INDIAN POLITY, GOVERNANCE AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
1. 1183 MOBILISATION CAMPS ORGANISED UNDER THE DDU-GKY
THE CONTEXT: As part of the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav (AKAM) celebrations, around 1183 ‘mobilisation camps’ were organised across the country under the Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY) programme between 13th and 19th August, 2021.
ABOUT DDU-GKY:
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY) launched on the 25th September, 2014, is a nationwide placement-linked skill training program funded by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD), Government of India (GoI).
- DDUGKY seeks to build the placement-linked skills of the poor rural youth and place them in wage employment across various sectors of the economy.
- The programme has an outcome led design with guaranteed placements for at least 70% trained candidates.
- The DDU-GKY programme is being implemented in 27 states and 3 UTs for rural poor youth with an emphasis on placements.
- More than 871 PIAs are training rural poor youth in close to 611- job roles through more than 2381 training centers.
- Cumulatively 10.94 lakh youth have been trained and 7.07 lakh youth have been placed till 31st July, 2021.
Reference: Indian express
2. AFGHANISTAN RETURNEES PROVIDED FREE POLIO VACCINATION
THE CONTEXT: The Health Ministry has decided to vaccinate returnees from Afghanistan with free polio vaccines as a preventive measure.
ANALYSIS:
- India received its polio-free certification along with the entire southeast Asia region on March 27, 2014. However, wild polio virus cases continue to be reported in neighbouring Pakistan and Afghanistan — the last two polio-endemic countries in the world.
- Failure to eradicate polio from these last remaining strongholds could result in as many as 200,000 new cases every year, within 10 years, all over the world.
- There are three types of wild polio viruses (WPV) — type 1, type 2, and type 3. Wild polio viruses are naturally occurring isolates known or believed to have circulated persistently in a community.
- The WHO has said that people need to be protected against all three types of the virus in order to prevent the occurrence of polio disease, and polio vaccination is the best protection.
Reference: The Hindu
ENVIRONMENT, GEOGRAPHY AND AGRICULTURE
3. MORE EARTHQUAKE OBSERVATORIES
THE CONTEXT: India to add 35 More Earthquake Observatories by end of this year and 100 more by year 2026.
ANALYSIS:
- In last six and a half decades since Independence, the country had only 115 Earthquake Observatories but now there is going to be a quantum leap in the number of Earthquake Observatories in India The Indian subcontinent is considered as one of the world’s most disaster-prone areas in terms of earthquakes, landslides, cyclones, floods, and tsunamis and the Government is taking all necessary steps to meet these challenges.
Reference: PIB
4. LARGEST FLOATING SOLAR PV PROJECT IN THE COUNTRY
THE CONTEXT: The National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) Ltd has commissioned the largest floating solar PV project of 25MW on the reservoir of its Simhadri thermal station in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
ANALYSIS:
- This is also the first solar project to be set up under the Flexibilisation Scheme, notified by the Government of India in 2018.
- The floating solar installation which has a unique anchoring design is spread over 75 acres in an RW reservoir.
- This floating solar project has the potential to generate electricity from more than 1 lakh solar PV modules.
- This would not only help to light around 7,000 households but also ensure at least 46,000 tons of CO2e are kept at arm’s length every year during the lifespan of this project.
- The project is also expected to save 1,364 million litres of water per annum. This would be adequate to meet the yearly water requirements of 6,700 households.
- The 2000MW coal-based Simhadri Station is the first power project to implement an open sea intake from the Bay of Bengal which has been functional for more than 20 years.
- NTPC is also planning to set up a hydrogen-based micro-grid system on a pilot basis at Simhadri.
- With a total installed capacity of 66900 MW, NTPC Group has 71 Power stations including 29 Renewable projects.
- NTPC has set a target to install 60 gigawatts (GW) of renewable energy (RE) capacity by 2032.
- NTPC is also India’s first energy company to declare its energy compact goals as part of the UN High-level Dialogue on Energy (HLDE).
Reference: PIB
5. OIL & GAS COMPANIES EXPLORING GREEN ENERGY OPTIONS
THE CONTEXT: State-owned Oil and Natural Gas Corporation is considering inorganic investments to reach a target of 10 GW of installed renewable energy capacity by 2040. Other oil and gas PSUs are also investing in renewable energy.
ANALYSIS:
- Global moves to reduce carbon emissions to slow down climate change have led to oil and gas companies around the world investing in renewable energy to reduce their carbon footprint and diversify offerings.
- State-owned upstream and downstream oil and gas companies are also taking part in energy investments to help achieve the government’s ambitious renewable energy targets.
- India is targeting 450 GW of installed renewable energy capacity by 2030 up from about 100 GW currently.
- India’s largest upstream oil and gas company, ONGC, is targeting 10 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2040, up from 178MW of renewable energy capacity at the end of FY20.
- GAIL is also looking at acquisitions to augment its 130 MW renewable energy portfolio. The company is aiming at reaching 1 GW of renewable capacity within 3-4 years.
- Indian Oil Corporation Ltd, India’s largest refiner, had a total installed renewable energy capacity of about 233 MW at the end of FY21. It has also set up 257 electric charging and battery swapping stations at 29 retail fuel outlets.
- The results of its battery swapping stations were positive and that the company was looking at a potential joint venture (JV) with Sun Mobility to provide battery swapping on a larger scale in the future. IOC is also setting up the first green hydrogen plant in India in Mathura.
- Indian Oil also has a JV with Israel-based battery technology startup Phinergy to develop aluminium-air technology based battery systems for electric vehicles and stationary storage.
- Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Ltd has tied up with Tata Power to set up electric vehicle charging at various retail points around the country. It has also set up about 133 MW of renewable energy capacity, including about 100 MW of wind energy capacity.
- Bharat Petroleum Corporation Ltd had installed renewable energy capacity of 43 MW at the end of FY20.
Reference: Indian express
6. DUST FROM THE ARABIAN DESERT IS MELTING HIMALAYAN GLACIERS AND AFFECTING THE SEAS
THE CONTEXT: Scientists say that catastrophic melting the glaciers is being exacerbated by dust blowing from West Asia.
ANALYSIS:
- Winds that sweep across Asia link the Hindu Kush Himalayas and the Gulf in an interconnected system. Globally, around 5 billion tonnes of desert dust from arid regions is swept into the atmosphere every year.
- These dust particles, travel long distances at an altitude of 2 km-5 km and reach the High Mountain Asia during summer. Dust from arid regions such as the Thar desert in Pakistan and Saudi Arabia gets lofted above the boundary layer [the lowest part of the planet’s atmosphere] of Earth by convection and gets transported to far places with wind at altitudes and deposited mainly above 3 km.
- The dust particles are thus deposited in the high Himalayan Mountains, blanketing glaciers in a layer of particles that are darker than snow.
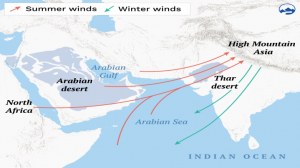
- Warming mountains mean warmer winds, which have begun to fundamentally shift monsoon patterns across Asia and West Asia.
- Widespread coral bleaching in the Gulf is the result of low shamal winds [strong north-westerly winds that blow across West Asia] during summer. Those shamal winds are generated by a pressure gradient driven by the monsoon. If the monsoon weakens, so will shamals, leading to more frequent and/or severe coral bleaching in the Gulf region.
- Altered monsoons have created the perfect conditions for a single-celled algal organism called Noctiluca scintillans to multiply by the millions.
Reference: SCROLL
7. CHILDREN IN INDIA AT EXTREMELY HIGH RISK OF CLIMATE CRISIS IMPACTS: UNICEF
THE CONTEXT: According to a new UNICEF report, India is one of four South Asian nations where children are most vulnerable to the effects of climate change, which jeopardise their health, education, and protection.
ANALYSIS:
- ‘The Climate Crisis Is a Child Rights Crisis: Introducing the Children’s Climate Risk Index’ (CCRI) is UNICEF’s first focused on children. It ranks countries based on children’s exposure to climate and environmental shocks such as cyclones and heatwaves, as well as their vulnerability to those shocks based on their access to essential services.
- Pakistan, Bangladesh, Afghanistan and India are among four South Asian countries where children are at extremely high risk of the impacts of the climate crisis, with a ranking of 14th, 15th, 25th and 26th respectively.
- CCRI has placed India as one of the 33 extremely high-risk countries with flooding and air pollution being the repeated environmental shocks leading to socio-economic adverse consequences for women and children.
- Approximately 1 billion children live in one of the 33 countries classified as extremely high-risk.
- It is estimated that more than 600 million Indians will face ‘acute water shortages’ in the coming years, while at the same time flash flooding is to increase significantly in the majority of India’s urban areas once the global temperature increase rises above 2° Celsius.
- Twenty-one of the world’s 30 cities with the most polluted air in 2020 were in India.
Reference: India today
INDIAN ECONOMY
8. FALL IN FOREX RESERVES
THE CONTEXT: Data released by the Reserve Bank showed that the nation’s forex reserves decreased by $2.099 billion to stand at $619.365 billion for the week ended August 13, as a result of a decline in core currency assets as well as gold reserves. In the previous week ended August 6, the foreign exchange had seen a rise of $889 million to reach a lifetime high of $621.464 billion.
ANALYSIS:
- The foreign currency assets (FCA), a vital component of the overall reserves, declined by $1.358 billion to reach $576.374 billion during the week ended August 13.
- Expressed in dollar terms, the FCA includes the effect of appreciation or depreciation of non-US currencies such as the euro, pound sterling and Japanese yen held in the foreign exchange reserves.
- The country’s reserve position with the IMF also decreased by $14 million to $5.111 billion.
- An increase in the forex reserves could bring some comfort to the government as well as the Reserve Bank in managing the nation’s external and internal financial issues at a time when the economy is facing Covid stress once again and it could have an impact on the gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate for the ongoing fiscal as states are announcing lockdowns.
- It is a big cushion in the event of any crisis on the economic front and enough to cover India’s import bill for a year. A higher forex kitty could also help strengthen the rupee against the dollar.
Reference: India express
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
9. EXERCISE KONKAN 2021
THE CONTEXT: Exercise Konkan 2021 was held between INS Tabar and HMS Westminster on 16 Aug 21 in the English Channel. .
ANALYSIS:
- The exercise included the participation of integral helicopters of the two ships and the Falcon Electronic Warfare aircraft.
- A wide range of exercises including co-ordinated anti-submarine procedures, firing drills; combined maritime picture compilation, combat formation maneuvering and replenishment at sea were conducted.
- These along with the diverse professional engagements held earlier in harbour, have enabled Exercise Konkan 2021 consolidate interoperability and helped cement the strong bonds of friendship the between the two navies.
- Konkan is an annual bilateral maritime exercise between the Indian Navy and the Royal Navy of United Kingdom. The Konkan series of exercises commenced in 2004.
Reference: PIB
10. EXERCISE MALABAR-21
THE CONTEXT: Indian Naval Ships Shivalik and Kadmatt arrived at Guam, an Island Territory of the USA. The two ships are scheduled to participate in the annual Exercise MALABAR-21, between navies of Australia, India, Japan and the USA.
ANALYSIS:
- MALABAR series of maritime exercises commenced in 1992 as a bilateral IN-USN exercise and has grown in stature over the years to include four prominent navies in the Pacific and Indian Ocean Region.
- Exercise MALABAR-21 will be conducted with USN, JMSDF and RAN at sea from 26-29 Aug 21.
- The exercise will provide an opportunity for common minded navies to enhance inter-operability, gain from best practices and develop a common understanding of procedures for Maritime Security Operations.
- MALABAR-21 would witness high-tempo exercises conducted between Destroyers’, Frigates, Corvettes, Submarines, Helicopters and Long Range Maritime Patrol Aircraft of the participating navies. Complex surface, sub-surface and air operations including Live Weapon Firing Drills, Anti-Surface, Anti-Air and Anti-Submarine Warfare Drills, Joint Manoeuvres and Tactical exercises will be conducted during the exercise.
- The participating Indian Ships Shivalik and Kadmatt are the latest indigenously designed and built, multi-role Guided Missile Stealth Frigate and Anti-Submarine Corvette respectively and form part of the Indian Navy’s Eastern Fleet based at Visakhapatnam, Eastern Naval Command.
- Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. it is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands and the largest island in Micronesia. Guam’s capital is Hagåtña.
Reference: PIB
11. HAZARAS- THE AFGHAN MINORITY GROUP HATED & TORTURED BY TALIBAN
THE CONTEXT: The Hazaras, an ethnic minority group in Afghanistan, have been subjected to repeated persecution and torture by the Taliban. According to a 2018 United Nations Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) report, most attacks by the Taliban on civilians in Afghanistan are directed towards the country’s minority population, most of whom are ethnic Hazaras.Just last month, the Taliban had captured and killed nine men of the Hazara community in Afghanistan.
WHO ARE THE HAZARAS?
- The Hazaras are the third largest ethnic group of Afghanistan and a religious minority.
- Around 10 per cent Muslims in Sunni-majority Afghanistan are Shiite and almost all of them are Hazaras. The Taliban as well as the Islamic State are Sunni groups.
- The Hazaras are said to be of Mongolian and Central Asian descent, and the descendants of Mongolian leader Genghis Khan, who invaded Afghanistan in the 13th Century.
- They are mostly based in the mountainous area of central Afghanistan known as ‘Hazaristan’, or the land of the Hazaras. Hazaras speak a dialect of Dari called Hazaragi, which is a Persian dialect.
HISTORY OF HAZARA PERSECUTION
- Not just the Taliban, Hazaras have been persecuted and repressed by the majority Sunni population in Afghanistan even as far back as in the reign of Pashtun leader Amir Abdul Rahman in the 1880s, when Sunni leaders had declared jihad on all Shias of the country.
- After the Taliban took over Afghanistan in 1996, ethnic minority groups, such as the Hazaras, and women bore the brunt of the Taliban torture.
- Even though the Constitution of Afghanistan gave equal rights to Hazaras in 2004 and former president Hamid Karzai had included Hazaras in his cabinet, the minority group continues to face discrimination and is placed at the bottom of the socio-economic ladder in the country.
WHY TALIBAN HATES THE HAZARAS?
- The Taliban’s hatred for the Hazaras is primarily due to their different sect and distinct ethnic origins, and they thus consider them to be ‘infidels’.
- Mohammed Alizada, a Hazara member of parliament, has said that the Hazaras’ “support for democracy and thirst for knowledge” have clashed with the strict religious and conservative values of the Taliban and Islamic State.
- Former Taliban governor of Mazar-e-Sharif Mullah Manon Niazi was also known to make provocative speeches at mosques and over radio against Hazaras.
- During the Taliban’s past rule in Afghanistan (between 1996 and 2001), Hazaras were massacred in 1998 in Mazar-e-Sharif and in central Bamian province in 2000 and 2001. The Buddhas of Bamian, gigantic statues that were held in respect by Hazaras because of their antiquity, were destroyed by the Taliban in 2001.
Reference: The print
Q 1. Consider the following statements about Guam island
1. Guam is territory of the United States.
2. It is located in the Polynesia.
Select the correct answer using code given below:
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both
a) None
Q 2. Which one of the following protected areas is well-known for the conservation of a sub-species of the Indian swamp deer (Barasinga) that thrives well in hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous ?
a) Kanha National Park
b) Manas National Park
c) Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
d) d) Tal Chhapar Wildlife Sanctuary
ANSWER FOR AUGUST 20, 2021 PRELIMS PRACTICE QUESTIONS (REFER RELEVANT ARTICLE)
Q.1 ANSWER: B)
Explanation:
- Therriaghat: Also in East Khasi Hills district, it is probably one of the best-preserved and most complete Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary sections in India. Most of the large vertebrates, planktons and many tropical invertebrates suddenly became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous period. A new assemblage of ammonites recorded recently probably represents a few of the last representatives just before the mass extinction in which the complete sub-class Ammonidea vanished from the face of the earth.
- Unakoti: This site in the Unakoti district has numerous rock-cut sculptures and temples made between the 7th and 9th centuries. The hilly environs and waterfalls are an added attraction at Unakoti, which means “one less than a crore”. The place is a historic Shaiva pilgrimage 172 km from Agartala. The central Shiva head, known as ‘Unakotiswara Kal Bhairava’ is about 30 feet high, including an embroidered headdress that is 10 feet high.
- Reiek Tlang: About 29 km from State capital Aizawl, this hill is a cuesta formed due to erosion of the tertiary sand shale alternations. Cuesta means a ridge with a gentle slope or dip on one side and a steep slope or scarp on the other. The local authorities host the annual anthurium festival at a heritage village near the Reiek peak.
- Stromatolite Park: At Mamley, about 80 km from State capital Gangtok, this site comprising stromatolitic (algal) development – boulder outcrops with circular structures – hosted in the limestone of Buxa Formation was discovered a little over a decade ago. It provides one of the rare examples of early life on earth in the Sikkim Himalayas. The age of the Buxa Formation is tentatively assigned as Meso-Neoproterozoic based on the available evidence of stromatolites and organic-walled microfossils.
Spread the Word


