Table of Contents
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. INDIA-BANGLADESH MOU ON KUSHIYARA RIVER
THE CONTEXT: During the 38th Ministerial Meeting of the India-Bangladesh Joint Rivers Commission, the two countries finalized a draft of a Memorandum of Understanding to share the waters of the Kushiyara River on an interim basis.
THE EXPLANATION:
• In this meeting, the two countries discussed many issues of mutual interest, including river water sharing of rivers, sharing of flood data, focus on river pollution, joint study on sedimentation management, river bank protection between the two countries. tasks etc.
• All aspects of issues related to Ganga, Teesta, Manu, Muhuri, Khowai, Gumti, Dharla, Dudhkumar etc. other rivers were also discussed during this meeting.
• Meanwhile, both sides welcomed the finalization of the design of Feni River Water Harvesting Site and its technical infrastructure to meet the drinking water requirements of Sabroom Town, Tripura. It is noteworthy that in this regard, an MoU came into existence between the two countries in October 2019.
VALUE ADDITION:
Kushiyara River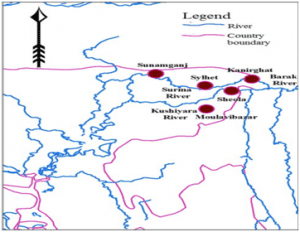
The Kushiyara River forms the Indo-Bangladesh border as a branch of the Barak River when it separates from the Surma, another branch of the Barak. After flowing some distance in Bangladesh, it meets again with Surma river and this combined river is now called Meghna river.
Manipur, Mizoram and Assam receive water through this river in India.
India and Bangladesh water sharing
• India and Bangladesh share 54 between them. All the rivers of Bangladesh either have their source in India or pass through it.
• The Ganges, the major river system in India, flows through Bangladesh into the Bay of Bengal. About 35 million people in about one third of Bangladesh’s area are directly dependent on the Ganges.
Joint River Commission
• The Joint River Commission between India and Bangladesh was formed in the year 1972 under the peace treaty, through which issues of mutual interest on the border, border rivers can be resolved.
• The JRC is headed by the Ministers of Water Resources of both the countries.
• Under this commission, meetings are organized to get mutual benefit from the rivers located between the two countries and to discuss river related issues from time to time.
THE HEALTH ISSUES
2. 75 TRIBAL DISTRICTS IDENTIFIED FOR TB INTERVENTIONS
THE CONTEXT: Recently 75 high burden tribal districts have been selected by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and the Central TB Division of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to become TB free in the coming months.
THE EXPLANATION:
For 75 such districts, a three-pronged strategy is presented, focusing on the following:
1. Generate demand for TB services through community mobilization, increasing awareness of TB symptoms, prevalence and treatment procedures, and continuing engagement with community influencers involved in the process of reducing stigma and fear associated with TB.
2. To improve the delivery of TB services by provision of customized solutions by leveraging PIPs and other sources of funding to bridge the implementation gap by increasing the infrastructure of TB testing or testing and diagnosis.
3. Reducing the risk and spread of disease through proactive case-detection campaigns.
Tribal TB Initiative
• The ‘Tribal TB Initiative’ is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and the Central TB Division of the Ministry of Health, supported by USAID as the technical partner and by Piramal Health as the implementation partner.
• Under this initiative, Aashwasan Campaign was launched from Nandurbar district of Maharashtra to detect active cases of TB in 174 tribal districts of India.
Aashwasan Campaign
• The campaign has brought together around 2 lakh community influencers, who participated with full dedication to make this campaign a success. These include tribal leaders, tribal doctors, PRI members, self-help groups (SHGs) and youth from tribal areas.
• Under this, door-to-door TB screening was done in 68,019 villages. Based on oral examination of 1,03,07,200 persons, 3,82,811 persons were identified as having TB.
• Of these, 2,79,329 (73 per cent) samples were tested for TB and 9,971 people tested positive for TB were treated as per the protocol of the Government of India.
End TB strategy
India is committed to eliminate tuberculosis from the country by 2025, five years ahead of the World Health Organization’s (WHO) global target i.e. 2030.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN NEWS
3. 8 YEARS OF PM JAN DHAN YOJANA
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the central government’s ambitious scheme Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana has completed eight years. The main objective of this scheme was to include the poor section of the country in the main banking system.
THE EXPLANATION:
Under this scheme more than 46 crore bank accounts have been opened in 8 years. It has deposits of Rs 1.74 lakh crore. With the help of this scheme, 67 percent of the rural population of the country has now got banking services and 56 percent of women also have Jan Dhan accounts.
Key Features of the Scheme
The schemes would provide the connectivity to the individuals through banking facilities. Several key features of the scheme include:
• Interest on deposit
• Accidental insurance cover of Rupee One Lakh.
• No minimum balance required
• Life insurance cover of Rs.30,000/-
• Easy Transfer of money across India
Further, the beneficiaries of Government Schemes would get Direct Benefit Transfer in these accounts; After satisfactory operation of the account for 6 months, an overdraft facility will be permitted; Access to Pension, insurance products.; Accidental Insurance Cover, RuPay Debit Card must be used at least once in 45 days; Overdraft facility uptoRs.5000/- is available in only one account per household, preferably lady of the household.
With the help of this scheme, the financial help sent by the central government to the poor during the covid-19 pandemic was directly transferred to their bank accounts. This made it possible for the financial assistance given under other schemes including Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi to reach the beneficiaries directly.
Challenges to Jan Dhan Scheme
• Usage of bank accounts is limited.
• Banking infrastructure has not reached rural areas, thus declining usage.
• Financial literacy is low.
• Availability of loans and credit for rural areas is less.
• A significant population is still without any bank accounts.
PMJDY is a significant scheme to ensure inclusive development and channelize savings in the economy. The focus should now shift to increasing bank reach in rural areas and including all unbanked population in a scheme rather than focusing on one member per family.
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
4. ALL MANIPUR SHUMANG LEELA FESTIVAL 2021-2022
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the 50th All Manipur Shumang Leela Festival 2021-2022 began at Iboyaima Shumang Leela Shanglen in Palace Compound, Imphal.
THE EXPLANATION:
• Shumang Leela is a traditional form of theatre in Manipur and the roles of female artists are all played by male actors and male characters are played by female artists in case of female theatre groups. The activities are done in the open air.
• During the festival, the Governor also distributed medals to the winners of the 49th All Manipur Shumang Leela Mahotsav 2020-21.
Background of Shumang Leela Festival
• Originally Shumang Leela began as a comedy genre presented to kings and nobles, which evolved into the present form of courtyard drama. The Shumang Leela of those days tried to preserve and promote humanity, tolerance, self-confidence, devotion, truth and justice through its performances.
• In the present day Shumang Leela is trying to focus on issues of moral values, unity and integrity. It is also striving to strengthen the bonds of brotherhood and friendship between different communities in the state.

5. AUGUST 29: NATIONAL SPORTS DAY
THE CONTEXT: The National Sports Day (NSD) is celebrated every year in India on 29th of August to mark the birth anniversary of legendary hockey player Major Dhyan Chand, who was known as ‘The Wizard’ or ‘The Magician’ of hockey for his superb ball control.
THE EXPLANATION:
About Major Dhyan Chand
• The legendary hockey player was born on 29 August 1905 in Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh. He is widely considered as the greatest field hockey player of all time. He had started playing hockey only after joining the Army at the age of 16.
• He won gold medals in Olympics for India in the years 1928, 1934 and 1936. He scored over 400 goals in his career, from 1926 to 1948. It is believed that after India defeated Germany in the 1936 Olympics final by 8-1, Adolf Hitler offered him a senior post in the German Army, to which Chand refused.
• His autobiography “Goal!” was published by Sport & Pastime (Madras) in 1952. The Government of India (GoI) awarded him the 3rd highest civilian honour of Padma Bhushan in 1956. Beside this, the most noted memorial for him is the Major Dhyan Chand Award, which is the highest award for lifetime achievement in sports and games in India.
• It has been awarded annually from 2002 to sporting figures that not only contribute through their performance but also contribute to the sport after their retirement.
6. SAREX 22 INDIAN COAST GUARD EXERCISE
THE CONTEXT: The Indian Coast Guard recently conducted its biennial National Maritime Search and Rescue Exercise SAREX 22 off the Chennai coast.
THE EXPLANATION:
• The objective of this exercise is to avoid accidents at sea and save lives by conducting rescue operations. During this, 24 observers from 16 countries participated in the exercise organized under the theme ‘Capacity Building Towards Maritime Security’.
• This was the 10th exercise conducted by the Coast Guard. During this exercise, new technology like remote controlled lifebuoys were demonstrated over the Bay of Bengal.
Indian Coast Guard
It is an armed force, search and rescue agency that protects maritime interests of India. It is a Maritime Law Enforcement Agency. It was established in 1978 by coast Guard Act, 1978. It operates under Ministry of Defence.
The following are the missions of Indian Coast Guard-
1. To protect artificial Islands
2. To protect marine ecology and environment
3. To protect fishermen and mariners at ea
The responsibilities of the Indian Coast Guard are Offshore security coordination, national maritime search and rescue, coastal security.
7. VAJRA PRAHAR: INDIA-US JOINT MILITARY EXERCISE, 2022
THE CONTEXT: The 13th edition of India-US Joint Special Forces Exercise Vajra Prahar recently concluded in Bakloh, Himachal Pradesh. Earlier, its 12th edition was held in October 2021 at Joint Base Lewis Mc Cord in Washington, USA.
THE EXPLANATION:
• During this 21-day joint training, the special forces of both the countries underwent training in special operations, air operations and counter-terrorism operations in a joint environment under the United Nations Charter.
• The exercise was conducted in two phases. The first phase includes combat adaptation and tactical level special mission training exercises. At the same time, under the second phase, 48 hours of verification of training received by both the parties has been included in the first phase.
Vajra Prahar
• ‘Vajra Prahar’ is an Indo-US Special Forces joint training exercise that began alternately in 2010 in India and the US.
• The aim of the exercise is to boost military ties between the two countries by enhancing reciprocity and mutual exchange of strategies between the Special Forces.
• This joint training helps in developing a joint strategy between the two armies by sharing best practices and rich pool of experiences of each other’s armies as well as expertise in operations in counter-terrorism and counter-terrorism environments.

