INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
1. THE CABINET APPROVED PM GATISHAKTI NATIONAL MASTER PLAN
THE CONTEXT: The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) has approved PM GatiShakti National Master Plan including an institutional framework for rolling out, implementation, and monitoring and support mechanism for providing multi-modal connectivity.
THE EXPLANATION:
- CCEA has also approved formation, composition and terms of reference for Network Planning Group (NPG) consisting of heads of Network Planning wing of respective infrastructure ministries and it will assist the EGOS.
- In view of the complexities involved in the overall integration of networks, enhancing optimization to avoid duplication of works for holistic development of any region as well as reducing logistics costs through micro-plan detailing, the Technical Support Unit (TSU)is approved for providing the required competencies. The structure of TSU has also been approved.
- shall have domain experts from various infrastructure sectors as Aviation, Maritime, Public Transport, Rail, Roads & Highways, Ports, etc. and Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) as Urban & Transport Planning, Structures (Roads, Bridges & Buildings), Power, Pipeline, GIS, ICT, Finance/Market PPP, logistics, Data Analytics, etc.
- The PM GatiShakti NMP is intended to break Departmental Silos and bring in more holistic and integrated planning and execution of projects with a view to addressing the issues of Multi-Modal connectivity and last-mile connectivity. This will help in bringing down the logistics cost. This will translate into enormous economic gains to consumers, farmers, youth as well as those engaged in businesses.
- With this approval, the rollout of PM GatiShakti will get further momentum which will result in a holistic and integrated planning framework for infrastructure development in the country.
- With this approval, PM GatiShakti shall bring various stakeholders together and help integrate different modes of transportation. PM Gatishakti NMP for multi-modal connectivity will ensure holistic governance at the Centre of which are people of India, industries of India, manufacturers of India and farmers of India.
SOURCE: PIB
2. INDIA INTERNET GOVERNANCE
THE CONTEXT: India Internet Governance Forum to be conducted in November 2021 to bring all stakeholders of internet governance on a single platform.
THE EXPLANATION:
- A curtain-raiser event of the India Internet Governance Forum (IIGF) concluded with an interesting insight into the roadmap for Digitisation in India.
- The curtain raiser event, is a precursor to the India Internet Governance Forum (IIGF), which will be conducted jointly by the Ministry of Electronics and IT, NIXI and Multistakeholder Group from 8th to 11th of November, 2021.
- The theme of IIGF 2021 is ‘Empower India through Power of Internet’. The event will witness enlightening discussions on the road to Digitization in India.
- The salient feature of the event will be the three plenary sessions on themes- India &Internet- India’s Digital Journey and Her Global Role, Equity, Access & Quality – High-speed Internet for All and Cyber Norms and Ethics in Internet Governance.
About IIGF
- The India Internet Government Forum is an initiative associated with the UN Internet Governance Forum (UN-IGF).
- The Internet Governance Forum (IGF) is a multi-stakeholder platform bringing representatives together from various groups to discuss public policy issues related to the Internet.
SOURCE: PIB
3. SUCCESS STORY OF VACCINATION IN INDIA
THE CONTEXT: India has completed vaccination of 100 crore doses on October 21, 2021, in just about nine months since starting vaccination.
THE EXPLANATION:
- India took 85 days to touch the 10-crore vaccination mark, 45 more days to cross the 20-crore mark and 29 more days to reach the 30-crore mark.
- The country took 24 days to reach the 40-crore mark from 30-crore doses and then 20 more days to surpass the 50-crore vaccination mark on August 6. It then took 76 days to go past the 100-crore mark.
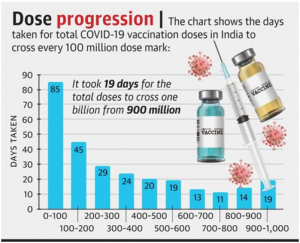
- India’s vaccine drive is an example of what India can achieve if citizens and the Government come together with a common goal in the spirit of Jan Bhagidari. When everyone takes ownership, nothing is impossible.
- People’s participation is the biggest strength of democracy.
- Only a handful of countries have developed their own vaccines. The credit should be given to Indian scientists and entrepreneurs for rising to the occasion.
- The Government partnered with the vaccine makers right from day one and gave them support in the form of institutional assistance, scientific research, funding, as well as accelerated regulatory processes.
- All Ministries of the Government came together to facilitate the vaccine makers and remove any bottlenecks as a result of our ‘whole of Government’ approach.
- In a country of the scale of India, it is not enough to just produce. The focus has to be on last-mile delivery and seamless logistics.
- These efforts were complemented by a robust tech platform in CoWIN. It ensured that the vaccine drive was equitable, scalable, trackable, and transparent.
SOURCE: TH
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
4. SC: ACT ON ILLEGAL CONSTRUCTION IN KAZIRANGA
THE CONTEXT: The Central Empowered Committee (CEC), constituted by the Supreme Court, has asked the Assam government to act on illegal construction in the identified wildlife corridors of the Kaziranga National Park and Tiger Reserve.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The court’s order disallowed new construction on private lands that form part of the nine identified animal corridors of the tiger reserve, considered the world’s safest address of the one-horned rhinos.
- The court had also banned all types of mining on these corridors.
SOURCE:TH
5. INDIAN RAILWAYS LIKELY TO BECOME WORLD’S FIRST ‘NET-ZERO’ CARBON EMITTER BY 2030
THE CONTEXT: Indian Railways is taking a multi-pronged approach to go green and decarbonise — from increasing its sourcing of renewable energy (RE) to electrifying its traction network and reducing its energy consumption. Its goal is to become a ‘net-zero’ carbon emitter by 2030. And it has ambitious plans to accomplish this goal.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The plan includes a significant goal of electrifying the entire network by December 2023. With the complete electrification of Indian Railways targeted by the financial year 2024, the total traction requirement is expected to increase to around 3,400 MW. It will be the world’s largest 100 per cent electrified rail transportation system by then.
- The second pillar consists of using solar power to meet its electricity needs, as well as having an environmentally friendly infrastructure and a microlevel cleanliness drive.
- The Indian Railways is committed to using solar energy to meet its traction power needs and becoming a fully green mode of transportation. It has decided to build massive solar power plants on its vacant land.
- The ministry has started up a 2.5-MW solar project in Diwana, Haryana, with state transmission unit connectivity. Work on a third pilot with a capacity of 50 MW has begun in Bhilai (Chhattisgarh).
- Some challenges the Indian Railways faces in terms of solar plant proliferation:
- No-objection certificate for open access: Open access has been granted as a deemed licensee in 11 states and the Damodar Valley Corporation area. The no-objection certificate (NoC) for open access to electricity flow for railways in West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala and Telangana has not been operationalised due to regulatory challenges that the railways are vigorously pursuing. If approval for procuring power through open access is granted in these states, solar deployment may increase.
- Wheeling and banking provision: Full deployment of solar potential will become more feasible if states provide wheeling and banking arrangements.
- The merger of solar purchase obligation and non-solar purchase obligation: The availability of a banking facility and the consolidation of solar and non-solar obligations will allow the railways to meet their Renewable Purchase Obligations.
- Unrestricted net metering regulations: Unrestricted net metering for rooftop solar projects would hasten the deployment of railway solar plants.
SOURCE: DTE
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
6. INNOVATIONS FOR YOU
THE CONTEXT: NITI Aayog’s Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) has launched – “Innovations for You” an attempt to showcase the success stories of Atal Innovation Mission’s Startups in different domains.
THE EXPLANATION:
- These startups have worked to create new, disruptive and innovative products, services, and solutions that can pave a path for a sustainable future.
- The first edition of this book is focused on innovations in Health Care and soon other sectors shall follow.
- The book is a compilation of 45health tech startups, incubated at Atal Incubation Centres spread across the country. These startups are leveraging frontier technologies such as AI, IoT, ICT and others to provide socially relevant solutions to problems like anemia, Malaria, dental care, mental health, neonatal and child care and monitoring human vitals, among others.
ABOUT ATAL INNOVATION MISSION OF NITI AAYOG
- The Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) is the Government of India’s flagship initiative to promote innovation and entrepreneurship culture in the country.
- AIM is mandated to create an umbrella structure to oversee the innovation ecosystem of the country and revolutionize the innovation eco-system – touching upon the entire innovation life cycle through various programs.
- The Atal Tinkering Laboratories (ATLs) create innovators, Atal Incubation Centres and support to Established Incubation Centres ensure innovations are taken to the market and help create enterprises around these innovations, Atal Community Innovation Centres are promoting benefits of technology-led innovation to the unserved/underserved regions of India.
- Atal New India Challenges are creating product and service innovations having a national socio-economic impact and ARISE ANIC Challenges promote innovation in a phased manner in the MSME/Startup sector.
SOURCE: PIB
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
7. PAKISTAN RETAINED FATF’S GREYLIST AGAIN
THE CONTEXT: The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) retained Pakistan in the ‘greylist’ yet again, observing that it needed to further demonstrate that investigations and prosecutions were being pursued against the senior leadership of U.N.-designated terror groups, which include Lashkar-e-Taiba, Jaish-e-Mohammed, al-Qaeda and the Taliban.
THE EXPLANATION:
- The FATF had asked Pakistan to work on the remaining recommendation by demonstrating that terror financing investigations and prosecutions targeted senior leaders and commanders of the U.N.-designated terrorist groups.
- It had advised that Pakistan should continue to work to address its six strategically important deficiencies, which included enhancing international cooperation by amending the money-laundering law and demonstrating that assistance was being sought from foreign countries in implementing the UNSCR 1373 designations.
ABOUT FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE (FATF)
- It is the global money laundering and terrorist financing watchdog.
- It was established by the G-7 Summit that was held in Paris in 1989.
- The Secretariat is located at the OECD Headquarters in Paris.
- Members- 39
- On June 25, 2010, India was taken in as the 34th country member of FATF.
- The FATF has developed the FATF Recommendations, or FATF Standards, which ensure a coordinated global response to prevent organised crime, corruption and terrorism.
- The FATF also works to stop funding for weapons of mass destruction.
- FATF has 2 types of lists:
-
- Black List: Countries knowns as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs) are put on the blacklist. These countries support terror funding and money laundering activities. The FATF revises the blacklist regularly, adding or deleting entries.
- Grey List: Countries that are considered a safe haven for supporting terror funding and money laundering are put in the FATF grey list. This inclusion serves as a warning to the country that it may enter the blacklist.
- Consequences of being in the FATF grey list: Those countries in the grey list may face economic sanctions from IMF, World Bank, ADB, Problem in getting loans from IMF, World Bank, ADB and other countries, Reduction in international trade, International boycott
SOURCE: TH
PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Q1. Consider the following statements about FATF:
- It is the global money laundering and terrorist financing watchdog.
- It was established by the G-20 Summit that was held in Paris in 1989.
- The Secretariat is located at the OECD Headquarters in Paris.
- India is the founding member of FATF.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 1, 3 and 4 only
d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
ANSWER FOR OCTOBER 20, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Answer: B
Explanation:
- Kushinagar – Mahaparinirvana
- Lumbini – Birth
- Sarnath – Dhamma Chakra Pravartana
- Bodh Gaya – Nirvana

