of property when the case is investigated by the said agency.
- The Act empowers the officers of the NIA, of the rank of Inspector or above, to investigate cases of terrorism in addition to those conducted by the DSP or ACP or above rank officer in the state.
- It also included the provision of designating an individual as a terrorist.
THE INDIAN AGRICULTURE
3. PADDY CULTIVATION SEES DECLINE
THE CONTEXT: According to the data released by the Union Agriculture Ministry, there is a decrease in the area of paddy cultivation is 22.90 lakh hectares, 5.62% less than the area covered in 2021.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The trend of decrease in paddy sowing has continued even as the monsoon season in north India is in its last legs.
- As of now, paddy has been cultivated in 383.99 lakh hectares of area and in the corresponding period of last year, it was 406.89 lakh hectares.
- States such as Jharkhand (decrease of 9.80 lakh hectares), Madhya Pradesh (6.32 lakh hectares), West Bengal (4.45 lakh hectares), Chhattisgarh (3.91 lakh hectares), Uttar Pradesh (2.61 lakh hectares) and Bihar (2.18 lakh hectares) are the major contributors for the decrease in the cultivated area of paddy in this kharif season.
- Meanwhile, States such as Telangana (increase of 4.71 lakh hectares), Haryana (0.94 lakh hectares), Nagaland (0.78 lakh hectares) and Gujarat (0.55 lakh hectares) showed an increase in the area of cultivation of paddy.
- Farmers’ organisations have been maintaining that the higher input cost, particularly the increase in prices of fertilizers, is the main reason for the decrease in paddy cultivation apart from scarcity of water. The government is hopeful about a normal monsoon this year.
Cultivation of pulses
- The coverage of pulses too witnessed a marginal decrease. In this kharif season, the cultivation so far is in 129.55 lakh hectares compared to 135.46 lakh hectares in 2021. Increase in area in cultivation is reported from States such as Madhya Pradesh (4.08 lakh hectares), Uttar Pradesh (0.22 lakh hectares) and Assam (0.11 lakh hectares) while Maharashtra (decrease of 3.23 lakh hectares), Telangana (1.70 lakh hectares), Jharkhand (1.33 lakh hectares) and Karnataka (0.94 lakh hectares).
- Tur/arhar cultivation was down marginally at 44.86 lakh hectares as against 47.56 lakh hectares in 2021.
- Oilseeds have been cultivated in 188.51 lakh hectares in the country, slightly less than 189.66 lakh hectares of 2021. In the case of sugarcane, the cultivation is 55.65 lakh hectares, a slight increase in the production as compared to 54.70 lakh hectares in 2021 kharif.
THE SECURITY AFFAIRS
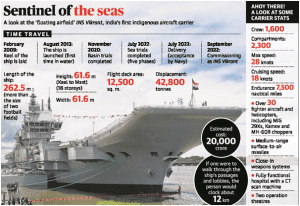
4. VIKRANT IS A REFLECTION OF SELF-RELIANT INDIA, SAYS PRIME MINISTER
THE CONTEXT: The nation’s first Indigenous Aircraft Carrier (IAC-1) is set to be commissioned soon in the presence of Prime Minister of India.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is the aircraft carrier INS Vikrant?
- The INS Vikrant – the 44,000-tonne indigenous aircraft carrier (IAC) – is the first to be designed and constructed in India.
- After its induction, the warship will be a key component of the Indian Navy’s push to establish itself as a “blue water” force, one with the ability to project its power on distant seas.
Features:
- The Vikrant stretches 262 metres in length, exceeding that of two football fields and is 62 metre wide. Around 20 aircraft can be parked in the hangar.
- It has a top speed of around 28 knots (more than 50 kmph) and a cruising speed of 18 knots with an endurance of about 7,500 nautical miles.
- Over 76 per cent of the material and equipment on board the carrier is indigenous, including 21,500 tonnes of special grade steel developed indigenously and used in Indian naval ships for the first time.
- This is the first time in the country that a ship of the size of an aircraft carrier is completely modelled in 3D and production drawings extracted from the 3D model.
- The Made-in-India warship is a feather in the country’s cap, as only five or six nations have the capacity of building an aircraft carrier.
It will be carrying:
- the Russian-made MiG-29K fighter jet,
- Kamov-31 early warning helicopters,
- the indigenously manufactured Advanced Light Helicopters and
- the MH-60R multirole helicopter made by the American defence major Lockheed Martin.
Why is it named Vikrant?
- INS Vikrant was India’s first aircraft carrier, which it acquired from the United Kingdom in 1961.
- It played a key role in the 1971 war with Pakistan which led to the creation of Bangladesh. It was decommissioned in 1997.
- Now India’s first homemade aircraft carrier will carry the name of her illustrious predecessor.
Other aircraft carriers:
- The Indian Navy has only one operational aircraft carrier at present – the INS Vikramaditya.
- The country’s two earlier carriers, INS Vikrant and INS Viraat, were originally the British-built HMS Hercules and HMS Hermes before being commissioned into the Navy in 1961 and 1987 respectively.
The commissioning of the warship, which will be christened ‘Vikrant’, will mark a “historical milestone of realisation of Nation’s commitment towards AatmaNirbharta” (self-reliance).
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES IN NEWS
5. MEGHALAYA: RURAL BACKYARD PIGGERY SCHEME
THE CONTEXT: Recently, Meghalaya Chief Minister launched an ambitious flagship program – “Rural Backyard Piggery Scheme” for farmers under National Livestock Mission at Byrnihat in Ri-Bhoi district of Meghalaya.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The objective of this scheme is to ensure that farmers earn a sustainable livelihood through various animal husbandry activities.
- Meghalaya receives 18,000 metric tonnes of pork from various states and there is acute shortage in supply and demand, the state is planning to bridge the supply shortfall through pig farming scheme.
- Under the Phase 1 of this scheme the government has earmarked Rs 15.18 crore, under which four high yielding improved varieties of pigs will be distributed to 6000 families and an additional Rs 25 crore will be earmarked for starting the second phase of the programme.
Meghalaya Piggery Mission
- The scheme launched on 10th August in Samanda block of East Garo Hills district has received good response and appreciation from the farmers.
- Under this scheme 4 pigs, 3 female and 1 male piglets will be distributed to the farmers to promote pig breeding to provide regular income to the farmers. This livestock package is Rs 25,000 per beneficiary.
- The scheme is envisaged to benefit 6000 poor and marginal farmers and increase the production of pork in the state.
National Livestock Mission
- National Livestock Mission is an initiative of the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare launched in 2014-15. The objective of this mission is to ensure quantitative and qualitative improvement in livestock production systems and capacity building of all stakeholders of livestock economy.
6. RAJASTHAN HANDICRAFTS POLICY-2022
THE CONTEXT: The Rajasthan cabinet has recently approved the “Rajasthan Handicrafts Policy-2022”. Through this policy, work will be done for the upliftment of handicrafts in the state and participation in the development of the state will be ensured by empowering them.
THE EXPLANATION:
- With this policy, new employment opportunities will increase in the state. Along with this, the extinct handicrafts will be revived.
- Under this, a national level handicrafts week will be organized every year in December, in which handicrafts men will be rewarded.
- At the same time, e-marketing, social security, loan facility, scholarship, assistance for participation in fairs, expansion of infrastructure facilities in Shilp Gram, Handicraft Park, Museum, Design Center, Sales Center for brand building of handicrafts.
- There will be many important works like support, design bank establishment. The government will also create an online platform to help artisans sell their products.
- Provision will be made by government departments to buy products up to Rs 10 lakh from registered artisans through e-market without tender.
- A Handicraft Design Center will also be set up in Jodhpur to study the techniques and designs used in other states and countries so as to promote new techniques or processes for the products in the state. This center will be set up as a ‘Centre of Excellence’.
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
7. VOSTOK MILITARY EXERCISE
THE CONTEXT: Recently, a contingent of soldiers from 7/8 Gorkha Rifles of the Indian Army arrived in Russia to participate in the multilateral tactical and command exercise Vostok – 2022 to be held from 1-7 September 2022.
THE EXPLANATION:
Important Facts about Vostok 2022
- In this exercise more than 50 thousand soldiers from India, China, Laos, Mongolia, Nicaragua, Syria and former Soviet countries will participate.
- The seven-day exercise comprises land, air and sea components. However, India has decided to stay away from the maritime component.
- There will be joint exercises of both attack and defense during this exercise. More than five thousand types of weapons will be used in this exercise. It will have 140 fighter aircraft, 60 warships, gunboats and allied ships.
- The one-week-long exercise has been organized under the auspices of Russia’s Eastern Military District (Theater Command) and Pacific-Fleet in Vladivostok.
- Vladivostok is located in the far east of Russia on the Sea of Japan. In such a situation, Japan has expressed its opposition to this military exercise.
- At the same time, America has also expressed its concern about each country participating in this military exercise, because Russia is fighting a barbaric war in Ukraine. The US has said that any country’s military exercises with Russia are a matter of concern.




