1. Attitude
Attitude is a learned/acquired predisposition to behave in a favorable or unfavorable manner against the given object or It is about how people react to different situations/objects hence attitude is reflected through reaction or behavior. It is learnt through the process of socialization. Its quality depends on the nature of socialization.
2. Aptitude
Aptitude deals with the innate ability of humans. It’s about the ability to perform / future potential of humans to perform. Hence, it is about competence, ability or potential to perform. It is
-
- Innate or inborn
- Natural quality
- Inherent potential which a human is born
Example: Handwriting speed, efficiency, knowledge & skill.
Since aptitude is an inborn quality, it is difficult to completely transform it. Although via grooming and training, there can be improvement in aptitude.
3. Anonymity
It means being impersonal and serving the government without taking credit & becoming too much personal i.e. ‘Serving behind the curtain’.
4. Affect
It refers to emotions or feelings, likes, dislikes, emotional bonds and emotional intelligence evoked by a particular person, item or event. If people face objects where the affect is high, they would face emotional reactions. Objects which are generally family, friends, relatives, image of the country, self-image, respect and dignity and objects towards which an individual has the strongest likes and dislikes.
5. Accountability
It means answerability of civil servants (administration or government as the case maybe) which is enforced against a set of defined legal standards and values. Hence, accountability is considered as a formal / legal concept as it has defined standards.

6. Actionable accountability
It emphasizes the importance of translating citizen engagement and demands for accountability into tangible actions and consequences within the formal governance system. By integrating social and formal accountability mechanisms, actionable accountability seeks to enhance the effectiveness and enforceability of accountability processes, thereby promoting transparency, integrity, and good governance.
7. Behavior
Behavior is a reflection of attitude. Attitude can’t be observed. It is observed through the behavior ofa person. In general, behavior is a true reflection of attitude simply because one cannot hide true attitude for long as one lives in a social environment. It is also due to the integrity and consistency factor. Although behavior is considered a reflection of attitude, it is behavior which also brings changes in attitude.
A<—>B
Wrong behavior reminds us about the problems in the existing attitude and knowing about the object so that next time- it is changed & there is the right reaction. In fact, humans have a tendency of self-correcting behavior, and it is possible only when attitude is changed.
8. Bureaucratic ethics
It refers to the moral principles and standards that guide the behavior and decision-making of individuals working within bureaucratic organizations. It encompasses values such as integrity, accountability, impartiality, fairness, and adherence to legal and organizational rules and regulations.
9. Bureaucratic attitude
It typically refers to a behavior characterized by excessive adherence to rules, procedures, and hierarchical structures within an organization, rigid adherence to formalities, focus on process over outcome, resistance to change. Bureaucratic attitude is when bureaucracy adheres to rationality, neutrality, impartiality and objectivity.
10. Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the disciplined and analytical process of scrutinizing, examining and observing information, ideas or situations with an aim to make reasoned and well-informed judgements.
11. Courage
It is the mental or moral strength to persevere and withstand adversity, danger, or fear, even in the face of challenges or risk. It is a vital component of good character & conduct as it demonstrates resilience, integrity and the willingness to do what is right. It means that the a person should speak his mind, speak truth and act against evil.
12. Constitutional morality
The ideals which guide the relationship between government and the governed are considered as constitutional morality. The ‘shared values’ have following characteristics:
a) Respecting the Constitution
b) Promoting free speech.
c) Obligation of the government and its machinery to act as per Constitution.
d) People contesting for political power and their opposition should have reverence for the Constitution.
13. Capability approach (Amartya Sen)
It is considered as a contemporary philosophy which focuses on humans in terms of freedom and empowerment. It is strongly against functional type of empowerment which is supported largely through programmes and schemes in the name of social justice. Adherence to this philosophy will bring quality of human development, greater freedom and autonomy in life & people living the life of their choice.
14. Classical conditioning
It is a process in which the formation of attitude happens through a conditioning known as repeated occurrence of an event which the child may or may not deliberately pay attention to like when parents consistently discuss certain topics like caste, religion, or negativity, even if a child is in a separate room, they indirectly influence the child. Over time, this exposure may lead the child to develop a negative attitude towards the object introduced by the parents.
15. Cognition
It is knowledge about objects. In fact, attitude is about reaction in favor or against objects and it is knowledge about objects which determine strength of reaction. If people have clear rational or broad knowledge- then they would have appropriate reactions. In fact, better knowledge can help in controlling emotions that is affect and reacting in appropriate manner in a given situation. However, even if people have knowledge- affect may dominate in some situations.
16. Civil servant
Civil servants are special types of public servants with unique roles and functions in the administration. They perform sovereign functions & their conduct is governed by specific conduct rules. E.g. All India Service (Conduct) Rules — Accountability, Neutrality.
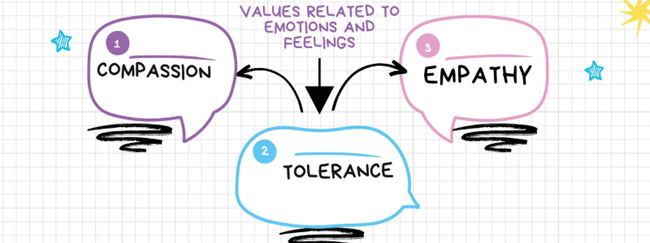
17. Compassion
An emotional urge in a civil servant to serve the downtrodden sections of society. Showing an act of positive discrimination. In general, it is about showing respect, care, empathy & emotional support. Compassion involves a sense of empathy. It does not end with pity. It involves sensibilities to understand and even feel the pain of others and motivates one to be truly helpful in overcoming this pain.
18. Courage of conviction
It involves a strong self-belief in one’s actions or decisions. It is the confidence that what one is doing right. It’s about trusting your own judgment / voice/ thinking and having the courage to stand by them even in the absence of external validation or guidance.
It refers to the bravery and determination to uphold one’s beliefs and principles, even in the face of adversity or opposition. It involves a steadfast commitment to one’s values and the willingness to act in accordance with those principles.
19. Conscience
Conscience is a human intellect/ faculty of sense which gives understanding about right & wrong. It’s a moral sense in humans. Humans are not born with the ability to logic, reason & understanding good or bad things rather there is moral development through the process of socialization. Therefore, conscience is also developed through socialization as explained by Kant and Lawrence Kohlberg.

20. Collective conscience of society
It refers to the shared set of values, beliefs, norms, and moral standards that are widely accepted and internalized by members of a community or society. It represents the collective understanding of what is considered right and wrong, acceptable and unacceptable within a particular cultural or social context.
21. Categorical Imperative
Immanuel Kant defines it as the inherent moral principle that commands individuals to act in accordance with universally applicable moral laws, regardless of personal desires or circumstances. It stems from the development of human conscience, which evolves through moral reasoning and rationality, ultimately leading to moral autonomy. It is this moral autonomy which is known as categorical imperative by Kant.
22. Corporate governance
It is the way a company is directed or controlled – Sir Adrian Cadbury (Father of corporate governance) or It is about management of a company with transparency and accountability or It is the process of management of a company which is run in the interest of all stakeholders. When a company is run with transparency and accountability in the interest of all stakeholders, it is an act of corporate governance.
What is good governance for administration, corporate governance is for the company or Corporate governance is good governance for the company.
23. Corporate Social Responsibility
It is a concept where businesses integrate social and environmental concerns into their operations and interactions with stakeholders. It goes beyond profit generation emphasizing a company’s commitment to contributing positively to society and minimizing its impact on the environment. It is a practice based on the rationals that businesses/ companies have responsibility towards society since it is due to society that they have registered success and now it is their turn to serve society. It is unacceptable from a just perspective that few people are rich, and they own most of the wealth of the society and rest of the people struggle for their livelihood in day to day life therefore, it is part of the ethics in the business that they contribute to the society in the form of CSR.
24. Crisis of conscience:
It is a state of extreme level of tension, dissonance in mind or emotional turmoil that may happen due to either of the following:
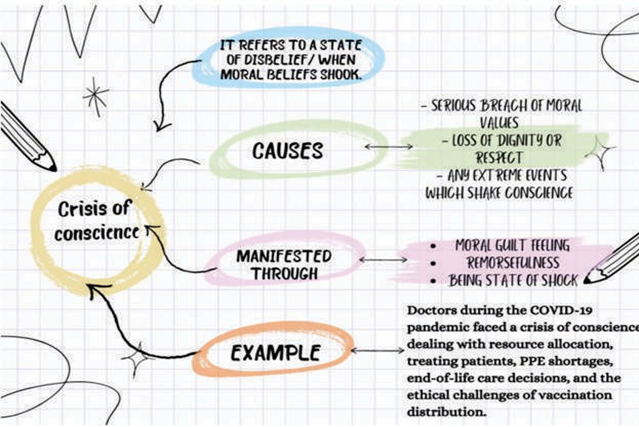
25. Compassionate capitalism
It is a concept propagated by Narayana Murthy which has following characteristics:
-
- There should be a minimum gap between the highest and lowest salary in an organization (or else there would be inherently injustice in the organization).
- Capping of highest salary
- Incentives should be given to all not only few
- In case of any economic loss or challenges of efficiency faced by the company, the weakest should not be fired first, rather there should be deduction from the salary of the strongest.
26. Comprehensive National Power (CNP)
It defines the strength of a country by how powerful it is vis-a-vis other countries. Its determinants are defense, technology, economy, human resource, peace, harmony, culture (Soft power) & leadership. A country is not strong merely because of its strong military; rather it must have peace, stability, order, stable government and good quality of human resources.
27. Conflict of interest
It means conflict between personal values and professional values of a civil servant or in professional commitments there is the role of private affairs which may affect impartiality/integrity in decision making. Receiving gifts, Post-retirement jobs, dealing in contracts & assets are the common situations in which conflicts of interest may arise in civil services.
An actual conflict of interest
An actual conflict of interest occurs when an individual or institution has two competing interests, one of which interferes or undermines the ability to fulfill responsibilities.
Potential conflict of interest
This refers to circumstances where it is foreseeable that a conflict may arise in future and steps should be taken now to mitigate that future risk.
Perceived conflict of interest
A perceived or apparent conflict of interest can exist where it could be perceived, or appears, that a public official’s private interests could improperly influence the performance of their duties — whether or not this is in fact the case.
28. Code of ethics
It deals with a set of moral principles. They deal with ‘do’s’ of civil servants. It is the spirit side of the law.
29. Code of Conduct
Civil servants are guided by their conduct rules. The Code of Conduct is a codified set of guidelines guiding the conduct of civil servants. Such guidelines are about what civil servants should do and what not to. They are enforceable especially for civil servants i.e. violation of conduct rules results in disciplinary action. It is represented through a set of laws and rules like Conduct Rules – The All-India Civil Services (Conduct) Rules, 1968, The Central Services (Conduct) Rules, 1964, The All-India services (Conduct) Rules (Amendment) 2014. It is the letter side of the law.

30. Corruption
Corruption is defined as the misuse of power to give any favor or disfavor, which results in pecuniary loss to the government. The term corruption is derived from ‘corruptus’ —Greek work — ‘to destroy’. So, corruption is the destruction of values. There is destruction of ethics in corruption since corruption has become a habit and ethics have been destroyed.
31. Democratic attitude
Democratic Attitude refers to those attitudes possessed by civil servants who promote participation of people in decision making, delegation of power or authority, valuing and promoting principles of democracy (respect for individual rights, equality, participation, and open dialogue) & willingness to listen to diverse perspectives, engage in fair decision-making processes, and uphold democratic values in interactions and decision-making. In place of rule and regulation, there is more focus on compassion, tolerance and inclusiveness.
32. Democratic ethics
It encompasses a set of norms and standards that guide the behavior of individuals, institutions, and governments within a democratic system. Democratic ethics emphasize principles such as equality, freedom, justice, respect for human rights, rule of law, accountability, and transparency. In a democratic society, adherence to democratic ethics is essential for ensuring the legitimacy and effectiveness of governance, fostering trust between government and citizens, and upholding the fundamental values of democracy.
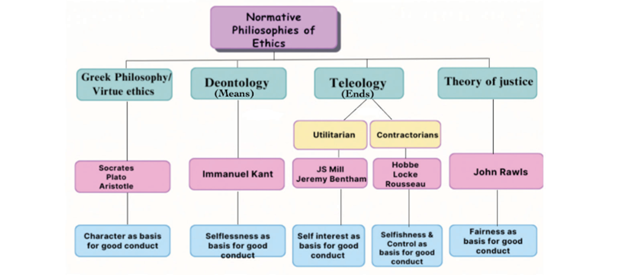
33. Deontology
It is the science of means. It means the inherent quality of human action should itself be right. Human action should not be right on the basis of its outcome.
34. Doctrine of mean
It’s the golden rule given by Aristotle that humans should avoid extremes in human action like Courage is the mean of Cowardice & Rashness in human action. It’s the doctrine of means which should guide human action and humans should also understand what is mean of human action by rational & critical thinking. It’s on the basis of Doctrine of mean that four principles of ethical conduct were given.
35. Dedication to public services
It means self-commitment and spirit for serving the people selflessly. Irrespective of what other people say/do /criticize – people with dedication to public service are focused towards their work. They always have a service motive, are not influenced by individualism & navigate easily amidst all the challenges, criticism & hard conditions.
36. Ethics
It deals with human character & conduct based on established standards with an aim to achieve the chief good/summon bonum & ultimate happiness or a field of moral philosophy which deals with rightness/ wrongness of human conduct.
‘The term ethics has been derived from the Greek word ‘ethicos’ which means habit/character /conduct’.
37. Empathy
It is like putting ourselves into other issues and thinking and feeling the way they think. Thinking and feeling the way others think demands a wider perspective or 360° thinking. Empathy demands compassion, tolerance, emotional intelligence & objectivity or impartiality. A prejudiced mind, stereotyping, patriarchal attitude, being feudal and egotist are manifestations of lack of empathy.
Empathy
|
Sympathy
|
|
|
| Example: | Example: |
| We extend help to poor people, even if they don’t seek assistance. Our empathy drives us to feel and address the problems of others. | We have someone when he is in need. Srushti Niyamam, North nuclear Jat. |
38. Ethical egoism
Proposed by Jeremy Bentham, it means seeking pleasure without thinking about others- whether others are harmed / not or ego needs fulfillment.
39. Ethical altruism
Proposed by JS Mill, it means seeking pleasure as per what’s good for society is good for me.
40. Environment ethics
It is a branch of applied ethics which deals with human moral relations with the environment. The essence is that humans should not harm the environment rather preserve it. Environmental Ethics deals with the ethical problems surrounding environmental protection. It aims to provide ethical justification and moral motivation for the cause of global environmental protection.
41. Ethical dilemma
An ethical dilemma emerges when a civil servant has to make a decision in a challenging situation in which two or more competing values are involved.

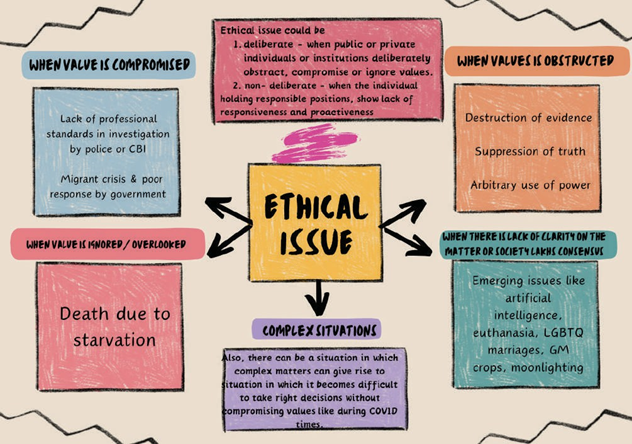
42. Ethical Issues
When any decision is taken, there will necessarily be compromised of some values & whenever there is compromise of values, it gives rise to Ethical Issues.
Ethical dilemma
-
- It is linked to the decision being taken.
- It indicates a challenging situation.
- It can be more linked to individual decisions.
- All ethical dilemmas will result in ethical issues due to compromise of one or more ethical values when action is taken.
- It arises in a situation before a decision is taken.
- Example:
Civil servant facing dilemma of taking decision for implementation of Prohibition of child labour law vs showing Compassion towards child and his family”
Ethical issue
-
- It may not necessarily be linked to a decision.
- It indicates a compromised situation.
- It is more linked to generic decisions involving several stakeholders.
- All ethical issues are not ethical dilemmas.
- It can arise before or after taking a decision.
- Example:
Lack of integrity (Corruption, Puja Singhal (IAS)
Lack of compassion (Deaths due to starvation in Jharkhand)
Lack of responsibility (Migrant crisis during COVID-19 pandemic)
Lack of social justice (caste conflict).
43. Ethical governance
Ethics in governance is about adherence to the principles of ethics in the process of governance. Since ethics indicate universal values, ethics in governance is also about universal principles of ethics in governance, which can be:

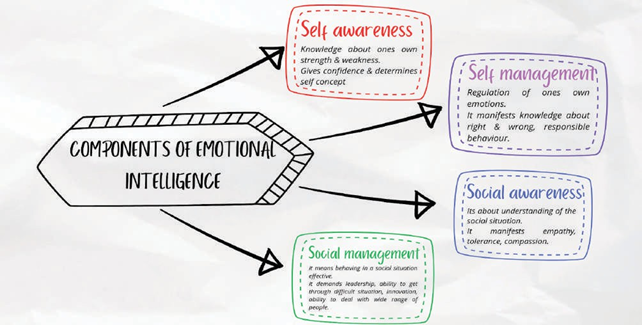
44. Emotional Intelligence
It is about behaving in a socially desirable manner by managing one’s own emotions & understanding others’ emotions. Daniel Goleman defines emotional intelligence as knowing one’s own and others’ emotions and behaving in a socially desirable manner by regulating one’s own emotions.
45. Ethics in public administration
It is an act of making administration accountable and responsive to people. Ethics in administration is an applied field of ethics which deals with problems of ethics and goes on setting ethical standards for administration which are also known as civil service values.
46. Ethics in Public & Private relationships
Ethics in public life is about ethical standards in a public context which is related to public relations like organizations and people behavior in organizations. They are formal, universal and professional. Ethics in private life deals with moral & ethical standards followed by people in their private life which can be linked to family, society, social relations or private affairs. They are informal, flexible & allow freedom & privacy.
47. Ethics in International Relations
Ethics in IR is a moral guide for conducting international relations. It is also a separate field which analyzes the descriptive status of ethics in IR, problems in IR & what should be the principle of ethics guiding IR. IR should be conducted on the basis of some principle of ethics / some standards of behavior & hence when IR are guided by moral principles, those acts are considered as ethics in international relations.
48. Ethics of care
Ethics of care propounded by Carol Gilligan and Claudia Card rejected male biases in ethics. e.g. considering males as courageous or associating such values with men and different values with women. They tried to rebalance ethics through ethics of care based on love, care, compassion etc. This has broadened the ethical standards by bringing gender perspectives and making them more rational.
49. Ethics of war
It is a branch of ethics that examines the moral principles governing the initiation, conduct, and resolution of armed conflicts. It addresses questions such as whether war is ever justified, under what conditions it is permissible to engage in war, and what ethical guidelines should be followed during wartime, including principles of proportionality, discrimination, and necessity. It is the field which has given the concept of ’just war theory’.
50. Fairness
It’s the quality of being just equitable and impartial in one’s actions, decisions and treatment of others. It involves treating all individuals without discrimination and ensuring that each person is given their due based on the principles of equality and justice. It leads to good quality of human conduct by promoting ethical and moral behavior fostering trust & cooperation and reducing conflicts.
51. Foundational Values
They are defined as values which determine the distinctive characteristics of an institution / organization / core values of any organization. Civil servants represent distinctive characteristics because of its role and function.
52. Fortitude
Fortitude refers to the moral strength and courage to withstand adversity, temptation or challenges in order to uphold one’s principles, values and ethical beliefs. It involves resilience in the face of moral dilemmas and the determination to do what is right even when it may be difficult or uncomfortable.
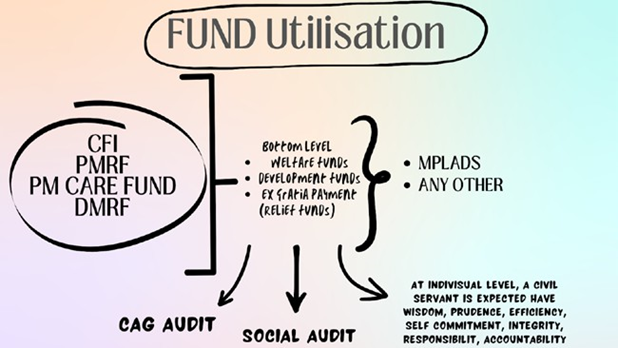
53. Fund utilization
Public Fund utilization is related to the utilization of tax-payers money, which are allocated in a formal eco, democratic state in many different ways including administrative expenditure, development expenditure, expenditure for welfare activities and some special purposes.
54. General will
General Will is the collective will of all the people living in a state. Free will gives voluntariness to people to live the life of their choice. Rousseau in his concept of General Will argues that people want to be free of chains and pursue their life according to them, and should be governed by the laws framed by the General Will. His idea was that laws based on General Will shall be the aim of the society, which will ensure rights, free will, equality and freedom which will further ensure that the chains around human life are broken down and people get true happiness. He also advocated social contract as basis for the protection of the General Will of people.
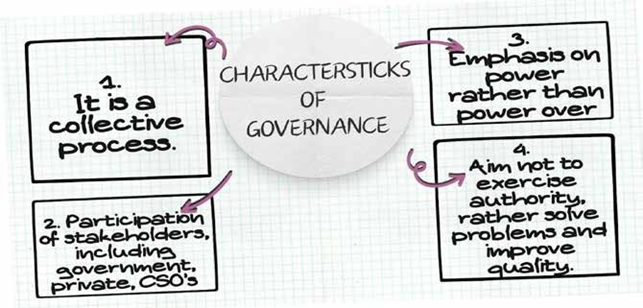
55. Governance
It is the process of collectively solving the problems of society or a process of collective governance.
The World Bank defined governance as, “In the manner authority is exercised for the utilization of social and economic resources for development”.
| Government | Governance |
| • It is an institution | • It is a process & phenomena |
| • It is about exercise of authority | • It is about solving problems |
| • Its dominant institution/ govern alone | • It is a collective process |
| • Power over/ top down | • Power with / bottom up |
56. Good Governance
PM Modi defines good governance as “ Pro-people and Proactive government” – a process which is people centric and people driven and he has given three characteristics for good governance which are accountability, responsibility & transparency. Good governance is about administration, civil servant, and government in relation to the citizens that the government must not govern in a traditional way which generated the passivity, inefficiency, secrecy culture, problems of social justice & lack of accountability.

| Governance | Good Governance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All acts of good governance are also governance. But not all acts of governance are good governance. It means governance is a broader term than good governance.
57. Geneva Convention on war
It is about adherence to some ethical standards or war ethics to protect human life and bring humanitarian interventions.
-
- Don’t attack or kill civilians
- Allow providing aid/help to war affected people
- Handover dead soldiers
- Don’t kill barbarically (mutilating, stomping on dead bodies)
58. Holistic competence
Holistic competence is the combination of ethics, ethos, efficiency and equity. Ethics is about adherence to moral standards, civil services values and having a good character. Ethos is about having understanding about society, culture, diversity and also respect for the same. Equity means working for social justice and being compassionate towards vulnerable sections of society. Efficiency means being result oriented, skillful and knowledge competent.
59. Health ethics
Health ethics pertains to the moral principles and values governing the conduct of individuals and institutions within the health sector. It encompasses the doctor- patient relationship, medical treatment practices, hospital operations, and regulatory frameworks. Key aspects include upholding trust, care, and responsibility in the doctor-patient relationship, adhering to medical standards to prevent negligence, and ensuring ethical conduct by healthcare professionals, hospitals, and pharmaceutical industries. Health ethics emphasizes the importance of upholding moral and ethical standards to promote the well-being and rights of patients and the public within the healthcare system.
60. Honesty
It means truthfulness, standing by what one says, or does. It is also a qualitative term & a desirable value. In general parlance, honesty & integrity are used interchangeably, and honesty is part of integrity value.

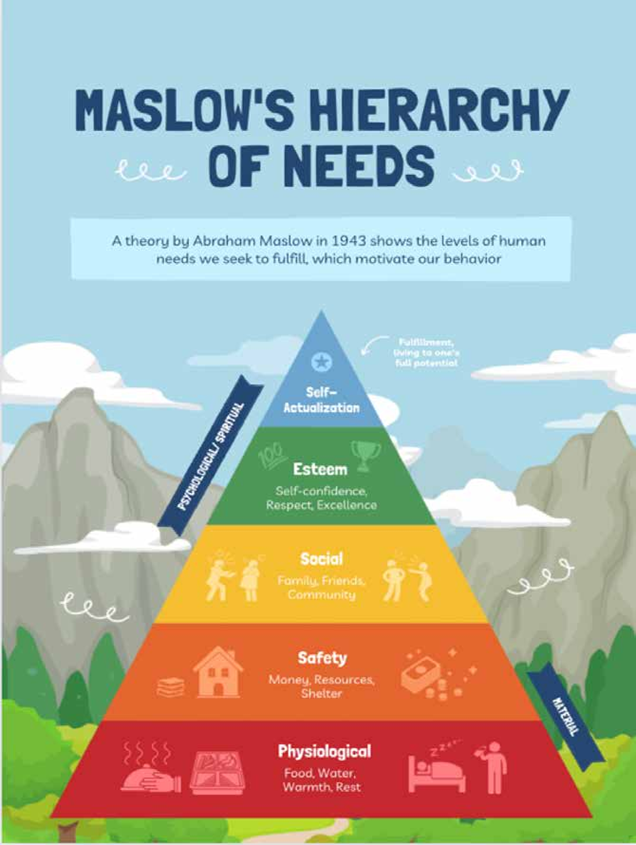
61. Hierarchy of Needs
The ‘Hierarchy of Needs’ given by psychologist Abraham Maslow proposes that people are motivated by five categories of needs – Physiological, Safety, Love, Esteem, and Self-actualization. These needs are represented as a pyramid, with basic physiological needs such as food, water and shelter at the base and the need for self- actualization at the top. Maslow further classified the bottom four levels of the pyramid as “deficiency needs,” noting that “a person does not feel anything if they are met, but becomes anxious if they are not.” He classified the fifth level “a ‘growth need’ because it enables a person to ‘self-actualize’ or reach his fullest potential as a human being. Maslow proposed that human behavior is purposeful and is motivated by the desire to satisfy needs and that lower-level needs must be met before a person can focus on the next level of needs.
62. Human values
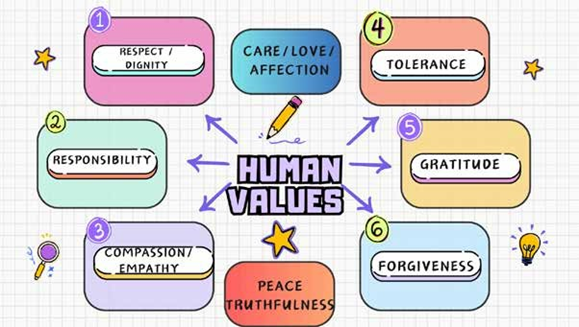
Human values are values which are very core to the human/ for being human or the inherent qualities which are desired to be called human are human values.
Human values deals with values associated with human emotions and feelings like given below:
63. Integrity
It means having strong moral principles/ value systems in one’s conduct. It represents honesty, the character of uncorrupted virtues, uprightness, something ‘whole’, not divisible or breakable & consistency between what you say and what you do (thought and action).
People with absolute integrity include Ajit Doval, JM Lyngdoh, TN Seshan, Porijes Mishra.
64. Intuition
It is a form of insight or understanding that arises spontaneously and often unconsciously, without relying on deliberate reasoning or evidence. While it can involve guessing, it typically goes beyond mere speculation and is influenced by past experiences, emotions, and subconscious processing. Intuition is not necessarily about being right or wrong but rather a sense of common sense or inner wisdom to guide decision-making and understanding.
65. Intellectual Integrity
It is honesty in the acquisition, analysis, and transmission of ideas. A person is being intellectually honest when he or she, knowing the truth, states that truth. It involves maintaining the authenticity and originality of one’s ideas, knowledge and information. It emphasizes the importance of producing work that is genuinely one’s own and not relying on unauthorized copying or plagiarism. Upholding intellectual integrity contributes to the credibility of individuals and overall quality of information and knowledge.
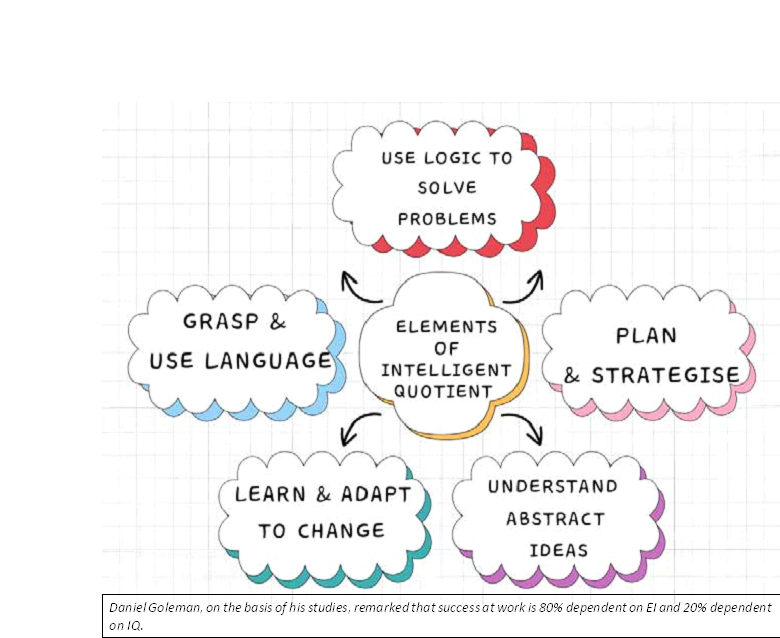
66. Intelligent quotient (IQ)
Intelligent Quotient (IQ) usually refers to our intellectual ability. Traditionally, there was emphasis on intelligence which was measured as IQ. Those who had better IQ were considered intelligent and were also respected in the society that they were capable people but 1980 onwards you to advancement in behavioral sciences (neuroscience) on the one hand and on the other, need for soft skills in public relations – resulted into studies and analysis of human emotions and emotional intelligence. It was found that those who have emotional intelligence were more successful and happier than those who had IQ but lack EI.
67. International funding
It refers to providing financial support from one country (developed) or international organization to another country (developing/ least developed). There is huge inequality in the world and there is a demand-supply gap for the resources available with the government, especially in developing and under-developed countries. For this reason, bodies like the World Bank, International Finance Corporation (of UN) were established to help the countries in need. Funding is provided for development activities (Roads, PPP) & livelihood of people, welfare (SBM), charity (Missionaries, Trusts), sustainable development & protection of environment (SDG Goals).
68. Impartiality & Non-partisanship
Impartiality means being fair, neutral & non- discriminatory in decision making and that a civil servant should take decisions purely on the basis of merit and objectivity.
Nonpartisanship also means being fair and non- discriminatory, but it’s more linked to society and politics. Since a civil servant have to serve
a) Society and people- Civil servants should be fair and non-discriminatory.
b) Government- Civil servants should be apolitical.
Impartiality is a broader value than nonpartisanship in a way that it also encompasses nonpartisanship.
69. Just war theory
The theory connotes that even knowing that doing war is unethical, we can do a just war if we are fighting. Just War Theory provides a framework for evaluating the ethical justifications for going to war and the conduct of warfare. It was given by St.Augustine & St.Thomas. According to this theory, war must meet certain criteria, including:

70. Laws
Laws are rules and regulations established by a governing authority to govern behavior within a society. They are enforced through various mechanisms and are intended to maintain order, protect rights, and promote justice. In general, they are rigid in nature & therefore difficult to change.
| LAW | ETHICS |
| • It has legal sanctions | • It has moral sanctions |
| • It is binding | • It is desirable |
| • It is enforced | • It is expected to be adhered |
| • It is external check | • It is internal check |
71. Layoffs
It refers to the practice of temporarily or permanently terminating the employment of a group of employees due to various reasons such as economic downturns, restructuring, technological advancements, or organizational changes. It is a strategic decision made by companies to streamline operations, cut costs, or adapt to market conditions. When conducted ethically, layoffs are part of a structured process that considers the well- being of employees and adheres to principles of fairness and transparency. However, when executed without proper communication, consultation, or consideration for employees’ rights, layoffs can be perceived as unethical and can undermine trust and morale within the organization.
72. Morality
The term ‘Moral’ deals with rightness/quality of behavior which has the connotation of ‘rightness’ of behavior. Morality is based on individuals standards / values / principles of behavior/ moral code of behavior. In nutshell, Morality is about rightness/ wrongness of human conduct based on individual standards of behavior. It is said that ethics is empty without morality.
| MORALITY | ETHICS |
| • Based on individual standards | • Based on established standards/universal standards |
| • There is relativism in moral standards | • There is absolutism in ethical standards |
| • It is qualitative term about human behavior | • Its a field of normative science/moral science that deals with moral conduct |
| • An individual has to conform to one’s own standards for moral conduct | • An individual has to confirm to ethical standards |
73. Moral attitude
It is an attitude based on the moral convictions of a person towards his/her actions. It is the quality of attitude of a person that determines whether a person has the right or wrong attitude. It will also not be the same for all individuals. It is influenced by moral values. It is developed over a period of time. The socialization process helps in the development of moral attitudes.
74. Media ethics
Media ethics refers to the moral principles and standards that guide the conduct of individuals and organizations within the media industry. It encompasses the responsibilities of journalists, reporters, editors, and media outlets in delivering accurate, fair, and truthful information to the public. Key aspects of media ethics include.
It also involves navigating complex ethical dilemmas, such as conflicts of interest, privacy concerns, and the balance between public interest and sensationalism. Overall, media ethics aims to promote ethical behavior and accountability in the media profession while serving the public interest and preserving the integrity of democratic societies.
75. Moral development
It is a product of socialization. Individuals aren’t inherently equipped with ethical knowledge. Instead, one acquires ethical insights through the process of learning and social interaction within the world. Children’s minds begin as blank slates, gradually filling with knowledge through the process of socialization- the same way attitude is formed. This learning journey includes understanding about right and wrong. Lawrence Kohlberg’s theory further delves into the stages of moral development through which individuals navigate in their moral understanding.
76. Moral accountability
It refers to the responsibility of individuals or institutions to adhere to ethical principles and standards in their actions and decisions. It involves being answerable not only for the legality of one’s actions but also for their ethical implications and adherence to moral values. It is a commitment to acting with integrity, honesty, fairness, and consideration for the well-being of others, even when there is no external oversight or enforcement mechanism. It encompasses the idea that individuals or organizations should hold themselves to a higher ethical standard and be willing to justify their decisions and behaviors based on moral principles.
77. Moonlighting
It is the practice of working for the second job in addition to the first job. In Covid times, the culture of work from home gave rise to people doing more than one job side- by-side, especially in IT sectors.
78. Moral Realism
It has been advocated by Kautilya, Thomas Hobbes, and Machiavelli. It says that power alone protects the interest of the people. It means a country should be powerful and resourceful to protect its national interest. It goes to an extent that even a country should go for acquisition of foreign territory to protect its interest.
79. Managerial ethics
It refers to the moral principles and standards that guide the behavior and decision-making of managers within an organization. It involves making ethical choices in areas such as employee treatment, customer relations, financial management, and corporate social responsibility. Managerial ethics require integrity, honesty, fairness, and accountability in dealing with stakeholders and making decisions that impact the organization and its stakeholders. In contemporary times, a need was felt for managerial ethics that bureaucracy should not only have neutrality, rationality, integrity & compassion but it should also have professional standards otherwise, it cannot become outcome oriented.
80. Moral Idealism:
It is about normative standards, principles and values to be adhered to in international relations. It is influenced by views of Jeremey Bentham, Mahatma Gandhi, Immanuel Kant. It gives importance to human rights, territorial integrity, respect to the sovereignty of the country, values of freedom, liberty and equality, and democracy. Moral idealism is based on ‘what ought to be of international relation’ that how ideally it should be conducted.

81. National interest
National interest refers to the set of objectives, goals, and priorities that a nation pursues to safeguard and advance its well-being, security, and prosperity. It encompasses a range of factors such as economic prosperity, political stability, territorial integrity, national security, and the promotion of values and principles that are deemed essential for the nation’s survival and development. It involves a balance between pursuing the welfare of the nation and contributing to global peace, stability, and cooperation.
82. Normative theories
Normative ethical theories provide frameworks for evaluating the ethical implications of actions and decisions. They are set on the basis of critical thinking, reasoning & logic, understanding human nature & formulating the golden rule of human life. Virtue ethics, Deontology, Teleology & Theory of justice are few of them.
83. Neutrality
It means acting as per orders/ law, which indicates political neutrality. It can also be considered similar to impartiality.
84. Office peacocking
It refers to the practice of making physical office spaces more attractive by adding appealing enhancements and extravagant amenities. This trend aims to entice employees back to the office after an extended period of remote work by creating an inviting and engaging environment. Renovations might include trendy designs, comfortable workspaces, and luxurious perks to boost morale, engagement, and in-person collaboration. However, the effectiveness of this strategy is debated, as some argue that remote work can be more productive and that employees value flexibility and autonomy over physical office perks.
85. Objectivity
Any decision based on facts, merit or observable phenomenon is said to be objective. Any decision which has objectivity will have connotations of impartiality, rationality, merit and facts. It is a manifestation of scientific temper or rationality in decision making.
86. Outcome oriented
It means being more innovative and focusing on the impact of action. It’s being advocated by the present Prime Minister that civil servants should be outcome oriented.
87. Persuasion
It’s a deliberate act of social influence. It could be mothers influencing their children or Judicial orders on social economic interventions like Live-in, LGBTQ rights or Government laws, policies and schemes.
88. Perseverance
Perseverance is the quality of persisting despite challenges, obstacles, or difficulties. It involves determination, resilience, and the willingness to keep working towards a goal even when faced with setbacks or failures. Perseverance often requires patience, endurance, and a positive mindset to overcome obstacles and achieve success. It’s about staying committed to one’s objectives and continuing to make progress, even in the face of adversity.
89. Public Service
It refers to the urge to serve weaker sections of society or being responsive to the needs and problems faced by the vulnerable sections of society. ‘Service’ is an important civil service objective for civil servants. It also includes selflessness, public service spirit, commitment to public service. Civil servants are supposed to be neutral and impartial but at the same time, they should have empathy and compassion towards weaker sections of society.

90. Patriotism
It is an attachment to a homeland. The love and adoration for the place where an individual is born, brought up, and the nation that place belongs to. These attachments can be related to ethnic, cultural, political or historical. Patriotism is also being proud of a country’s virtues but with an eagerness and readiness to correct its deficiencies to be better. It acknowledges the patriotism of citizens of other countries and respects their virtues.
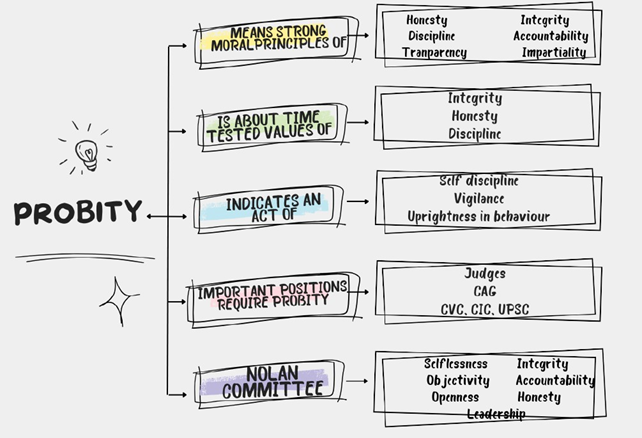
91. Probity
It is integrity plus discipline in public life. It is also an action-oriented value which is about how public servants should remain vigil, active & maintain disciplined standards in public life.
92. Professional accountability
It is the obligation of individuals within a specific profession or occupation to uphold high standards of performance, ethics, and conduct in carrying out their duties and responsibilities. It involves being answerable for one’s actions, decisions, and the outcomes of those actions within the context of one’s professional role. It encompasses aspects such as competence, adherence to professional codes of conduct, commitment to meeting established performance standards, and taking responsibility for the consequences of one’s actions and making improvements to ensure the delivery of quality services or outcomes.
93. Political attitude
It means belief, values and views towards political objects such as the constitution, political parties, governments, their policies, etc. It depends on history, geography, socio- cultural-religious-economic-political and administrative factors. Since ethics is also about normative values of society, therefore, the nature of political attitude in a country is manifestation of prevailing values of that society for example- plural and secular political attitude in India are the overarching features also two important values.
94. Public servant
All those who work for the government and derive their salary from the public funds or Consolidated Fund of India are called public servants. They perform tasks of government not necessarily related to sovereign function & their conduct is governed by general conduct rules or respective conduct rules of different departments and organizations.
95. Probity in governance
Probity is considered as an act of vigilance and public scrutiny in public office. It is about uprightness, integrity, uncorruptiveness and rectitude i.e. straight forwardness. Probity in governance deals with civil servants in the context of their behavior in an organization that they should adhere to the moral principles of integrity, honesty, uprightness, rectitude and state of vigilance and discipline should be maintained. Therefore, probity in governance indicates a set of moral standards.
| Probity | Integrity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
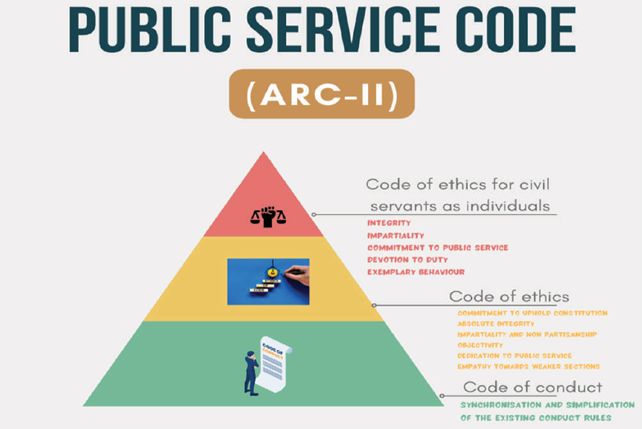
96. Public service code
ARC-II in its report recommends bringing a Public Service Code to increase accountability of civil servants. Public service code consists of three components/ 3 layers of hierarchy.
97. Quality of service
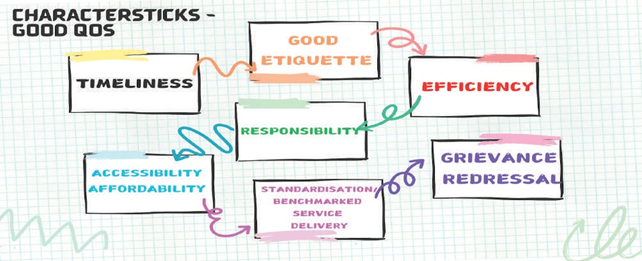
It refers to ensuring certain standards/benchmarks in service delivery. The government or administration should not only deliver services but rather quality services as the government has a moral obligation for ensuring not only the best return on every coin spent but also the satisfaction of the people receiving those services.
98. Rationality
Rationality is about the act of reasoning and logic based on objectivity which has consistency in human behavior. Rationality can be on the basis of statements based on facts or knowledge and is expressed in an objective fashion which has justification. It’s a process which brings us close to truth and therefore includes objectivity.
99. Religion
It is a structured set of beliefs, practices, and systems that relate humanity to spirituality and moral values. Each religion encompasses its own philosophical principles, which include universal ethical principles such as truth, forgiveness, compassion, equality, dutifulness, and selflessness. While these values are universal, religions also incorporate other values and practices that may not be universal, often referred to as the social morality of that religion.
| RELIGION | ETHICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
100. Responsiveness
It means promptness in action & agility in action (minimum time taken to respond to a situation & solve a problem). It depends on the level of preparedness, efficacy and capability. Responsibility + Accountability + Transparency helps with responsiveness.
101. Rules
Rules are specific guidelines or directives created by a governing authority, typically within the framework of existing laws, to regulate behavior or conduct within a particular context or domain. Rules are extensions of laws & they must confirm laws especially to the fundamental law of state.
| Laws | Rules |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
102. Regulation
Regulation refers to the process of enforcing laws and rules to ensure compliance within a given system or context. It involves the implementation and monitoring of rules and standards established by a governing authority to maintain order, protect rights, and promote safety and fairness. Enforcement of regulations typically involves various measures such as imposing penalties, fines, or other disciplinary actions to encourage adherence to the established rules.
103. Refugee
According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), a refugee is someone who has been forced to flee their country because of persecution, war, or violence for reasons of race, religion, nationality, political opinion, or membership in a particular social group.

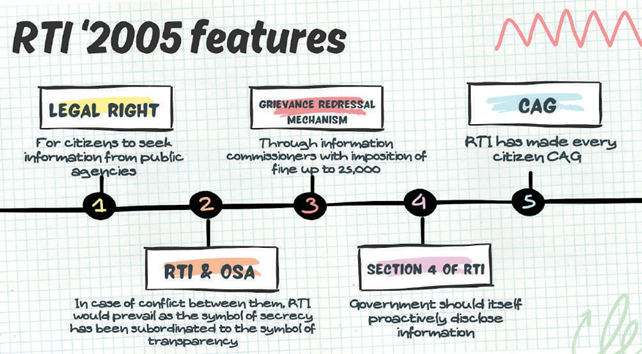
104. RTI
RTI stands for Right to Information. It is a fundamental right enacted by the government to empower citizens to access information held by public authorities. It aims to promote transparency and accountability in governance by allowing individuals to request and receive information about government actions, decisions, and expenditures.
It is considered as an innovative and effective tool to promote transparency in the working of the State & therefore regarded as a human right and fundamental right. It is a tool to share power with citizens & is a democratic tool.
RTI marks the beginning of era of light and ends the era of darkness (secrecy culture) ARC-II
“A popular government without popular information or the means of acquiring it, is but a prologue to a farce or a tragedy, or perhaps both” – James Madison.
105. Reward & punishment
It is a major learning technique for formation of attitude in the children through socialization. By reward- positive behavior is encouraged & by punishment- negative behavior isn’t discouraged. If there is a right blend of rewards and punishment, a child can learn to have a positive attitude.
106. Responsibility
| Responsibility | Accountability |
|
|
|
|
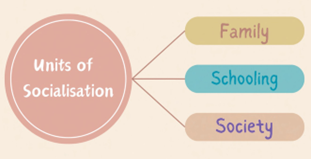
107. Socialization
It’s a process through which humans learn & acquire values including human values. It’s an interplay of family, society, schooling & other objects of society which influence human behavior. Therefore, human values are learnt through socialization process which has three basic units:
108. Superstition
Contrary to critical and rational thinking is superstition- a belief or practice resulting from ignorance, fear of the unknown, trust in magic or chance or a false conception of causation. Superstition has no scientific evidence or causal relationship with reality. Studies by psychologists have shown that superstitious beliefs, if practiced, have a definite impact on outcomes and have social cost. For example, if a Surgeon believes that he should not conduct medical procedures on a particular day, it may cause unintended suffering to his patients.
109. Social Justice
It is about justice for downtrodden sections of society by taking socio-economic interventions as envisaged in DPSP’s. It has become an important value for civil servants as social justice has become one of the most important objectives of the state.
110. Social norms
Social means people, norms mean standards. Social norms mean people’s standards. They are unwritten standards of behavior which guide the behavior of people. They are based on tradition, culture, custom and practices of society which have evolved with the evolution of society. Since social norms are derived from society, they become a sort of foundation for all other values & standards including moral and ethical standards although social norms differ society to society because each society is different & so its traditions, customs & values.
111. Social Contract
It’s a contract by people that they should be governed by a state which is a modern development. It was conceptualized by Thomas Hobbes, although Socrates is considered the first philosopher to bring the concept of Social contract when he refused to leave the territory. Social contract is not a written document, rather it’s a mutually agreed concept by people that the state should govern on their behalf. This concept was given on the basis of explanations about human nature.
112. Social ethics
It refers to the moral principles and values that govern behavior and interactions within a society. These principles guide individuals, groups, and institutions in their relationships with one another and in their roles as members of a community. Social ethics encompass values such as justice, fairness, equality, human rights, respect for diversity, compassion, and responsibility towards others. Social ethics emphasize the importance of considering the well-being and dignity of all individuals and promoting the common good.
113. Social capital
Robert Putnam defines it as social networks and the norms of reciprocity associated with them. It is related to trustworthy relations between different groups of society. Social capital involves relationships that are embedded within a group. Those relationships can have intrinsic value for the individual members, creating a sense of belonging or being connected to others. Social capital, in short, is the glue that makes a society work. It includes social, infrastructure and its elements like civil society groups, NGOs, SHGs etc. (Kudumbshree of Kerala as women led SHGs).
114. Sport ethics
It encompasses the principles and values that guide ethical behavior within the realm of sports. It involves upholding fairness, integrity, and sportsmanship while promoting respect for opponents, adherence to rules, and honesty in competition. Sport ethics also entails ensuring transparency, merit-based opportunities, and accountability within sports organizations, while striving to mitigate conflicts of interest and unethical practices.
115. Social observation / Role modeling
It is the process of observing and analyzing social interactions, behaviors, and patterns within a society or community. It involves paying attention to how people interact with each other, the norms and values they uphold, and the social dynamics at play in various contexts. Social observation can occur through direct observation in real-life settings, as well as through the study of media, including social media, films, fashion, and other cultural artifacts. By observing social phenomena, individuals can gain insights into societal norms, values, and attitudes, which can shape their own beliefs and behaviors.
116. Social influence
It is defined as an influence by the real or imaginary presence of any person. This influence can be deliberate/indeliberate. In general, society has an influence on children or people.
117. Social accountability
It refers to the process by which citizens, civil society organizations, and other stakeholders actively engage in monitoring, evaluating, and influencing the actions and decisions of public officials, government institutions, and other entities to ensure transparency, responsiveness, and effectiveness in governance. Unlike traditional top-down accountability mechanisms, social accountability involves the direct involvement of individuals and communities in holding public officials and institutions accountable for their actions and outcomes. This approach emphasizes the importance of citizen participation, transparency, and collaboration in promoting good governance and addressing social issues. Social accountability tools such as RTI (Right to Information), citizen charters (CC), social audits, and e-governance platforms empower citizens to demand information, voice their concerns, and contribute to decision-making processes, thereby enhancing accountability and promoting democratic principles.
118. Social audit
Social Audit is the examination and assessment of a programme/scheme conducted with the active involvement of people and comparing official records with actual ground realities. Thus, social audits examine and assess the social impact of specific programmes and policies. The process of Social Audit combines people’s participation and monitoring with the requirements of the audit discipline. It is necessary to promote people’s participation in the audit along with support provided by an independent social audit organization that facilitates the process.
119. Temperance
It is emotional balance. Anyone can become angry at any person at any time but to become angry at the right person at the right time in the right proportion demands temperance. It leads to good character and conduct by promoting balance, self-control and ethical behavior. A person with temperance makes thoughtful and measured choices leading to better behavior.
120. Teleology
It is the science of ends. It means that human action rightness/ wrongness is judged on the basis of the consequence/outcome of the action. If the end is well, all is well.
121. Tolerance
It is having a permissive or receptive attitude towards others’ beliefs, feelings, views, values, caste, religion etc. Tolerance is respect, acceptance, and appreciation of the rich diversity of our world’s cultures, our forms of expression and ways of being human. It is fostered by knowledge, openness, communication and freedom of thought, conscience and belief. Tolerance is harmony in difference.
122. Terrorism
It is defined as creating terror in the minds of people. Largely it has been linked to non-state actors. When nonstate actors by violent means, create terror (feeling of insecurity & fear psychosis) and fear in the minds of people it is called terrorism.
123. Transparency
It means government decisions are accessible to the people. There is practice of openness through disclosure of information by the government. Transparency is considered as the invention of democracy. Democracy seeks to share power with people. People have the right to know what their representatives are doing or have done. It seeks a culture of openness in the administration. Thus, it is the opposite of secrecy.
| Transparency | Open Accountability |
|
|
124. Theory of Justice
This philosophy was given by John Rawls during the 1960s which advocates for establishing a just society through consensus and reflective equilibrium. It prioritizes equality, liberty, and fairness, ensuring social and economic advantages for all, particularly the vulnerable. This “justice as fairness” principle is applied across societal spheres, promoting rationality, objectivity, and impartiality to combat injustice. It is concerned about the establishment of a society which is just rather than merely focusing on individual conduct.
125. Utilitarian Philosophy

Proposed by philosophers like Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill, it evaluates the morality of actions based on their consequences. It states that human action should aim to maximize the utility. It is based on pain-pleasure principle i.e. human action should result in minimizing pain and maximizing pleasure.
Utilitarian philosophy of “the greatest good to the greatest number of people” is related to the principle of survival of the fittest in society. This philosophy in general supports capitalism and support those who are placed in strong positions in society. This means that some people in society who are poor, weak and vulnerable will remain weak e.g. concentration of wealth in the hands of few people in society.
126. Principle of Universalizability
There is a clear criterion of universalizability and reversibility in I. Kant’s Categorical Imperative.
What would happen if the entire community started acting out of hate? The principle of universalizability will serve as our guide toward moral behavior, as this principle states that the justification for any action should be rooted in the idea that everyone else should act the same way in a comparable situation. In simpler terms, this means that if you perform an action, then others should also have the ability to do it.
127. Ubuntu Ethics
The African word Ubuntu, which means ‘humanity to others’, invokes a spirit of collective, global and regional inter-governmental action, as well as communal and individual efforts.

128. Ultimate good
Ethics is defined as established standards of moral principles. It helps people in critical questioning while evaluating conduct human conduct and improve it to achieve chief good (Summum Bonum).
The concept of Ultimate Good is a key idea in many philosophical traditions, representing the pinnacle of moral or spiritual benefit that individuals can achieve. In Buddhism, it relates to the attainment of enlightenment and the development of bodhicitta for both oneself and others. Vedanta aims for a union with Brahman, and Mahayana focuses on the well-being of all beings through the aspirations of Bodhisattvas.
In essence, Ultimate Good encompasses the highest possible state of benefit and fulfillment within these spiritual traditions.
129. Virtue Ethics
The virtue ethics of Aristotle deals with the quality of human actions based on his character. He emphasizes on virtues(quality) which is always a positive and is an objective standard. According to virtue ethics, human being has five sense which are physical senses (sight, hearing, smell, taste and touch) and there is sixth sense called wisdom. Controlling senses is the ultimate test of our character.
According to him, the rightness or wrongness of person’s action depends on his/her character which should be scrutinized. To build a strong character he gave four cardinal virtues which are Justice, Temperance, Courage and Wisdom.

130. Veracity
It is the principle of telling the truth and is related to the principle of autonomy. This principle expresses the concept that professionals have a duty to be honest and trustworthy in their dealings with people.
131. Values
Values are standards of behavior which guide the human conduct. For example, Gandhiji withdrawn Non- Cooperation Movement after the Chauri Chaura incidence of violence as he advocated the value of non-violence. People die for values such as self-dignity and respect.
Positive argument: Human beings are social and benign animals (Aristotle). They possess human values such as love, affection, care and non-violence by the virtue of being human. Therefore, on can say that they have natural tendency to do good and avoid evil such as violence, hate.
Negative argument: Human being is selfish, brutish and short (Thomas Hobbes). Human always try to preserve and protect self-interest. Therefore, when there is no law, rule people tend to preserve their own interest even at the cost of others.
|
Values |
Ethics |
They are based on: 1. People’s knowledge,understanding 2. Norms, tradition, customs. 3. Family, society, organizational values. 4. Individual preferences, belief.
|
|
Relationship Between Ethics & Values:
Ethics is evaluation of values (Mahabharata) i.e. values are scrutinized on the basis of ethical standards. It means all values will not be ethical but ethics will be based on values.
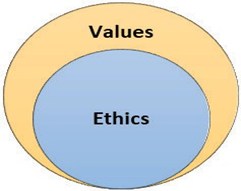
All values are not ethical e.g. some values may be individual or social but not ethical values. However, there are some values which are respected and followed across the world, these are called Universal values. E.g. love, compassion, forgiveness, peace, truth, gratitude etc. All Universal values are ethical values. The world propagates them as shared values.
132. Victimization
Victimization occurs when an individual is treated unfairly due to their association with a complaint related to discrimination or harassment. Examples of how someone might be victimized include being called a troublemaker or being excluded from activities.
133. Whistleblowing
A whistleblower is someone who shares accurate information with the appropriate authorities. In other words, lawful whistleblowing involves an individual conveying information they reasonably believe indicates misconduct to an authorized party.
Categories of Whistleblowing include:
-
- Internal: Alerting senior management of the organization, such as the Head of Human Resources or the CEO, about misconduct, fraud, or violations of rules.
- External: Reporting wrongdoing to individuals outside the organization, including the media, government officials at higher levels, or law
Satyandra Dubey, the young whistleblower who had exposed corruption in the Golden Quadrilateral highway project in Bihar in 2003.
134. Welfare State
“Happiness of kind lies in happiness of his subjects.”- Kautilya.
A welfare state refers to a government approach where the state plays a central role in ensuring the economic and social welfare of its citizens. This system is founded on the ideals of equal opportunity and fair distribution of resources. Additionally, it emphasizes the government’s duty to support those who cannot access the basic necessities for a decent life. In this model, it is the state’s obligation to safeguard the well-being of its citizens.
It describes that those who rule should work for welfare of people of State. In democracy, people elect their representatives who rule on their behalf. Therefore, it is their responsibility to work for people’s welfare. State should give social assistance to those who are not able to sustain by themselves such as old age people, Divyang people.
Government is for protection and welfare of the people. Unless and until it succeeds in this objective, people will not have trust in the government or public institutions.
135. Work culture
It is about way of life of people in organisations. It is totality of values, objectives, processes, procedures communication, decision making, leadership and interface with citizen/clients etc. by organisations.
Work Culture of ISRO
It promotes more informal environment in an organisation.
The organisation has more autonomy in terms of its management and work culture (independence from line ministries is important for a high performing organisation.)
The right ecosystem to attract talent and build its knowledge capabilities.
It is considered as one of the best work cultures in the world.
Determinants of good work culture:
-
- Foundational values
- Aims & objectives
- Rules, Procedures
- Technology
- Leadership
- Communication
- Subject matter dealt by organization
- Personnel management/policies.
In India, there are 3 types of work culture in organizations:
Bureaucratic
-
- In government sector or civil sector.
Bureaucratic work culture in India is famous for red tapism, elitism, status quo, secrecy and corruption while delivering the services to people.
Semi-professional
-
- In PSUs.
- Less formal culture.
- 1990 onwards they are trying to match corporate sector.
Professional
-
- In corporate sector.
- Reflects western culture, management practices.
- Efficiency/profit is main motive.

