Capital Market
-
- The main purpose of capital market is to ensure long-term investment and borrowing in the market.
- It is an alternative to taking loans from bank.
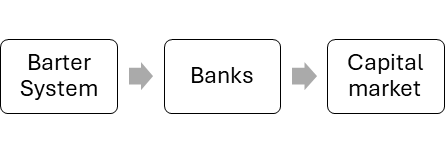
Evolution of formal financial market
-
- Investment Period: More than 1 year
- It strives to fund capital formation in the country by channelising surpluses into investments.
- It includes both debt (bonds) as well as equity (shares).
- It has dual regulations:
1. Government Securities (bonds): Regulated by RBI
2. Other issues: Regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
There are mainly 4 types of capital market instruments:
1. Equity (or Shares)
2. Debt (Bonds or debentures)
3. Mutual Funds, Exchange Traded Funds
4. Derivatives
Primary Market and Secondary Market
Primary Market
-
- When fresh capital is raised for the company
- It is also known as ‘new issue market’.
- Eg – Initial Public Offer (IPO), Follow-on Public Offer (FPO)
- Prior permission of SEBI is taken before issuing securities.
- Bonds as well as equity can be issued in the primary market.
Secondary Market
-
- It is a marketplace where trading of already issued securities happens.
- It is processed through stock exchanges.
- It involves both buying and selling of securities (known as trading).
- For this purpose, the participants need to have demat account.