THE HEALTH ISSUES
1. INDIA’S FIRST INDIGENOUS MONKEYPOX TEST KIT
THE CONTEXT: The Andhra Pradesh Medtech Zone recently launched the first indigenously manufactured RT-PCR kit for testing monkeypox. With the help of this kit, infection can be detected quickly.
THE EXPLANATION:
Infection will be easily detected
If we talk about the merits of this kit, then TransAsia-Erba Monkeypox RT-PCR Kit is highly sensitive. Its accuracy is very good, with the help of which people will be very comfortable in use with investigation.
First Case of Monkey Pox in India
- On July 14, the Kollam district of Kerala announced the country’s first case of monkeypox. According to the World Health Organization Monkeypox is a viral zoonosis, or a virus that spreads from animals to humans. It has symptoms resembling those of smallpox but is clinically less serious.
- It can also be transmitted through direct contact with body fluids or lesions, and indirect contact with lesion material such as through contaminated clothing or linen of an infected person.
- India so far has reported ten cases of monkeypox.
ICMR may do Sero Survey
- Recently the Indian Council of Medical Research had said that it can conduct a sero-survey to check antibodies among the contacts of patients with monkeypox. Apart from this, it will also be investigated how many of those patients were asymptomatic. Significantly, monkeypox usually manifests with fever, rash and swollen lymph nodes.
- The disease is usually accompanied by symptoms lasting two to four weeks. The ‘Guidelines on the Management of Monkeypox Disease’ issued by the Center states that human-to-human transmission occurs through respiratory droplets.
VALUE ADDITION:
About Monkeypox:
- Monkeypox is an ongoing outbreak. First case of the viral disease was reported in May 2022 in the United Kingdom. First case was reported in individual with travel links to Nigeria. Monkeypox disease is endemic to Nigeria. For the first time, this disease is being reported outside Central and West Africa. It was declared a public health emergency of international concern on July 23, 2022.
- Monkeypox cases have been reported in over 80 countries. Considering this, the WHO has declared it as a global health emergency. The confirmed cases have reached over 32,000. In Delhi, 5 monkeypox cases have been reported.
Symptoms of monkeypox:
Monkeypox is a viral infection, that displays week or two after exposure with the virus. Common symptoms include fever, followed by rash with lesions. The lesions last for 2–4 weeks before falling off.
THE SOCIAL ISSUES
2. RAT HOLE MINING IN MEGHALAYA
THE CONTEXT: Recently an accident at an illegal coal mining in Meghalaya killed one person and left battling for his life.
About Rat Hole Mining
- It is a primitive and hazardous method of mining for coal, with tunnels that are only 3-4 feet in diameter (hence, rat-hole), leading to pits ranging from 5-100 sq. mt deep.
- It involves digging of very small tunnels in which workers, more often children, enter and extract coal.
- Although the coal is of bad quality, people see it as a treasure chest.
- In backward regions, where there is the loss of livelihood, lack of employment opportunities and under-education, people see rat-hole mines as an opportunity to earn daily bread.
- A major portion of these employees are children, who are preferred because of their thin body shape and ease to access depths.
Despite a ban
The National Green Tribunal banned rat-hole mining in Meghalaya in 2014 on a petition that said acidic discharge from the mines was polluting the Kopili River. But the practice continues unabated.
Threats of such mining
- Water from rivers and streams in the mining area has become unfit for drinking and irrigation and is toxic to plants and animals.
- Layers of rock above the coal removed during mining contain traces of iron, manganese and aluminium that get dissolved from mining sites through the acid run-off or are washed into streams as sediment.
- There are several mishaps where workers get trapped to death due to the sudden collapse of such mines.
THE ENVIRONMENT, ECOLOGY AND CLIMATE CHANGE
3. ‘KRISHNA KUNJ’, A PLANTATION DRIVE
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the Chhattisgarh Chief minister launched ‘Krishna Kunj’, a plantation drive aimed at creating urban forests comprising “culturally significant and other useful trees”.
THE EXPLANATION:
- “Krishna Kunj is a step to promote eco-friendly environment in state and trees like peepal, banyan, kadamb, carrying mythological and cultural importance are being planted at 162 urban locations in state on Janmashtami festival”.
- The environment-friendly initiative is aimed at increasing the green cover of the state and imparting awareness about the importance of trees to the coming generations. The chief minister said that the rapid felling of trees in urban areas in the name of development has created a huge environmental problem.
Aim of the Initiative:
- In a bid to motivate people to plant trees and to save our cultural heritage, “ Krishna Kunj” is being developed in the state. These trees are disappearing due to urbanisation in the last few years, leading to the indiscriminate felling of trees. The initiative of “Krishna Kunj” is being undertaken to aware the forthcoming generations about the importance these trees.
Chhattisgarh Forest Cover: The recorded forest area in the State is 59,772km², which is 44.21% of the geographical area. Reserved, Protected and Unclassed Forests constitute 43.13%, 40.21% and 16.65% of the total forest area respectively.
VALUE ADDITION:
- The Nagar Van (Urban Forests) aims to develop 200 Urban Forests across the country in the next five years.
- Warje Urban Forest in Pune (Maharashtra) will be considered as a role model for the Scheme.
- The Scheme enforces people’s participation and collaboration between the Forest Department, Municipal bodies, NGOs, Corporates and local citizens.
- These urban forests will primarily be on the existing forest land in the City or any other vacant land offered by local urban local bodies.
4. INDIAN TEAM DELIBERATING ON OCEAN DIVERSITY PACT
THE CONTEXT: Recently, a delegation from India and other member countries of the United Nations are in New York to deliberate on a one-of-its-kind agreement to conserve marine biodiversity in the high seas, namely the oceans that extend beyond countries’ territorial waters.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The agreement follows a resolution by the UN General Assembly in May 2022 and is expected to be the final in a series set in motion since 2018 to draft an international legally binding instrument under the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS). The high seas comprise nearly 45% of the Earth’s surface.
- According to the sources, a key aspect of the agreement is deciding on the rights of companies that undertake exploration for biological resources in the high seas: do companies have absolute rights on any discovery or extraction in these regions or should they share their gains, in terms of intellectual property and royalties with a UN-prescribed body.
- Typically, the focus of mining activity in the sea has been for gas hydrates, precious metals and other fossil fuel resources. However with advances in biotechnology and genetic engineering, several companies see potential in exotic microbes and other organisms – several of them undiscovered – that abide in the deep ocean and could be used for drugs, vaccine and a variety of commercial applications.
- In June 2021, the Union Cabinet approved a ‘Blue Economy’ policy for India, a nearly ₹4,000-crore programme spread over five years, that among other things will develop a manned submersible vessel as well as work on “bio-prospecting of deep-sea flora and fauna including microbes”. Studies on sustainable utilisation of deep sea bio-resources will be the main focus. Also, officials noted that there were already companies carrying out such exploratory activities though little was known about them. “Hence an international agreement that spells out obligations and permissible activities is important”.
VALUE ADDITION:
About UNCLOS:
- Adopted and signed in 1982. It became effective in the year 1994.
- It replaced the four Geneva Conventions of April, 1958, which respectively concerned the territorial sea and the contiguous zone, the continental shelf, the high seas, fishing and conservation of living resources on the high seas.
- The Convention has become the legal framework for marine and maritime activities.
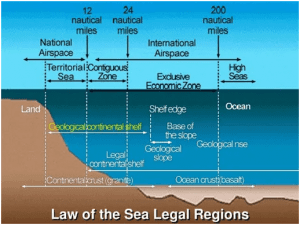
- Also known as Law of the Sea, it divides marine areas into five main zones namely- Internal Waters, Territorial Sea, Contiguous Zone, Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and the High Seas.
- UNCLOS is the only international convention which stipulates a framework for state jurisdiction in maritime spaces. It provides a different legal status to different maritime zones.
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
5. IAF PARTICIPATION IN EXERCISE PITCH BLACK 2022 AT DARWIN, AUSTRALIA
THE CONTEXT: The Indian Air Force (IAF) will join 16 other nations, including Quad partner countries for Exercise Pitch Black, the biennial exercise hosted by the Australian Air Force.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The warfare exercise takes place once every two years and is hosted by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF).
- The aim of this exercise is to practice Offensive Counter Air (OCA)and Defensive Counter Air (DCA) combat. The exercise takes place in a simulated war environment.
- The first Pitch Black exercise took place on June 15-16 1981 between the RAAF units.
Australia India Defence Relationship:
- Building on a long history of cooperation – including our shared experience in the trenches of World War I in Gallipoli and along the Western Front – Australia and India have a positive defence relationship, underpinned by the 2006 Memorandum on Defence Cooperation and the 2009 Joint Declaration on Security Cooperation.
- The Australia–India defence relationship now encompasses almost every major function of the military: strategic dialogues, coordination, and information exchanges; military exercises involving ground, air and maritime forces.
Strategic Dialogue:
- In June 2020, Australia and India decided to upgrade their Secretaries 2+2 dialogue(Defence and Foreign Affairs) to the Ministerial level.
AUSINDEX:
- Australia and India are committed to working together to enhance maritime cooperation and have had AUSINDEX since 2015.
Shared Military Platform:
- India and Australia both border the Indian Ocean and have a shared interest in the maintenance of freedom of navigation and trade.
- Australia recognises India’s critical role in supporting security, stability and prosperity of the Indian Ocean region.
IFC-IOR:
- The Information Fusion Centre – Indian Ocean Region in Gurugram is an Indian initiative to boost maritime security and response through the exchange of information related to the ships in the Indian Ocean Region. Both countries are working together on this.
Civil Nuclear Cooperation:
- A Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement was signed in September 2014which came into force in November 2015.
- The deal ensures that Uranium mining companies of Australia can supply uranium to India for civil use.
THE MISCELLANEOUS
6. WORLD HUMANITARIAN DAY
THE CONTEXT: World Humanitarian Day was observed on August 19, 2021. Every year, WHD is celebrated under a specific theme. According to the United Nations, the theme for this year is ”to show the importance, effectiveness, and positive impact of humanitarian work”.
THE EXPLANATION:
- This day focuses on boosting up the global action in order to combat climate change and stand in solidarity with the vulnerable populations.
- On the occasion, the United Nations has urged the people, especially social media users, to mark the day by showing their solidarity for vulnerable populations.
- UN urged social media user to run, ride, swim, walk and do any activity of their choice for 100 minutes in between August 16 to August 31.
- UN further asked the users to tell the leaders across world that they expect developed countries to deliver on their pledge of $100 billion in order to do climate mitigation and adaptation across developing countries.
About World Humanitarian Day
It is an international day which is observed to recognize humanitarian personnel and those who lost their lives while working for humanitarian causes. United Nations General Assembly designated this day as part of a Swedish-sponsored GA Resolution A/63/L.49 that seeks to Strengthen the Coordination of Emergency Assistance of the United Nations. Every year, the day is observed on August 19. August 19 is the day on which Special Representative of the Secretary-General to Iraq, Sergio Vieira de Mello and his 21 colleagues were killed in a bombing event at UN Headquarters in Baghdad.
Significance of the day
The day is observed to honour all those who chose a difficult life to serve, despite the odds and those who are trapped in challenging circumstances worldwide. It pays tribute to humanitarian workers who were killed and injured. On the day, all aid and health workers are honoured who continue to provide life-saving support and protection to needy people.
Spread the Word



