THE POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. THE 24TH NATIONAL CONFERENCE ON E-GOVERNANCE 2021
THE CONTEXT: The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) and Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India, in association with the State Government of Telangana organized the 24th Conference on e-Governance (NCG) 2021.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The theme of this Conference is “India’s Techade: Digital Governance in a Post Pandemic World”. At the Valedictory Session ‘Hyderabad Declaration’ on e-Governance was adopted after intensive deliberations during the sessions.
- The discussions were held on six sub-themes in Plenary sessions- AatmaNirbhar Bharat: Universalization of Public Services; Innovation– Platformization, Emerging Technologies; Ease of living through Technology Interventions for Good Governance; Government Process Re-engineering and Citizen’s participation in Government Processes; India’s Techade – Digital Economy (Digital Payments – Building Citizen’s Confidence).
HYDERABAD DECLARATION:
The Conference resolved that Government of India and State Governments shall collaborate to:
- To bring citizens and government closer through digital platforms.
- Transform citizen services through use of technology by leveraging the artifacts of India Stack that include Aadhaar, UPI, DigiLocker, UMANG, e Sign and consent framework.
- Fast track the implementation of the national level public digital platforms in key social sectors viz. Health, Education, Agriculture, etc by adopting open interoperable architecture for joined up connected services.
- Operationalize the data governance framework to facilitate data sharing within Government entities as also make available all data on data.gov.in except for a negative list. Enable protocols for data collection, data harvesting, data privacy, data anonymization, data security, and data preservation that can help build a data economy.
- Foster responsible use of emerging technology such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Blockchain, 5G, Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, etc for Social Empowerment.
- Use technology for propagating end to end service delivery without human interference to the citizen at the grass root level.
- Make “digital” the primary aspect of government service design and delivery and provide requisite infrastructure to achieve that.
Value Addition:
What is e-Governance?
- E-governance is the application of ICT to the processes of government functioning for good governance. In other words, e-governance is the public sector’s use of ICTs with the aim to improve information and service delivery, encourage citizen participation in decision-making and make government more accountable, transparent and efficient.
- So in essence, e-governance is the application of ICT in government functioning to bring in SMART governance implying: simple, moral, accountable, responsive and transparent
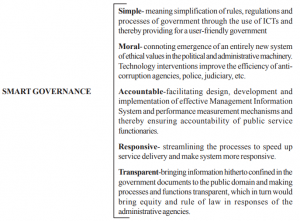
SMART governance, thus, helps in:
- improving the internal organizational processes of governments;
- providing better information and service delivery;
- increasing government transparency in order to reduce corruption;
- reinforcing political credibility and accountability; and
- promoting democratic practices through public participation and consultation.
THE ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
2. THE RARE MICROBES
THE CONTEXT: Researchers from the University of Southern Denmark have discovered that oxygen is also produced without sunlight, possibly deep below the ocean surface. Researchers have discovered that some of the invisible microorganisms living in water columns produce oxygen in an unexpected way.
THE EXPLANATION:
Scientists say there would be no oxygen on Earth were it not for sunlight: the key component in photosynthesis.
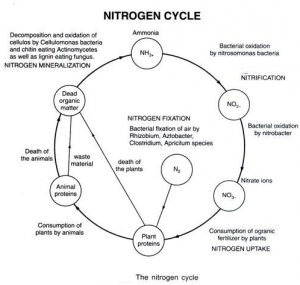
Nitrogen cycle
- A few microbes are known to make oxygen without sunlight, but so far, they have only been discovered in very limited quantities and in very specific habitats.
- But the ocean living microbe Nitrosopumilus maritimus and its cousins, called ammonia-oxidizing archaea play an important role in the nitrogen cycle. For this, they need oxygen. So it has been a long-standing puzzle why they are also very abundant in waters where there is no oxygen.
- The researchers found that N. maritimus was using the oxygen present in water, but the oxygen levels started increasing again in water. The micro-organisms were able to make oxygen even in a dark environment. Not sufficiently high to influence oxygen levels on Earth, but enough to keep itself going.
- maritimus couples the oxygen production to the production of gaseous nitrogen. By doing so they remove bioavailable nitrogen from the environment.
What are Microbes?
A microbe, or “microscopic organism,” is a living thing that is too small to be seen with the naked eye. We need to use a microscope to see them.It is used to describe many different types of life forms, with dramatically different sizes and characteristics:
- Bacteria
- Archaea
- Fungi
- Protists
- Viruses
Microscopic Animals
The human body is home to microbes from all of these categories. Microscopic plants are also considered microbes, though they don’t generally live on or in the human body.
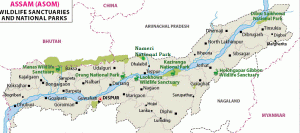
3. THE RETURN OF GHARIAL TO ORANG NATIONAL PARK
THE CONTEXT: The Assam government issued a preliminary notification for adding 200.32 sq. km to the 78.82 sq. km Orang National Park as it is to be expanded to more than thrice its existing size; to include Gharials, dolphins, turtles.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The gharial, wiped out from the Brahmaputra River system in the 1950s, could be the prime beneficiary of a process to expand an Assam tiger reserve.

- Orang, on the northern bank of the river, is strategic to the Kaziranga Orang Riverine Landscape. Tigers and rhinos are known to use the islands in this riverine landscape, about 180 km long, to hop between Orang and Kaziranga.
- “The government is pursuing a policy for the reintroduction of the gharial that became locally extinct more than six decades ago. With better protection, the stretch of Kaziranga-Orang landscape is ideal for sustaining the gharial,”
- The Gangetic dolphin is also expected to be a beneficiary of the final notification of the addition to Orang, expected to take at least three months after the rights and claims are settled.
- Other national parks in Assam are Kaziranga, Manas, Nameri, Dibru-Saikhowa, Raimona and DehingPatkai.
About Gharials
Gharials (or gavials) are a type of Asian crocodilian distinguished by their long, thin snouts. Crocodilians are a group of reptiles that includes crocodiles, alligators, caimans, and more.
India has three species of Crocodilians namely:
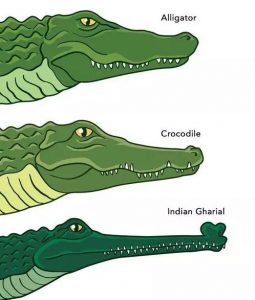
- Gharial: IUCN Red List– Critically Endangered
- Mugger crocodile: IUCN-
- Saltwater crocodile: IUCN- Least Concern.
- All the three are listed on Appendix I of CITES and Schedule I of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972.
- However, Saltwater Crocodile populations of Australia, Indonesia and Papua New Guinea are included in Appendix II of CITES.
Habitats include:
- Fresh waters of the northern India – Chambal river, Ghagra, Gandak river and the Sone river (Bihar).
- Population of Gharials is a good indicator of clean river water.
Conservation Efforts:
- Breeding Centres of Kukrail Gharial Rehabilitation Centre in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, National Chambal Sanctuary (Gharial Eco Park, Madhya Pradesh).
Orang National Park
- The Orang National Park also known as Rajiv Gandhi Orang National Park is located on the north bank of the Brahmaputra River in the Darrang and Sonitpur districts of Assam and covers an area of 78.81 square kilometers.
- It was established as a wildlife sanctuary in 1985 but was declared as National Park in 1999. It is also 49th Tiger Reserve of the country, being notified in 2016.
- It is also known as the mini Kaziranga National Park (IUCN site) since the two parks have a similar landscape made up of marshes, streams, and grasslands.
- Pachnoi River, Belsiri River and Dhansiri River border the park and join the Brahmaputra River.
THE DEFENCE AND SECURITY
4. THE LIGHT COMBAT AIRCRAFT PROGRAMME
THE CONTEXT: According to the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), HAL expects to deliver all Final Operational Clearance (FOC) variant aircraft to the Indian Air Force (IAF) in 2022 pending some systems from Israel, while the LCA-MK1A is expected to take flight in June 2022. There is another 20 to 24 months of testing after which deliveries would begin with manufacturing activities going parallel to the testing.
THE BACKGROUND:
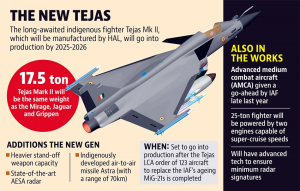
- The term Tejas means ‘radiance’. Developed as a joint venture between Aeronautical Development Agency and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited, Tejas is a lightweight aircraft technically described as a multi-role, singing-engine tactical fighter. The Light Combat Aircraft (LCA)-Tejas was conceptualized in the year
- Specially manufactured for induction into the Indian Navy and Indian Air force, Tejas comes with two variations.
- Tejas is an indigenously manufactured Light Combat Aircraft (LCA). Notably, this is among the world’s smallest and lightest multi-role fighter aircraft belonging to the Supersonic class. The highlights of this tailless Aircraft include a single-engine and a compound delta wing. In the mission of its development, we see ADA and HAL partners also making use of the expertise of DRDO, CSIR, BEL, DGAQA, IAF and IN. Upon its deployment, Tejas will meet the diverse requirements of the Indian Air Force (IAF) and Indian Navy (IN).
Tejas aircraft Performance
- Altitude: 50,000 feet; Max Speed at all altitudes: Supersonic; and ‘g’ limits: +8/-3.5.
- The efficiency and worth of any modern fighter aircraft depend on the weapons it is capable of delivering on the target. Tejas can carry a veritable plethora of air to surface, air to air, standoff and precision-guided weaponry. In the air-to-air arena, Tejas can carry long-range and beyond-visual-range weapons. It can also tackle any kind of close combat threat by handling highly agile and high off-boresight missiles.
- A broad range of air to ground munitions and highly accurate navigation and attack system makes it possible for the aircraft to prosecute the surface targets both over the land or at the sea with the mission accomplished with a high degree of accuracy. These features bestow the multi-swing role capabilities to this highly touted fighter jet aircraft Tejas.
What is the status of the LCA programme?
- Two decades since the first flight, in February 2021, the Defence Ministry signed a ₹48,000 crore deal with HAL to supply 83 LCA-Mk1A to the IAF. This includes 73 LCA Tejas Mk-1A fighter aircraft and 10 LCA Mk-1 trainer aircraft at the cost of ₹45,696 crores along with the design and development of infrastructure sanctions worth ₹1,202 crores.
- The MK-1A will have over 40 modifications over the MK1 variant including some major ones like a new Electronic Warfare system, Advanced Electronically Scanning Array (AESA) radar, Beyond Visual Range (BVR) missiles and network warfare system including Software Defined Radio (SDR).
- The first IOC fighter aircraft was delivered in 2016 and the first LCA squadron No. 45 “Flying Daggers” in the IAF was formed in July 2016 with two aircraft. The first squadron is now complete and the second LCA squadron No. 18 ‘Flying Bullets’ was operationalized in May 2020.
What is the way forward?
- To ramp up production, HAL has already set up two additional assembly lines which are operational. Some back-end activities are also being finished at the moment, according to HAL.
- The indigenous content in LCA is currently about 52% and HAL said it is looking at ways to increase it to 65%.
- An ambitious fifth-generation fighter aircraft Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), and a new Twin Engine Deck Based Fighter (TEDBF) to operate from the Navy’s aircraft carriers are being developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA).
- The AMCA is envisaged as a 25-tonne aircraft with an internal carriage of 1,500kg of payload and a 5,500kg external payload with 6,500kg of internal fuel with the rollout planned in 2024 and first flight planned in 2025, according to ADA officials.
- The TEDBF is being designed based on lessons learned from the Naval LCA programme and the first flight is planned for 2026. In addition to supplying to the IAF, HAL is aggressively pitching its helicopters and Tejas to countries in South East Asia and West Asia and LCA is in the contest in Malaysia.
THE DISASTER MANAGEMENT
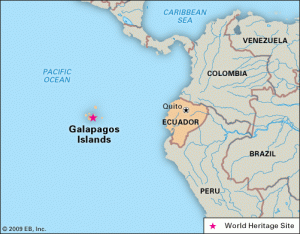
5. THE GALÁPAGOS ISLANDS VOLCANO ERUPTS
THE CONTEXT: According to Ecuador’s Geophysical Institute the tallest mountain in the Galápagos islands has erupted, spewing lava down its flanks and clouds of ash over the Pacific Ocean.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The 1,701-meter volcano is one of the numerous active volcanos in the Galápagos, which are nearly 1,000km (600 miles) from mainland South America.
- A cloud of gas and ash from Wolf Volcano rose to 3,793 meters (12,444 feet) above sea level after the eruption.
- The volcano last erupted in 2015.
Value Addition:
A volcano is an opening in the earth’s crust through which gases, molten rocks materials (lava), ash, steam etc. are emitted outward in the course of an eruption. Volcanic activity is an example of an endogenic process.

Difference between Magma and Lava:
- Magma is the term used to denote the molten rocks and related materials seen inside the earth. A weaker zone of the mantle called the asthenosphere usually is the source of magma.
- Once this magma came out to the earth’s surface through the vent of a volcano, it is called the Lava. Therefore, Lava is nothing but the magma on earth’s surface.
- The process by which solid, liquid and gaseous material escape from the earth’s interior to the surface of the earth is called Volcanism.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES AND INITIATIVES IN NEWS
6. NEW MICROCHIP IN E-PASSPORTS
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of External Affairs signed an agreement with Tata Consultancy Services Limited for the second phase of the Passport Seva Programme (PSP), one of the several Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) of the Government of India.
THE EXPLANATION:
The latest agreement will facilitate the next phase of the PSP termed PSP-V2.0. The $1 billion agreement will focus on faster delivery of passports to the citizens and create a more effective integration between various wings of the Government like the MEA and the local police network that can work in harmony for verification of applicants and quick tracing in case of emergency situations.
What are the features of the new passport initiative programme?
- The new initiative is aimed at creating a digital platform that would be “transparent, more accessible and reliable” and that it would be backed by a trained workforce. This will create a state-of-the-art digital ecosystem, overhaul existing processes and integrate various wings of Government that is involved in the issuance of passports.
- The overall system would be connected to all the Indian diplomatic missions abroad and will allow monitoring and supervision through the state-of-art Network Operation Centre, and Security Operation Centre.
- “The programme has recently been connected to more than 176 Indian Missions/Posts through Global Passport Seva Programme (GPSP), providing seamless delivery of passport services to the Indian diaspora,”
What will be the new features of PSP-V2.0?
- The new programme is expected to have technology upgrades including the use of the latest biometrics technology, Artificial Intelligence, Advanced Data Analytics, Chat-Bot, Auto-response, Natural Language Processing, Cloud Enablement.
- The newest feature under the PSP-V2.0 will be the issuance of the new generation of passports called e-passports. Under this, new and renewed passports will be fitted with a microchip that will hold all biometric information regarding the applicants
How different will e-passports be from the current passports?
- Current passports are scanned at the immigration counters to reveal the travel record of the citizen using the same document and the e-passport is also expected to perform the same function. However, unlike the current passports, the e-passport users will have physical storage of their biometric data in a chip which will reduce risk of data leakage.
THE PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
QUESTION OF THE DAY 10TH JANUARY 2022
Q1. Consider the following statements about AIIB.
- It is a multilateral development bank headquartered in Beijing.
- India is the second-largest shareholder in AIIB.
- Japan is not a member of AIIB.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Spread the Word
