THE HEALTH ISSUES
1. INDIA’S FIRST INDIGENOUSLY DEVELOPED QHPV AGAINST CERVICAL CANCER
THE CONTEXT: Recently Serum Institute of India (SII) and Department of Biotechnology (DBT) launched indigenously developed quadrivalent Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) vaccine for prevention of cervical cancer.
THE EXPLANATION:
• The Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) last month granted market authorization to Serum Institute of India (SII) for the production of this indigenously developed vaccine against cervical cancer.
• It will be the first Quadrivalent Human Papillomavirus vaccine (qHPV) in India, to prevent cervical cancer.
• After the launch of this vaccine, the government will soon run a national immunization program for girls in the age group of 9-14 years.
• In 85 percent to 90 percent of cervical cancer cases, it has been seen that the cancer used to grow in the absence of a vaccine, but now it will not happen. If we give this vaccine to young children and daughters in advance, then they will be safe from infection and it is possible that they may not get cervical cancer after 30 years.
Cervical cancer in India
Cervical cancer is the second most common cancers among women in India, even though it is preventable. This cancer is commonly diagnosed among women aged 15 to 44 years of age. According to Globocan 2020, cervical cancer stood at 9.4% of all cancers and 18.3% of new cancer cases in 2020. During 1990-2016, cervical cancer was the second main factor of cancer deaths for women across 12 Indian states.
National Cancer Control Programme (NCCP)
National Cancer Control Programme was first started in India in 1975. Under the programme, priorities were given to equip existing cancer hospital and institutions. Central assistance of Rs 2.50 lakhs was provided to each cancer institution, in a bid to purchase cobalt machines for radiotherapy.
VALUE ADDITION:
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) :
Types: HPV is a type of virus, of which there are more than 100 types.
Transmission: More than 40 types of HPV are spread through direct sexual contact.
Symptoms:
• Most people do not develop any symptoms.
• The virus can sometimes take years before it causes any symptoms.
Impacts:
• Out of these 40, two cause genital warts, while about a dozen of HPV cause different types of cancer including cervical, anal, oropharyngeal, penile, vulvar and vaginal.
• India is home to 16-17 percent of the world’s population, globally 27 per cent of total cervical cancer cases are from here.
• In India, about 77 percent cases of cervical cancer are caused by HPV 16 and 18.
HPV Vaccines:
• Quadrivalent vaccine (Gardasil) – Protects against four types of HPV (HPV 16, 18, 6 and 11).
• Bivalent vaccine (Cervarix)- Protects against HPV 16 and 18 only.
• Non valent vaccine (Gardasil 9) – Protects against nine strains of HPV.
HPV vaccination in India:
• In India, bivalent and quadrivalent HPV vaccines were licensed in 2008 and a non valent vaccine was licensed in 2018.
• HPV vaccines are given as a two-dose regimen, six months apart for girls below the age of 14 years.
• For those who are 15 and older, the vaccine is given in a three-dose regimen.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2. INDIA-NEPAL MOU ON BIODIVERSITY CONSERVATION
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Union Cabinet has approved a Memorandum of Understanding with the Government of Nepal on Biodiversity Conservation proposed by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
THE EXPLANATION:
• This MoU has been signed to strengthen and enhance coordination and cooperation between the two countries in the fields of forestry, biodiversity conservation and climate change.
• It will also help in restoration of corridors and connecting regions and sharing of knowledge and best practices between the two countries.
• The shared Indo-Nepal border of over 1,850 km touches five Indian states – Sikkim, West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand. India and Nepal are already cooperating on a number of wildlife-related issues, but this will strengthen bilateral cooperation and strengthen the management of important cross-border wildlife habitats.
The joint border of India and Nepal includes many border wildlife habitats. For example, the Valmiki Tiger Reserve in Bihar connects to the Chitwan National Park and Parsa Wildlife Sanctuary in Nepal. Similarly, Dudhwa Tiger Reserve in Uttar Pradesh shares its boundary with Shukla Phanta National Park in Nepal. Thus, this MoU is expected to have a significant focus on the management of the marginal landscape.
VALUE ADDITION:
Kunming Biodiversity fund
The funding issue for the Kunming Biodiversity Fund will be taken up in January 2022 at negotiations in Geneva. China’s pledge is below the $4 billion committed by Britain for conservation projects across the world as well as France’s commitment to spend 30 percent of its climate finance on protection of biodiversity.
UN Convention on Biological Diversity
This convention has been ratified by 195 countries and the European Union. However, United States is not ratified it even though it has been world’s biggest polluter historically.
3. SPIKE IN HAND, FOOT, AND MOUTH DISEASE
THE CONTEXT: Recently there has been a spike in cases of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) in Mumbai. As per data provided by the state’s public health department, till August 28, Maharashtra has reported 250 cases of hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Of the total cases reported in the state, all but one were from Mumbai circle.
THE EXPLANATION:
What is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease, and how does it spread?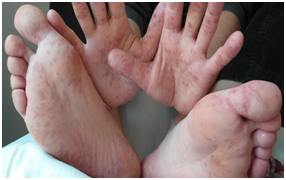
• Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease is common in children under the age of 5, but anyone can get it. It is most commonly caused by a coxsackievirus, which belongs to a group of viruses called nonpolio enteroviruses. The illness is usually not serious, but is very contagious. It spreads quickly at schools and daycare centers.
Are children with HFMD requiring hospitalisation?
• A majority of children have recovered at home and rarely require hospitalisation. As it is a self-limited illness, the symptoms last up to 7-10 days and fade away.
• However, doctors also cautioned to keep a close eye on children with weak immunity or who haven’t improved even after 10 days. “Some children may develop complications due to dehydration because of poor oral intake. Also, they may develop viral meningitis, encephalitis, paralysis and loss of nails”.
• The child may need admission only if there is a severely reduced oral intake or persistent high fever.
What are symptoms, treatment for Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
• Patients usually develop fever, sore throat, painful blister-like lesions on the tongue, gums and inside of the cheeks. “The children may develop ulcers inside their mouths. Also, rashes are noticed on the palms, soles and sometimes the buttocks”.
• Children are mostly treated with anti-allergic medicines and ointments. The lesions usually disappear in five to six days. “Drink enough liquids. Mouth sores can make it painful to swallow, so your child may not want to drink much. Make sure they drink enough to stay hydrated,” stated the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Reye’s syndrome
In Reye’s syndrome, a child’s blood sugar level typically drops while the levels of ammonia and acidity in his or her blood rise. At the same time, the liver may swell and develop fatty deposits. Swelling may also occur in the brain, which can cause seizures, convulsions or loss of consciousness
THE ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
4. EXPLAINED: WHAT IS ‘ZOMBIE ICE’, HOW IT THREATENS TO RAISE GLOBAL SEA LEVELS BY OVER 10 INCHES
THE CONTEXT: According to a study published in the journal Nature Climate Change where scientists for the first time calculated minimum ice loss in Greenland, and the corresponding rise in global sea level.
THE EXPLANATION:
The melting of the Greenland ice sheet will unavoidably raise the global sea levels by at least 10.6 inches or 27 centimetres, no matter what climate action the world decides to take right now. This is because of ‘zombie ice’, which is certain to melt away from the ice cap and blend into the ocean.
What is ‘zombie ice’?
• Also referred to as dead or doomed ice, zombie ice is one that is not accumulating fresh snow even while continuing to be part of the parent ice sheet. Such ice is “committed” to melting away and increasing sea levels.
• Experts noted that “This ice has been consigned to the ocean, regardless of what climate scenario we take now….more like a foot in the grave”.
What has led to this?
According to researchers, this is on account of warming that has already happened. The research points to an equilibrium state where snowfall from the higher reaches of the Greenland ice cap flows down to recharge edges of the glaciers, and thicken them. It says that over the last several decades there has been more melting and less replenishment.
What happens next, and by when?
• By calculating minimum committed ice loss based on the ratio of recharge to loss, the scientists have projected that 3.3% of Greenland’s total ice volume will melt, and this will happen even if the global temperature is stabilized at the current level. But given that global warming is predicted to get worse, the melting and the corresponding rise in sea level could be much worse. The study says it could reach as much as 30 inches (78 centimetres) if Greenland’s record melt year (2012) becomes a routine phenomenon.
• However, the research team has not given a timeline. All that it mentions is that this committed melting is likely “within this century”.
• But while some have questioned the timeframe being left out as an unknown, others have said the study gives a solid conservative estimate of what is likely to happen.
What does a 10-inch rise in sea-level mean?
• The inevitable sea-level rise that the study predicts is particularly a bad news for millions that live in coastal zones. According to the UN Atlas of the Oceans, 8 of the world’s 10 largest cities are near a coast. Rising sea levels will make flooding, high tides and storms more frequent and worse as their impact will reach more inland. This, in turn, means a threat to local economies and infrastructure. Also, low lying coastal areas will take a harder hit.
• The World Economic Forum’s 2019 Global Risks Report noted that “already an estimated 800 million people in more than 570 coastal cities are vulnerable to a sea-level rise of 0.5 metres by 2050”.
THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
5. NSO DATA ON INDIA’S GDP RATE IN Q1
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation released the estimates of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at constant (2022-23) and current prices for the first quarter (April-June) of 2022-23.
THE EXPLANATION:
• In the first quarter (April-June) of the current financial year, the country’s economy has registered a growth of 13.5 percent. However, this growth has been around 3 per cent lower than the estimate expressed by the RBI earlier this month.
• The GDP growth rate in the April-June quarter of the last financial year (2021-22) was 20.1 per cent.
• At the same time, real GDP at constant prices (2011-12) is estimated at Rs 36.85 lakh crore in the first quarter of 2022-23. It was Rs 32.46 lakh crore in the same quarter last year.
• Gross Value Added (GVA) refers to the total value of goods and services in a country’s territory over a given period of time.Gross value added (GVA) grew 12 per cent to Rs 34.41 lakh crore in the April-June quarter this year.
• The growth rate of GVA in the agriculture sector stood at 4.5 per cent in Q1 as against 2.2 per cent in the same quarter a year ago. However, the growth rate of GVA in the manufacturing sector declined to 4.8 per cent from 49 per cent in the same quarter a year ago.
• According to the data, GVA growth in the mining sector stood at 6.5 per cent from 18 per cent in the April-June quarter of 2021-22 a year ago. The growth rate of GVA in the construction sector declined to 16.8 per cent in the quarter ended June 2022 from 71.3 per cent in the same quarter a year ago.
• On the other hand, in services sectors such as trade, hotels, transport, communication and broadcasting, it has a GVA growth rate of 25.7 per cent in the first quarter of the current fiscal.
• Eight infrastructure sectors which include coal, crude oil, natural gas, refinery products, fertilisers, steel, cement and electricity. In this, the production growth rate in April-July in the current financial year was 11.5 percent, which was 21.4 percent a year ago.
National Statistical Office (NSO)
• NSO as an agency that was formed on the recommendation of the Rangarajan Commission. The office was set up to implement and maintain the statistical standards and coordinate the statistical activities of Central and State agencies in accordance with the National Statistical Commission (NSC).
• The Rangarajan Commission had also recommended to set up the NSC. NSC is headed by a person having a “Minister of State-Level designation”. NSC will serve as a nodal body for all core statistical activities in India. NSO was formed after merging the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) and Central Statistics Office (CSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES IN NEWS
6. RASHTRIYA POSHAN MAAH 2022
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Women and Child Development is celebrating 5th Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2022 from 1st to 30th September 2022. This year, with the main focus on “Mahila aur Swasthya” and “Bacha aur Shiksha”,PoshanMaah is to be started as Poshan Panchayat through Gram Panchayats.
THE EXPLANATION:
• Pregnant and lactating women, children below six years of age and adolescent girls will be given special attention in this month-long Poshan Maah. Along with this, they will be made aware about the importance of nutrition through sensitization campaigns, outreach programs, and camps.
• Awareness activities will be conducted at the Panchayat level by the concerned District Panchayati Raj Officers, CDPOs, local officials.
• This time a national level toy manufacturing workshop will also be organized to promote the use of indigenous and local toys for teaching children in Anganwadi centers.
• Under this program, the importance of rainwater harvesting will be emphasized among women at Anganwadi centers as well as information related to traditional food items for healthy mother and child in tribal areas will be provided.
• Under the state level activities, ‘Amma ki Rasoi’ of traditional nutritious dishes will also be operated. Also, extensive efforts will be made to integrate traditional foods with local festivals during Poshan Maah.
About POSHAN Abhiyaan
POSHAN Abhiyaan is the flagship programme of government of India to improve nutritional outcomes for pregnant women, lactating mother, children and adolescent Girls. This mission was launched by Prime Minister on the occasion of International Women’s Day on March 8, 2018. POSHAN stands for “Prime Minister’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nutrition” Abhiyaan. This mission was announced in Budget 2021-2022.
Aim of the Mission
POSHAN Abhiyaan divert the attention of country towards the problem of malnutrition and address it in a mission-mode. This mission focuses on the aims of POSHAN Abhiyaan, Mission Poshan 2.0. it seeks to strengthen nutritional content, delivery, outreach and outcomes in order to develop practices that nurture health, wellness and immunity on disease as well as malnutrition.
Jan Andolan
POSHAN Abhiyaan is a Jan Andolan or People’s Movement. It incorporates inclusive participation of public representatives of local bodies, government department from States or UTs, Public & Private sector and social organizations.
THE DATA POINT