THE HEALTH ISSUES
1. EBOLA REARS HEAD AGAIN IN DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF CONGO
THE CONTEXT: The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has reported a fresh outbreak of Ebola virus disease (EVD).
THE EXPLANATION:
The Ministry of Health of the DRC declared an outbreak of EVD on April 22, 2022, after a casualty was confirmed in the country, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The WHO warned of the virus spreading within healthcare workers since the IPC measures were not good enough. “The exposure of the first case remains unknown and therefore, it is difficult to assess the extent of the outbreak at this stage,” the global body noted.
- “Some of the improvements achieved by establishing capacities such as IPC measures in health facilities during previous outbreaks have not been maintained over time to tackle the current outbreak.
- “There is a need to support the province’s health professionals to conduct an effective response. In addition, logistical support is needed to reactivate the health infrastructure that was put in place during previous epidemics,” it added.
- EVD is endemic in the country so these cases are not a surprise. Nevertheless, the WHO has assessed the risk to be moderate at the regional level and low at the global level.
VALUE ADDITION:
What is Ebola Virus Disease?
Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a deadly disease with occasional outbreaks that occur mostly on the African continent. EVD most commonly affects people and nonhuman primates (such as monkeys, gorillas, and chimpanzees). It is caused by an infection with a group of viruses within the genus Ebolavirus:
- Ebola virus (species Zaire ebolavirus)
- Sudan virus (species Sudan ebolavirus)
- Taï Forest virus (species Taï Forest ebolavirus, formerly Côte d’Ivoire ebolavirus)
- Bundibugyo virus (species Bundibugyo ebolavirus)
- Reston virus (species Reston ebolavirus)
- Bombali virus (species Bombali ebolavirus)
Of these, only four (Ebola, Sudan, Taï Forest, and Bundibugyo viruses) have caused disease in people. Reston virus can cause disease in nonhuman primates and pigs, but there have not been cases in people. Bombali virus was first identified in bats in 2018, and experts do not know yet if it causes disease in either animals or people.
When was the first instance?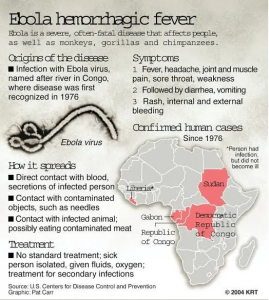
- Ebola virus was first discovered in 1976 near the Ebola River in what is now the Democratic Republic of Congo. Since then, the virus has been infecting people from time to time, leading to outbreaks in several African countries.
Vaccines:
- An experimental Ebola vaccine, called rVSV-ZEBOV proved highly protective against EVD in a major trial in Guinea in 2015.
- The rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine is being used in the ongoing 2018-2019 Ebola outbreak in DRC. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should have access to the vaccine under the same conditions as for the general population.
- The public mistrust and militia attacks have prevented health workers from reaching some hard-hit areas for administering the vaccines.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2. OVER 60 COUNTRIES JOIN HANDS FOR OPEN, FREE AND SECURE GLOBAL INTERNET
THE CONTEXT: The US, all the European Union (EU) member states and 32 non-EU countries have signed a “Declaration for the Future of the Internet” that calls for an “open, free, global, interoperable, reliable, and secure” internet.
THE EXPLANATION:
- India is not among the 60 countries that have signed a global declaration to keep the Internet open, free, and neutral. The countries that have signed the declaration include the US, European Union, United Kingdom, Canada and France. Called the ‘Declaration for the Future of the Internet’, the document is an agreement to prevent digital authoritarianism.
- According to a White House statement, “Globally, we are witnessing a trend of rising digital authoritarianism where some states act to repress freedom of expression, censor independent news sites, interfere with elections, promote disinformation, and deny their citizens other human rights. At the same time, millions of people still face barriers to access and cyber security risks and threats undermine the trust and reliability of networks”.
- India, China and Russia are among the large nations that are not part of this declaration.
- The Declaration’s principles include commitments to protecting human rights and fundamental freedoms of all people, promote a global Internet that advances the free flow of information, advancing “inclusive and affordable” connectivity, promote trust in the global digital ecosystem, including through protection of privacy and protecting and strengthening the multi stakeholder approach to governance that keeps the Internet running for the benefit of all.
| POINTS TO REMEMBER:
According to the report, total of 182 internet crackdowns were reported globally in 2021. Out of 106 shutdowns in India, 85 were reported in Jammu and Kashmir. India was one of among 18 countries that blocked mobile internet during protests. The number of countries that shut down the internet in 2021 has increased to 34 from 29 in 2020. |
3. MISSION SAGAR IX
THE CONTEXT: With the overarching aim of providing critical medical aid to Sri Lanka during the ongoing crisis, INS Gharial as part of Mission SAGAR IX arrived at Colombo on 29 Apr 22 and delivered over 760 kgs of 107 types of critical lifesaving medicines
THE EXPLANATION:
- In line with GoI’s vision of SAGAR – Security and Growth for All in the Region – the Indian Navy undertakes several deployments titled ‘Mission SAGAR’ to assist friendly IOR littorals. Since May 2020, Indian Navy has successfully concluded eight such missions, deploying ten ships to 18 Friendly Foreign Countries.
- With a steadfast intent of delivering a high quantum of humanitarian assistance to our neighbors, personnel from ships and shore organizations of Indian Navy have invested close to a million man-hours to bring succor to our friends, overseas.
Value Addition:
Mission SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region)
- SAGAR is a term coined by Prime Minister in 2015 during his Mauritius visit with a focus on the blue economy.
- It is a maritime initiative which gives priority to the Indian Ocean region for ensuring peace, stability and prosperity of India in the Indian Ocean region.
- The goal is to seek a climate of trust and transparency; respect for international maritime rules and norms by all countries; sensitivity to each other`s interests; peaceful resolution of maritime issues; and increase in maritime cooperation.
- It is in line with the principles of the Indian Ocean Rim Association.
THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
4. NABARD PLANS FARMER DISTRESS INDEX
THE CONTEXT: With small and marginal farmers getting a raw deal in farm loan waivers, National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) is planning to formulate a farmer distress index (FDI) to track, identify and support the real needy and distressed farmers.
THE EXPLANATION:
- According to a study jointly conducted by NABARD and Bharat Krishak Samaj (BKS), a farmers producers’ organization, in Punjab, more than 60 percent of the ‘very high’ and ‘high’ distress small and marginal farmers (SMFs) did not receive farm loan waiver (FLW) benefits. The exclusion rate was also 60 percent for the medium distress category SMFs.
- In Maharashtra, SMFs that were relatively better off as they were categorized as ‘low’ distress received the maximum FLW benefits. Close to 42 percent of the SMF whose distress category was ‘very high’ did not receive FLW benefits.
- In UP, 47 percent of the ‘very high distress’ category, and 45 percent of the ‘high distress’ category SMF did not receive FLW benefits. In the three states together, more than 40 percent of the ‘very high distress’ farmers did not receive any FLW benefits.
- NABARD study says this farmer distress index can integrate the available high-frequency data on key agricultural variables like deviation of monsoon rains, excessive rainfall, drought and dry spells, variations in temperature and soil moisture, yield of major crops in the district, proportion of area under irrigation, depth of underground water, unusual frost, marketing opportunities available to the farmer that may include the proportion of wheat, paddy, chana, tur, groundnut, soybean etc. produced and procured at MSP.
- NABARD also noted that “Use of weather data derived from remote sensing technology, automatic weather stations, mobile telephony and artificial intelligence can help in identifying the distressed villages”.
- “Use of data of claims received for crop insurance is also likely to help in identification of distressed regions. These can be tracked on a real-time basis and be used to monitor and predict the level of farmer distress,” the study said.
- Technology breakthroughs like use of space technology, AI and block chain in agriculture can be harnessed to bring dynamism and credibility to the system.
- Further, depending on the kind and severity of distress, the support can be given as a combination of unconditional grants, loan restructuring and/or a complete debt waiver. The assistance to individual farmers can be based on a combination of district index and individual farmers’ distress captured via irrigation status of his land, income from crops grown by him, average productivity of the district and the average price in APMC markets of this district as compared to the average price of the state.
VALUE ADDTION:
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
- NABARD is a development bank focusing primarily on the rural sector of the country. It is the apex banking institution to provide finance for Agriculture and rural development. It headquarter is located in Mumbai, the country’s financial capital.
- It is responsible for the development of the small industries, cottage industries, and any other such village or rural projects.
- It is a statutory body established in 1982 under Parliamentary act-National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development Act, 1981.
NABARD and RBI
- Reserve Bank of India is the central bank of the country with sole right to regulate the banking industry and supervise the various institutions/banks
- This also include NABARD defined under Banking Regulation Act of 1949.
- RBI provides 3 directors to NABARD’s Board of Directors.
- NABARD provides recommendations to Reserve Bank of India on issue of licenses to Cooperative Banks, opening of new branches by State Cooperative Banks and Regional Rural Banks (RRBs).
5. CORE INDUSTRIES GROW BY 10.4% DURING FY 2021-22
THE CONTEXT: According to DPIIT, cumulative growth rate of Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) during April-March 2021-22 was 10.4% (provisional) as compared to the corresponding period of last Financial Year. The combined Index of Eight Core Industries stood at 157.3 in March 2022, which increased by 4.3 per cent (provisional) as compared to the Index of March 2021.
THE EXPLANATION:
- Final growth rate of Index of Eight Core Industries for December 2021 is revised to 4.1% from its provisional level 8%.
- The Office of Economic Adviser, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade released the Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) for the Month of March 2022. ICI measures combined and individual performance of production in selected eight core industries viz. Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilizers, Steel, Cement and Electricity. The Eight Core Industries comprise 27 percent of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP). Details of yearly and monthly indices and growth rates are provided at Annex I & II respectively.
- The production of Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilizers, Steel, Cement and Electricity industries increased in March 2022 over the corresponding period of last year (2021).
The summary of the Index of Eight Core Industries is given below:
- Coal – Coal production (weight: 10.33 per cent) declined by 0.1 percent in March, 2022 over March, 2021.
- Crude Oil – Crude Oil production (weight: 8.98 per cent) declined by 3.4 per cent in March, 2022 over March, 2021.
- Natural Gas – Natural Gas production (weight: 6.88 per cent) increased by 7.6 per cent in March, 2022 over March, 2021.
- Petroleum Refinery Products – Petroleum Refinery production (weight: 28.04 per cent) increased by 6.2 per cent in March, 2022 over March, 2021.
- Fertilizers – Fertilizers production (weight: 2.63 per cent) increased by 15.3 per cent in March, 2022 over March, 2021.
- Steel – Steel production (weight: 17.92 per cent) increased by 3.7 per cent in March, 2022 over March, 2021.
- Cement – Cement production (weight: 5.37 per cent) increased by 8.8 per cent in March, 2022 over March, 2021.
- Electricity – Electricity generation (weight: 19.85 per cent) increased by 4.9 per cent in March, 2022 over March, 2021.
VALUE ADDITION:
- The eight industries have a combined share of 27 per cent in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP), which gives the growth rates of different industry groups in a specified period.
Eight core industries weightage
- The eight Core Industries in decreasing order of their weightage: Refinery Products> Electricity> Steel> Coal> Crude Oil> Natural Gas> Cement> Fertilizers.
| Industry | Weight (In percentage) |
| Petroleum & Refinery production | 28.04 |
| Electricity generation | 19.85 |
| Steel production | 17.92 |
| Coal production | 10.33 |
| Crude Oil production | 8.98 |
| Natural Gas production | 6.88 |
| Cement production | 5.37 |
| Fertilizers production | 2.63 |
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN NEWS
6. GOOGLE SIGNS MOU WITH TELANGANA GOVERNMENT
THE CONTEXT: Technology giant Google signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with the Telangana government to bring benefits of digital economy to youth and women entrepreneurs.
THE EXPLANATION:
- As part of the partnership, Google will collaborate with the State through its various arms to extend scholarships for Google Career Certificates to Telangana’s youth, support women entrepreneurs through digital, business and financial skills training, and strengthen the government’s school modernization efforts with digital teaching and learning tools and solutions.
- As part of the joint effort, Google will also support the Telangana government’s efforts to improve public transportation and use of digital technologies in agriculture.
Expanding presence in Telangana
- The company also unveiled the design of its ground-up development at the 7.3-acre site it acquired in Gachibowli in 2019. Upon commissioning, the three million square foot building will offer a highly skilled tech workforce a healthy, collaborative workplace that is both resilient and adaptable, designed to serve the city for years to come.
Components of the MoU
Google will collaborate with the Telangana government to:
- Provide Google Career Certificate Scholarships to undeserved youth: Google will collaborate with Telangana Academy for Skill and Knowledge to provide scholarships and wrap-around training for pursuing Google Career Certificates in high demand fields like IT Support, IT Automation, UX Design, Data Analytics, and Project Management.
- Roll out Women Will programme to equip women with training and tools for their entrepreneurship journeys: Together with WE-Hub, Google will roll out its Women Will programme to deliver digital, business and financial skills to nano, micro and small women-led businesses and entrepreneurs across Telangana.
- Empower public schools with digital education through Google for Education’s shareable devices and collaborative tools: Google for Education will partner in the State’s education modernization efforts through needs assessment, impact demonstrations, and student and educator training on the use of e-Learning technologies for improved learning outcomes.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTIONS OF THE DAY
Q1. Which of the following statements is correct?
a) The chief justice is appointed by the President after consultation with the chief justice of India and the governor of the state concerned.
b) Constitution has prescribed minimum age for appointment as a judge of a high court.
c) Constitution prescribes a fixed tenure of a judge of a high court.
d) Constitution prescribes the procedure relating to the removal of a judge of a high court by the process of impeachment.
ANSWER FOR 29TH APRIL 2022
Q1. Answer: D
Explanation:
- Odissi dance uses Jayadeva’s ‘Gita Govinda’ extensively.
Q2. Answer: B
Explanation:
- Giddha, Sammi, and Kikli are folk dances from Punjab state.




