WINTER PARLIAMENT PROCEEDINGS 2021
MODERNIZATION OF AGRICULTURE
THE CONTEXT: Agriculture exports excluding allied products (Marine, Meat etc.) have set a record in 2020-21 with total Agri export of Rs. 213513.38 Crore which has been highest since last two decades.
THE EXPLANATION:
According to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmer’s Welfare, the Government has taken various steps to modernize agriculture for sustainable growth in the agriculture sector. Some of the interventions in this direction are:
- Creation of a network of 722 KrishiVigyanKendras (KVKs) for dissemination of knowledge and information about modern technology etc.
- Initiatives under Agriculture Technology Management Agency (ATMA) Scheme like Extension Reforms, Mass Media Support to Agricultural Extension, Kisan Call Centres, Agri-Clinics and Agri-Business Centres, Exhibitions/ Fairs etc.
- Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM)
- Promotion of Agricultural Mechanization for In-Situ Management of Crop Residue in the States of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and NCT of Delhi.
- National Agriculture e-Market platform (e-NAM) has been established
- Soil Health Card (SHC) Scheme.
- Per Drop More Crop (PDMC)
- The mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture.
- Promotion of 10,000 FPOs.
The top 10 agriculture commodities which are in demand in the international market are Rice (other than basmati), rice-basmati, spices, sugar, cotton, oil-meals, castor oil, fresh fruits, tea and fresh vegetables.
COVERAGE OF PMKSY-PDMC
THE CONTEXT: According to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmer’s Welfare, the Per Drop More Crop Component of the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY-PDMC) scheme is operational in the country from 2015-16 which focuses on enhancing water use efficiency at the farm level through Micro Irrigation (MI).
THE EXPLANATION:
- According to the Ministry, the total area of 59.37 lakh ha has been covered under Micro Irrigation in the country under PMKSY-PDMC from 2015-16 to 2021.
- During the last three years, Central assistance of Rs. 8141.96 crore was released to States and an area of 32.68 lakh ha covered under Micro Irrigation through the scheme.
- With the objective of facilitating the States in mobilising resources for expanding coverage of micro-irrigation, a Micro Irrigation Fund (MIF) with a corpus of Rs. 5000 crore was created with National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) during 2018-19.
- The States are encouraged to access MIF for innovative projects / additional incentives to farmers for the installation of Micro Irrigation systems by interest subvention of 3% than the cost of funds mobilized by NABRAD from the market. So far, projects with loans under MIF amounting to Rs. 3970.17 Crore have been approved for 12.81 lakh ha of Micro Irrigation area.
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY-PDMC)
The PMKSY- PDMC is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme and the funds under the scheme are shared between the Central Government and State Government in the ratio of 60:40 for all States except the North Eastern and Himalayan states wherein sharing pattern is 90:10. In the case of Union Territories, the funding pattern is 100% granted by the Central Government.
Its objectives are:
- Convergence of investments in irrigation at the field level,
- To expand the cultivable area under assured irrigation (Har Khet ko pani),
- To improve on-farm water use efficiency to reduce wastage of water,
- To enhance the adoption of precision-irrigation and other water saving technologies (More crop per drop),
- To enhance recharge of aquifers and introduce sustainable water conservation practices by exploring the feasibility of reusing treated municipal based water for peri-urban agriculture and attract greater private investment in a precision irrigation system.
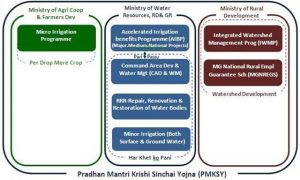
STATUS OF NIRBHAYA FUND
THE CONTEXT: According to the Ministry of Home Affairs, the Centre approved Rs 3856.70 crore under the Nirbhaya Fund for projects for women safety in 2021
THE EXPLANATION:
- The data states that the Centre released Rs 2282.59 crore of Rs 3856.70 crore allocated funds to the states and union territories. The funds are released to the states and union territories, as per project guidelines, in instalments, and depending on the demand specific to each project.
- As per information available, the total budgetary allocation for Nirbhaya Fund by the Government in the last three years is as below:
Year Allocation (in Rs. Crore)
2018-19 550.00
2019-20 550.00
2020-21 1355.23
What is Nirbhaya Fund?
Post-2012, Nirbhaya Gang rape case, a dedicated fund was set up in 2013 with the focus on implementing the initiatives aimed at improving the security and safety of women in India. The fund was called “Nirbhaya Fund”, Nirbhaya meaning fearless, the pseudonym given to the gang-rape victim to conceal her identity.
The government’s contribution towards the non-lapsable corpus fund was Rs. 1000 crores.
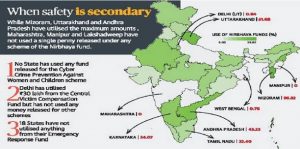
Nodal agency: Department of Economic Affairs under the Ministry of Finance is responsible for the administration of the fund. While the Women and Child Development Ministry is the nodal agency for expenditure from the Nirbhaya Fund. It is involved in appraising, reviewing, and monitoring the progress of those schemes sanctioned under the Nirbhaya Fund. Earlier, it was the one releasing the funds but now it examines the programs submitted to it by the states under the Nirbhaya scheme, approves them and recommends to the Department of Economic affairs for allocating funds.
Under the Nirbhaya Fund, the Centre gives money to the states, which in turn spend it on programs meant for ensuring women’s safety.
Nirbhaya Fund – 3 Schemes
Considering the need to have a schematic intervention and a complete mechanism for providing support to the women in distress, three schemes are being implemented by the Ministry of Women and Child Development under the Nirbhaya Fund.
Keeping in mind the need to have schematic interventions and a proper mechanism for handholding of women in distress, 3 schemes have been implemented by the Ministry of Women and Child Development
- ‘One Stop Centre’
- ‘Universalisation of Women Helpline
- ‘Mahila Police Volunteer’
Schemes being implemented by the Ministry of Home Affairs are as follows:
- Emergency Response Support System
- Central Victim Compensation Fund
It aims at creating awareness among the representatives of the public, different agencies of the government, scientists, industry and the communities on the threat posed by climate change and the steps to counter it. There are 8 National Missions.
THE INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
THE GLOBAL GATEWAY PLAN
THE CONTEXT: The European Commission announced a plan to mobilise €300 billion ($340 billion) in public and private infrastructure investment around the world, a move seen as a response to China’s Belt and Road strategy.
THE EXPLANATION:
- “Global Gateway will aim at mobilising investments of up to 300 billion euros between 2021 and 2027… bringing together resources of the EU, member states, European financial institutions and national development finance institutions.
- The money to be made available will not come from EU and member state coffers, and the plan will need funding from international institutions and from the private sector if it is to get anywhere near its target.
- The West, however, sees it as a tool for China to influence poorer countries. They criticise Beijing for inciting emerging economies to take on too much debt and allege the secretive tender process is prone to corruption.
- The EU strategy is an offshoot of a plan by G7 countries to offer developing countries an alternative to the Belt and Road Initiative, presented in June at the industrial powers’ summit in Cornwall.
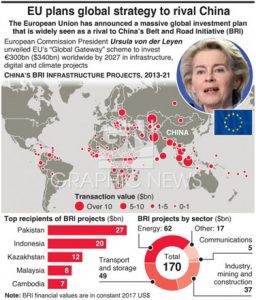
China’s Belt and Road initiative:
- China Belt and Road initiative is a flagship project of the country launched in 2013. Officially, it aims to develop land and sea infrastructure to better connect China to Asia, Europe and Africa for trade and development. Many countries have become a part of this initiative. INDIA is not a part of the BRI project.
- There is a growing concern that China is using the BRI as a tool to influence poorer countries. China is being blamed for pushing forward financially unviable infrastructural projects which could push the countries into a debt trap.
- There are also concerns that China’s contractual terms ignore abuses of human, labour and environmental rights while also being a major cause of corruption in the recipient countries.
THE ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
- KYHYTYSUKA SACHICARUM: NEW MARINE REPTILE
THE CONTEXT: An international team of researchers has discovered a new marine reptile. The specimen, a metre-long skull, has been named Kyhytysuka sachicarum.
THE EXPLANATION:

- A new 130-million-year-old swordfish-shaped marine reptile fossil sheds light on the evolution of hypercarnivory of these last-surviving ichthyosaurs.
- It is an extinct species. It was discovered from fossils found in central Columbia. Earlier scientists believed that it belonged to Platypterygius genus. Recently, it was discovered that it is a different species. And thus it is now named as Kyhytysuka sachicarum.
Kyhytysuka sachicarum honours Muisca tribal
- Kyhytysuka means “the one that cuts with something sharp”. The word belongs to the indigenous language of central Columbia.
- The new species has been named Kyhytysuka sachicarum to honour the Muisca culture of central Columbia. The Muisca are also called Chibcha. They were conquered by the Spanish in 1537. They were mainly agrarians. They also extracted salt from the sea.
Features of Kyhytysuka
- It was a mid–sized ophthalmosaurian. The Ophthalmosaurus belonged to the Jurassic period.
- It had extremely large sized eyes, dolphin – shaped body.
- The jaws had many robust teeth.
- It had several adaptations.
- It was a macro predatory vertebrate hunter, which means, it hunted larger vertebrates. Vertebrates are organisms with a backbone. Organisms without a backbone are called invertebrates.
- The species were mostly found in shallow waters.
Unique Feature: Teeth
- The dentary is the longest bone of the species. It measures 720 mm. The dentition is the most unique feature of the species. The teeth are seated in continuous grooves. The teeth are slightly curved posteriorly. Also, an alternating wave-like pattern is observed.
IMD DATA ON RAINFALL
THE CONTEXT: According to the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) the country saw 645 events of heavy rainfall and 168 events of very heavy rainfall in November 2021 the highest in the month in five years.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The IMD said India recorded 11 extremely heavy rainfall (more than 204.5 mm) events in November 2021 equalling the number reported last year. The country reported zero, four and one events of extremely heavy rainfall in November in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
- Peninsular India reported most of the extremely heavy to very heavy rainfall events which claimed 44 lives in Andhra Pradesh, 16 in Tamil Nadu, 15 in Karnataka and three in Kerala .
- Peninsular India comprises five meteorological subdivisions — Tamil Nadu, Puducherry and Karaikkal; coastal Andhra Pradesh and Yanam; Rayalaseema; Kerala and Mahe, and South Interior Karnataka.
- The IMD also said the region is most likely to see above-normal rainfall (more than 132% of the long period average) in December.
- Based on the data of the 1961-2010 period, the long period average of rainfall in peninsular India in December is 44.54 mm.
- To put things in perspective, the number of heavy rainfall events this November was more than the total such events in the last four years — 247 in 2020; 116 in 2019; 135 in 2018 and 139 in 2017.

What is a Retreating Monsoon?
During the months of October-November, the south-west monsoon winds become weaker and start to retreat from the skies
of North India. This phase of the monsoon is known as the retreating monsoon.
Impact of Retreating Monsoon
The retreating monsoon brings rainfall in an uneven amount to different places across India. Some places receive heavy rainfall and places that witness scanty rainfall.
Areas of Heavy rainfall
- The western part of Western Ghats (200-400cm)
- North-eastern India (Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, etc)
Areas of low rainfall
- Karnataka
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
‘1,160 ELEPHANTS KILLED IN A DECADE’
THE CONTEXT: According to the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), a whopping 1,160 elephants were killed in the country for reasons other than natural causes in the 10 years up to December 31, 2020.
THE EXPLANATION:

- While electrocution claimed the lives of 741 elephants, train hits led to the death of 186 pachyderms, followed by poaching (169) and poisoning (64).
- Karnataka and Odisha lost 133 elephants each to electrocution during the period and Assam reported 129 deaths. Among elephant casualties due to train hits, Assam stood first with 62 deaths, followed by West Bengal at 57. A total of 169 elephants were killed by poachers in the 10 years and Odisha reported the highest of 49, followed by Kerala 23. Assam reported the highest number of elephants poisoned, 32, and Odisha stood second with 15.
- According to the Ministry, India had a total of 29,964 wild elephants as per an estimate done in 2017. The southern region comprising Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra accounted for the highest population — 14,612 elephants.
- A Permanent Coordination Committee has been constituted between the Ministry of Railways and the MoEFCC for preventing elephant deaths due to train hits.
Value Addition:
Elephants
- There are three subspecies of Asian elephants – the Indian, Sumatran and Sri Lankan. The Indian has the widest range and accounts for the majority of the remaining elephants on the continent.
- IUCN Red List of threatened species status- African elephants are listed as “vulnerable” and Asian elephants as “endangered”.
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) status- Appendix I. Appendix I lists species that are the most endangered among CITES-listed animals and plants. They are threatened with extinction and CITES prohibits international trade in specimens of these species except when the purpose of the import is not commercial, for instance for scientific research.
Conservation Efforts
- Project Elephant was launched by the Government of India in the year 1992 as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- Establishment of elephant reserves and adoption of the “World Elephant Day” (August 12) to help conserve and protect elephants in India and improve their welfare.
- ‘Gaj Yatra’ is a nationwide awareness campaign to celebrate elephants and highlight the necessity of securing elephant corridors.
- The Wildlife Trust of India (WTI), had come out with a publication on the right of passage in 101 elephant corridors of the country in 2017, stressed on the need for greater surveillance and protection of elephant corridors.
- The Monitoring the Killing of Elephants (MIKE) programme launched in 2003 is an international collaboration that tracks trends in information related to the illegal killing of elephants from across Africa and Asia, to monitor the effectiveness of field conservation efforts.
THE BUTTERFLY SPECIES RECORD INCREASE
THE CONTEXT: The butterfly survey was conducted by the Kerala Forest Department and the Travancore Nature History Society (TNHS).
THE EXPLANATION:

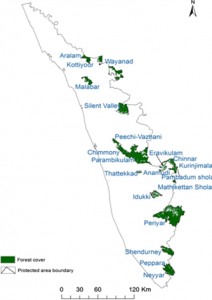
- A butterfly survey at the Peechi-Vazhani wildlife division has recorded a remarkable increase in the species’ numbers. Southern Birdwing, the largest butterfly in India, and Grass Jewel, the smallest, were found during the survey. Buddha Peacock, the State butterfly of Kerala, was also recorded. Of the 326 found in Kerala, 156 species were recorded in the 242-sq. km. division.
- Peechi-Vazhany Wildlife sanctuary had 132 species of butterflies, Chimmony had 116 species, while Chulannur recorded 41 species. The survey noted 80 species, almost double, to the older record of Peechi-Vazhany, 33 to Chimmony, and 41 species to Chulannur.
- “The survey marks the beginning of a series of biodiversity assessments to prepare a new management plan for the region. It has a specific section targeting invasive species that are a threat to the indigenous biodiversity”.
- Other notable species are Nilgiri Grass Yellow, Travancore Evening Brown, Malabar Flash, Orange Tailed Awl, Southern Spotted Ace and Common Onyx. The report of Common Tinsel at Chulannur was another highlight. Altitudinal migration of Common Albatross was recorded in Chimmony.
- The division had 23 species of butterflies red-listed by the IUCN. Sixty-three species were protected under the Indian Wildlife Protection Act 1972. The survey teams also recorded birds, odonates, reptiles, amphibians, and spiders — 152 bird species were recorded in Peechi-Vazhany, in Chimmony and 77 in Chulannur.
Peechi-Vazhani wildlife Sanctuary
- The sanctuary was established in 1958 consisting of Palappilli- Nelliyampathi forests including the area of Chimmony Wildlife sanctuary and is the second oldest sanctuary in Kerala.
- Kuthiran Tunnel, first road tunnel in Kerala, runs through the Peechi-Vazhani wildlife sanctuary.
THE GOVERNMENT SCHEMES/ INITIATIVES IN NEWS
SUPPORT FOR MARGINALIZED INDIVIDUALS FOR LIVELIHOOD & ENTERPRISE (SMILE)
THE CONTEXT: The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has formulated a scheme “SMILE – Support for Marginalized Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise”, which includes sub-scheme – “Comprehensive Rehabilitation of persons engaged in the act of Begging”.
THE EXPLANATION:
The scheme covers several comprehensive measures including welfare measures for persons, who are engaged in the act of begging. The focus of the scheme is extensively on rehabilitation, provision of medical facilities, counselling, basic documentation, education, skill development, economic linkages and so on.
About Support for Marginalized Individuals for Livelihood & Enterprise (SMILE)
- Support for Marginalized Individuals for Livelihood & Enterprise (SMILE) which is a new Scheme after merger of existing Schemes for Beggars and Transgenders.
- The budgetary outlay is Rs 70.00 crore.
- Objective: is to cover the welfare measures for both transgender persons and persons who are engaged in the act of begging.
- Focus: On rehabilitation, provision of medical facilities, counseling, education, skill development etc with the support of State Governments/UTs/Local Urban Bodies, Voluntary Organizations, Community Based Organizations (CBOs) and institutions etc.
- It is estimated that an approximate 60,000 poorest persons would be benefited under this scheme for leading a life of dignity.
Comprehensive Rehabilitation Scheme of Beggars
Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
Highlights:
- It will be a comprehensive scheme for persons engaged in the act of begging.
- The scheme will cover identification, rehabilitation, provision of medical facilities, counselling, education, skill development with the support of State Governments, Local Urban Bodies and Voluntary Organizations.
- The scheme will be implemented in the selected cities having large concentrations of Beggar community during the financial year 2020-2021.
- The government is working in a mission mode with complete commitment to ‘Har Ek Kaam, Desh Ke Naam’.
Implementation
- 100% Assistance under the Scheme shall be provided to the States/UTs for its implementation.
- During the year 2019-20, this Ministry has released an amount of Rs. One Crore to National Institute of Social Defence (NISD) and Rs. 70.00 Lakh to National Backward Classes Finance & Development Corporation (NBCFDC) for skill development programmes for beggars.
National Backward Classes Finance & Development Corporation:
- NBCFDC was incorporated 13th January 1992 as a non-profit company under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India to improve and develop the economic activities for the members of Backward Classes who are living below double the poverty line.
- The Corporation can assist loans for their self-employment ventures in sectors like agriculture, transport and service etc.
- NBCFDC also provides Micro Financing through SCAs/ Self Help Groups (SHGs).
- The Corporation can assist a wide range of income generating activities to assist the poorer section of these classes in skill development and self-employment ventures.
PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Q1. Which one of the following effects of the creation of black money in India has been the main cause of worry to the Government of India?
a) Diversion of resources to the purchase of real estate and investment in luxury housing.
b) Investment in unproductive activities and purchase of precious stones, jewellery, gold etc.
c) Large donations to political parties and growth of regionalism.
d) Loss of revenue to the state Exchequer due to tax evasion.
ANSWER FOR DECEMBER 1ST 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
ANSWER: C
Spread the Word