Table of Contents
THE HEALTH AND SOCIAL ISSUES
EXPLAINED: WHAT IS ANTHRAX, THE INFECTIOUS DISEASE FOUND IN KERALA?
THE CONTEXT: After finding several carcasses of wild boar, Kerala health officials confirmed the presence of anthrax, a serious infectious disease caused by spore-forming bacteria, in Athirappilly of Thrissur district.
THE EXPLANATION:
Anthrax has usually been found in India’s southern states and is less frequently found in the northern states. Over the past years, it has been reported in Andhra Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Tamil Nadu, Assam, Odisha and Karnataka.
What is Anthrax?
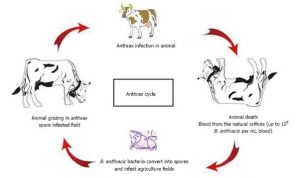
- Anthrax, also known as malignant pustule or woolsorter’s disease, is a rare but serious disease caused by rod-shaped bacteria known as Bacillus anthracis. It occurs naturally in soil and, according to the WHO it is primarily a disease of herbivores, with both domestic and wild animals being affected by it.
- Anthrax is a zoonotic disease, meaning that it is naturally transmissible from animals (usually vertebrae) to humans. People can get the disease through contact with infected animals or animal products that are contaminated with bacteria.
- According to the WHO, Anthrax is generally regarded as non-contagious. There have been instances of person-to-person transmission, however, such instances are extremely rare.
How do animals get Anthrax?
- Domestic and wild animals can get infected when they breathe in or ingest spores in contaminated soil, plants or water.
- According to the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare’s National Health Portal, Herbivorous animals can get the disease through contaminated soil and feed, while omnivorous and carnivorous animals get infected through contaminated meat, bones and other feeds. Wild animals get sick through feeding on anthrax-infected carcasses.
How do humans get infected?
- Humans almost always contract the disease directly or indirectly from animals or animal products.
- People get infected with anthrax when spores enter the body, through breathing, eating contaminated food or drinking contaminated water, or through cuts or scrapes in the skin. The spores then get “activated” and multiply, spreading across the body, producing toxins and causing severe illness.
Use in Bioterrorism:
- Anthrax has been used in biological warfare by agents and by terrorists to intentionally infect.
- It was spread in the US through mail. It killed 5 people and made 22 sick.
THE ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
EXPLAINED: HOW KERALA HAS STRUGGLED TO IDENTIFY BUFFER ZONES AROUND ITS PROTECTED FORESTS
THE CONTEXT: Recently, the three-judge bench of the Supreme Court, in its order on (June 3, 2022) said national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and such protected forests must have an ESZ of a minimum 1 km from their boundaries.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The court said the guidelines issued by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MEF & CC) on 9 February 2011, which have either banned or regulated a bunch of activities within the ESZ, should be strictly adhered to.
- In 2011, the environment ministry had issued a set of guidelines, which either completely banned or regulated certain activities in ESZ. The banned activities are mining, running of sawmills, polluting industries, commercial use of fire woods, mega hydel-power projects and manufacturing of hazardous objects. Mining would be allowed only for loc
 al use, the guidelines said.
al use, the guidelines said. - The permissible activities are ongoing agricultural and horticulture practices, rainwater harvesting, organic farming and the adoption of green technology for all activities.
About ESZs:
- Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs) or Ecologically Fragile Areas (EFAs) are areas notified by the MoEFCC around Protected Areas, National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries.
- The purpose of declaring ESZs is to create some kind of “shock absorbers” to the protected areas by regulating and managing the activities around such areas.
- They also act as a transition zone from areas of high protection to areas involving lesser protection.
- The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 does not mention the word “Eco-Sensitive Zones”.
- An ESZ could go up to 10 kilometres around a protected area as provided in the Wildlife Conservation Strategy, 2002.
- Moreover, in the case where sensitive corridors, connectivity and ecologically important patches, crucial for landscape linkage, are beyond 10 km width, these should be included in the ESZs.
Significance of ESZ:
- The purpose of declaring ESZs around national parks, forests and sanctuaries is to create some kind of a “shock absorber” for the protected areas.
- These zones would act as transition zone from areas of high protection to those involving lesser protection.
VALUE ADDITION:
SIGNIFICANCE OF WESTERN GHATS:
- Older than the Himalayan mountains, the mountain chain of the Western Ghats represents geomorphic features of immense importance with unique biophysical and ecological processes.
- The site’s high montane forest ecosystems influence the Indian monsoon weather pattern. Moderating the tropical climate of the region, the site presents one of the best examples of the monsoon system on the planet.
- It also has an exceptionally high level of biological diversity and endemism and is recognized as one of the world’s eight ‘hottest hotspots’ of biological diversity.
- The forests of the site include some of the best representatives of non-equatorial tropical evergreen forests anywhere and are home to at least 325 globally threatened flora, fauna, bird, amphibian, reptile and fish species
Connect the Dots:
- Madhav Gadgil and Kasthurirangan Committees are related to the Western Ghats.
EXPLAINED: IS GROWING SPACE TOURISM POSING A RISK TO THE CLIMATE?
THE CONTEXT: Recently, an article published in the journal, Earth’s Future wherein researchers from University College London (UCL), the University of Cambridge and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) found that the soot emissions from rocket launches are far more effective at warming the atmosphere compared to other sources.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The researchers state that routine launches by the rapidly growing space tourism industry “may undermine progress made by the Montreal Protocol in reversing ozone depletion.”
- They argue that there is an urgent need for environmental regulation to reduce the climatic damage from this fast-growing industry.
Space tourism industry
- According to the authors of the recent study published in Earth’s Future, “The space industry is one of the world’s fastest-growing sectors”.
- From $350 million in 2019, the industry is forecasted to grow to more than $1 trillion by 2040. With companies like Virgin Galactic, SpaceX and Blue Origin launching commercial space flights, space tourism has become, at least theoretically, a possibility for enthusiasts.
What are the study’s findings?
- Unlike other sources of pollution, the study finds that environmental damage caused by rockets is far greater, as they emit gaseous and solid chemicals directly into the upper atmosphere.
- The space tourism’s current growth trends also indicate a potential for the depletion of the ozone layer above the Arctic. This is because the pollutants from rocket fuel and heating caused by spacecraft returning to Earth, along with the debris caused by the flights are especially harmful to the ozone layer.
- What is of great concern is the black carbon (BC) soot that is emitted by rockets directly into the atmosphere. These soot particles have a far larger impact on the climate than all other sources of soot combined, as BC particles are almost 500 times more efficient at retaining heat.
- “Soot particles from rocket launches have a much larger climate effect than aircraft and other Earth-bound sources, so there doesn’t need to be as many rocket launches as international flights to have a similar impact. According to researchers, what we really need now is a discussion amongst experts on the best strategy for regulating this rapidly growing industry”.
- The team of researchers showed that within only 3 years of additional space tourism launches, the rate of warming due to the released soot would more than double.
- This is because of the use of kerosene by SpaceX launches and hybrid synthetic rubber fuels by Virgin Galactic.
Undermining Montreal Protocol
- While the loss of ozone from current rocket launches is “small”, the researchers argue that in the likelihood of weekly or daily space tourism rocket launches, the recovery of the ozone layer caused by the Montreal Protocol could be undermined.
- Researchers also noted, “The only part of the atmosphere showing strong ozone recovery post-Montreal Protocol is the upper stratosphere, and that is exactly where the impact of rocket emissions will hit hardest.
VALUE ADDITION:
MONTREAL PROTOCOL
- The Montreal Protocol is a landmark international treaty that was adopted in Montreal in 1987 and was aimed at protecting the Earth’s ozone layer by regulating the production and consumption of nearly 100 chemicals called ozone-depleting substances (ODS).
- The treaty phases down the consumption and production of various ODS in a stepwise manner.
- As per the Montreal Protocol, developing and developed countries have equal and differentiated responsibilities, however all countries have to follow binding, time-targeted and measurable commitments.
- Considered to be one of the most successful environmental interventions on the global scale, it is the first treaty to achieve universal ratification by all countries in the world.
- The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) states that without this treaty, ozone depletion would have increased by more than ten times by 2050, as compared to current levels.
THE PRELIMS PERSPECTIVE
MAYURBHANJ’S SUPERFOOD ‘ANT CHUTNEY’ READY FOR GI-TAG
THE CONTEXT: In Odisha, scientists are now fine-tuning their research to make a presentation for the Geographical Indications (GI) registry of Kai chutney.
THE EXPLANATION:

- Applied under food category, the GI tag will help develop a structured hygiene protocol in the preparation of Kai chutney for standard wider use. Geographical Indications labels enhance the reputation and value of local products and support local businesses.
- People often keep a safe distance from red weaver ants as their sting inflicts a sharp pain and reddish bumps on the skin. Despite this, weaver ants are popular among the tribes of the Mayurbhanj district in Odisha for the mouth-watering dish made of them — the Kai chutney.
- This savoury food item, rich in proteins, calcium, zinc, vitamin B-12, iron, magnesium, potassium, sodium, copper, fibre and 18 amino acids, is known to boost the immune system.
- Weaver ants, Oecophylla smaragdina, are abundantly found in Mayurbhanj throughout the year. They make nests with leaves of host trees.
VALUE ADDITION:
About GI tag:
- A GI is primarily an agricultural, natural or manufactured product (handicrafts and industrial goods) originating from a definite geographical territory.
- Typically, such a name conveys an assurance of quality and distinctiveness, which is essentially attributable to the place of its origin.
Security:
- Once the GI protection is granted, no other producer can misuse the name to market similar products. It also provides comfort to customers about the authenticity of that product.
Who is a registered proprietor of a geographical indication?
- Any association of persons, producers, organisation or authority established by or under the law can be a registered proprietor.
- Their name should be entered in the Register of Geographical Indication as registered proprietor for the Geographical Indication applied for.
How long the registration of Geographical Indication is valid?
- The registration of a geographical indication is valid for a period of 10 years. Also, It can be renewed from time to time for further period of 10 years each.
- In India, Geographical Indications registration is administered by the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 which came into force with effect from September 2003. The first product in India to be accorded with GI tag was Darjeeling tea in the year 2004-05.
EXPLAINED: WHY AUSTRALIA HAS HAD TO KILL MILLIONS OF BEES TO SAVE ITS HONEY INDUSTRY
THE CONTEXT: The recent outbreak of the deadly varroa mite, a sesame seed-sized parasite that was first spotted at a port near Sydney, Australia poses a massive threat to the country’s multimillion-dollar honey industry.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Recently, Australia was one of the few countries that was able to successfully clamp down on the spread of Varroa mite-induced plagues, known to be the biggest threat to bees worldwide.
- According to the Australian Honeybee Industry Council, Colonies of honeybees have been put under “lockdown” as part of a wide range of biosecurity measures to limit the outbreak. “It is critically important that beekeepers in the Newcastle area do not move any hives or equipment in or out of the area”.
What is the Varroa mite?
- The Varroa mite, or Varroa destructor, is a parasitic insect that attacks and feeds on honeybees. Reddish-brown in colour, the tiny pests are known to kill entire colonies of honeybees. They often travel from bee to bee and also via beekeeping equipment, such as combs that have been extracted.
- The spread of the mite is largely blamed for a sharp decline in the number of honeybee colonies worldwide. It has plundered bee colonies across the globe.
- According to Australian beekeeping website Bee Aware “Although Varroa mites can feed and live on adult honeybees, they mainly feed and reproduce on larvae and pupae in the developing brood, causing malformation and weakening of honey bees as well as transmitting numerous viruses.”

Why do bees’ matter?
- According to a report, the latest lockdown could adversely impact the growth of several crops — including almonds, macadamia nuts and blueberries — that are dependent on hives for pollination.
THE MISCELLANEOUS
EXPLAINED: ARE HUMANS OLDER THAN WE THOUGHT? EXPLAINING THE STUDY OF THE SKELETAL REMAINS FROM SOUTH AFRICA
THE CONTEXT: According to a new study published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, the fossils of our earlier human ancestors, located in a cave in South Africa, is a million years older than previously understood.
THE EXPLANATION:
The researchers analysed the fossilised remains of Australopithecus from Sterkfontein caves and argued they lived at the same time as their East African counterparts like the famous Lucy, complicating the way scholars have understood human evolution.
What is Australopithecus?

- Australopithecus, meaning “southern ape”, was a group of hominins or now-extinct early humans, that was closely related to and almost certainly the ancestors of modern humans.
- They inhabited the planet 4.4 million to 1.4 million years ago, likely encompassing a time period longer than our own genus, Homo. Their fossils have been found across sites in eastern, northern, central and southern Africa.
- Australopithecus was originally defined by the anthropologist Raymond Dart in 1925, after the discovery of the first australopith fossil (a small child’s skull) in Tuang, South Africa. Through his research, Dart argued that early humans first evolved in Africa, challenging the conventional wisdom that they had done so in Europe and Asia.
- Our early ancestors were bipedal in nature and travelled on the ground (but used trees for food and protection), had large teeth with thick enamel caps for chewing, and their brains were only slightly larger than apes. The facial and dental features suggest that they were able to consume tough foods, such as nuts, seeds, tubers and roots.
- They stood at a height of around 3 ft 9 inches to 4 ft 11 inches, and likely weighed around 30 to 50 kg, with males almost double the size of females.
What are the Sterkfontein caves?
The “Cradle of Humankind” is a 47,000-hectare paleoanthropological site, declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. Located 40 km northwest of Johannesburg, it contains a complex system of limestone caves, where a significant number of hominin fossils have been found.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION OF THE DAY
Q.The Athirappilly Falls is located in which state?
a) Kerala
b) Tamil Nadu
c) Karnataka
d) Maharashtra
ANSWER FOR 2ND JULY 2022
Answer: D
Spread the Word

 al use, the guidelines said.
al use, the guidelines said.